By Karen Rubin, Travel Features Syndicate, goingplacesfarandnear.com
There is a cold, institutional feel to the National Constitution Center – as if you fell into a law book. And oddly, even though this place more than any other, recognizes the impact of words on paper – the decisions, pronouncements, laws – on each and every person’s everyday life, there is that struggle between the “rule of law” without fear or favor, that objective, dispassionate application, and any sense of what is right and good for ordinary people. What emerges is a sense that law and government, like evolution, is not good or bad, but reflects politics and power: look at the restrictions on voting to “white men over 21;” the Dred Scott Decision based on 5th amendment property rights; the evolution of rulings that elevate corporations to the status of people (despite fact “corporation” is not mentioned in the Constitution) including Citizens United which established that cash is equivalent to speech and corporations have a right to spend as much as they want on political speech regardless if it is corporations spending the cash or a person (so speech is not really “free”, but whoever has more cash has more speech) and Hobby Lobby which determined that corporations could possess religious “conscience” in order to deny their female employees access to contraceptives. You realize that the progressive change on behalf of ordinary people occurred during brief episodes.
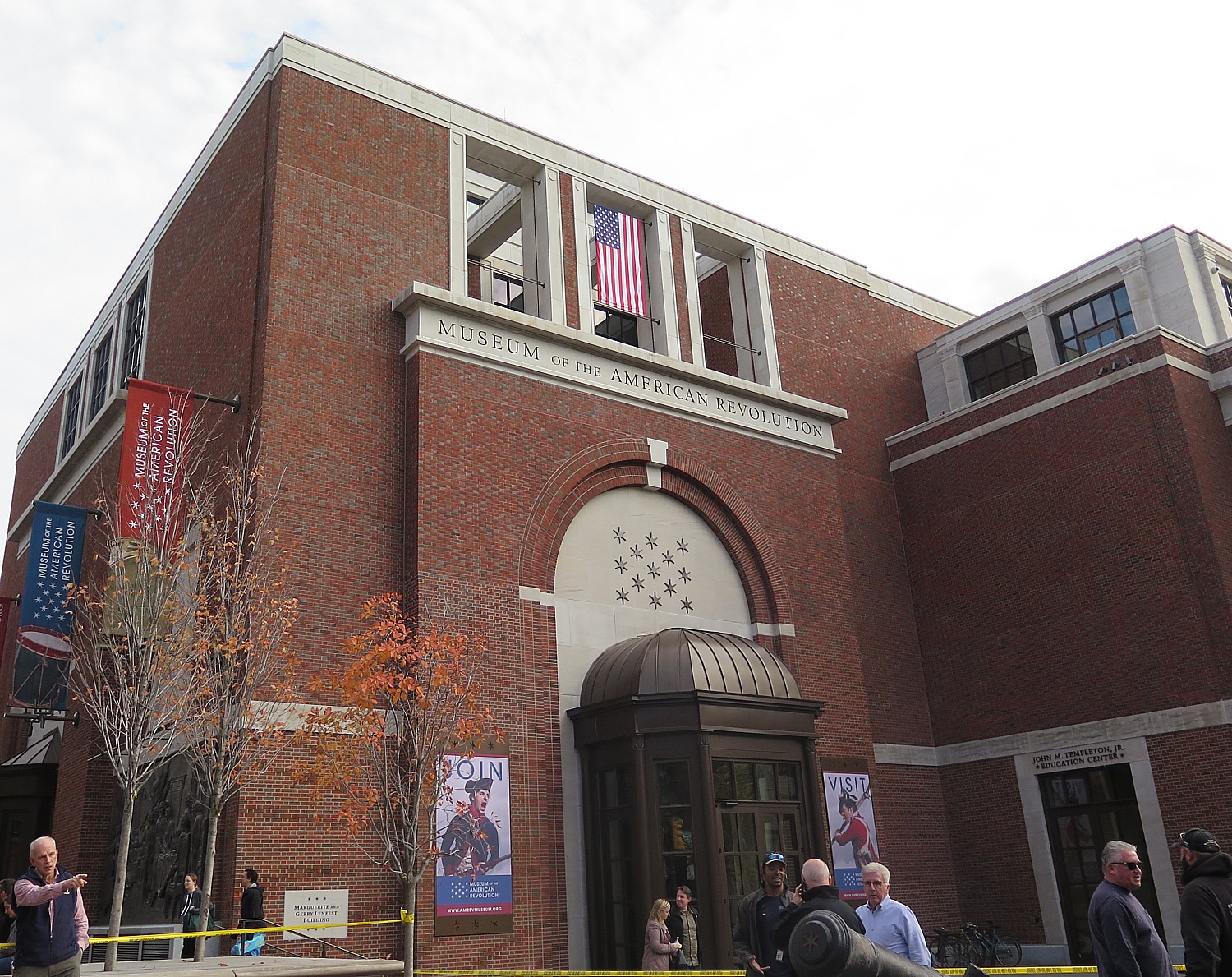
I used the opening of the brand new Museum of the American Revolution as the theme for my three-day visit to Philadelphia – a really deep dive probe of the Revolutionary War era, a return to understanding the founding of the nation through, as it were, original documents, materials and artifacts, at a time when we need to be reminded – everything from the off-hand comment by Trump Chief of Staff John Kelly that the Civil War could have been averted if only there were compromise (he should go to the National Constitution Center), to the quixotic amazement of a US Treasury official pining on his research into what’s this thing, “The American Dream,” all about before adopting the biggest redistribution of wealth since the Gilded Age, to the pronouncements by some politicians that America is a Christian Nation, to Trump’s remarks about immigrants coming from s-hole countries. I felt a driving need to go back to the beginning, the foundations, remind myself of those values and debates and compromises and circumstances.
So far, during my three-day visit to Philadelphia, I have visited the new Museum of the American Revolution, the National Museum of Jewish American History, the Ben Franklin Museum, the Betsy Ross House, the Old Burial Ground – each one adding to my understanding and appreciation of the founding values of this nation – and now I have arrived at my last stop, the National Constitution Center.
The National Constitution Center, which opened in 2003, is on federal land but is a private, independent, nonprofit, nonpartisan institution. It is the first and only institution in America established by Congress to “disseminate information about the United States Constitution on a non-partisan basis in order to increase the awareness and understanding of the Constitution among the American people.” Its mission is to spark constitutional debates that impact citizens and inspire active citizenship.
“As the Museum of We the People, the Center aims to bring the Constitution to life for visitors of all ages through interactive programs and exhibits that include coming face to face with original documents, rare artifacts and hearing personal stories. As America’s Town Hall, the Center brings the leading conservative and liberal thought leaders together to debate the Constitution on all media platforms. As a center for Civic Education, the Center delivers educational programs and online resources that inspire, excite, and engage citizens about the U.S. Constitution.”
I arrive just in time for a multi-media orientation experience, “Freedom Rising” in a theater that has the metallic feel and design of a 21st century dystopian gladiator arena. For some inexplicable reason there is a live person who is not so much a narrator as a ringmaster as video images flash around the ceiling so you can’t fully see them or process them.
‘Freedom Rising’
“Freedom Rising” is intended to highlight the primary themes of the main exhibit gallery, making an effort to tell the story of “We the People” in two senses of that phrase: First, the Constitution’s vision of “popular sovereignty,” or rule by the people; Second, how the definition of citizenship has expanded over more than 200 years of American history to gradually include those who were left out in the 18th century – white men without property, women, African Americans, other people of color. It rang hollow to me.

You walk out of the arena to the Richard and Helen DeVos Exhibit Hall, which is designed as two concentric rings. The outermost ring is presented chronologically with 13 sections which relate American history through the lens of the Constitution from 1765 until today and a central ring focused on civics and how government operates.
Exhibits along the outermost ring use multiple techniques to bring the story to life: a short general video introduction to each section; text-and-graphic based story panels and reading rails; maps and images; game-like computer interactives; video and audio segments focusing on specific historical moments; selected artifacts; and walk-in immersive environments that render key ideas, moments, and stories in three dimensions.
For instance, you enter a re-creation of the floor of the Senate during the impeachment trial of Andrew Johnson and listen to the debate; you can step into a 1940s living room and hear one of Franklin D. Roosevelt’s famous fireside chats playing on the radio.
A device that is used to fairly good effect is presenting a major Supreme Court decision or milestone event as if told as a news story that day, making it more immediate and relevant.
The “Founders’ Library,” presents a sampling of the books that the Library Company of Philadelphia made available to the delegates during the Constitutional Convention – giving visitors a sense of the intellectual origins of the Constitution and make it more accessible.
What’s on that bookshelf that helped shape the Constitution? Jonathan Swift’s Gulliver’s Travels, King James Bible, Magna Carta, Machiavelli, John Locke, Cato’s Letters, Baron Montesquieu, David Hume, Sir William Blackstone, Adam Smith, Thomas Jefferson, Thomas Paine, John Adams, John Dickerson, among others. What’s missing: anything about the Iroquois Confederacy which provided a framework for democratic leadership and a confederation of states, not to mention women’s rights.
Other features include the Civil War alcove, an exploration of the turning point year of 1863, which features a rare copy of the Emancipation Proclamation signed by Abraham Lincoln as well as pages from an autograph book with the only-known Lincoln signature from the day that he gave the Gettysburg Address. Here I encounter a docent who lets us handle some artifacts from the Civil War.
I pose to him my theory that the Civil War could have been avoided had the slave-holding states accepted the entreaty from Zachariah Kingsley, a plantation owner in Florida, which was part of Spain until 1845 when it became part of the United States and subject to its laws regarding slavery; he entreated Congress that the United States use the Spanish model of slavery that was much less cruel (if any form of slavery could be less cruel), that provided a pathway to freedom and did not automatically enslave future generations. It was ignored. (I saw a copy of Zachariah Kingsley’s letter to Congress at Kingsley Plantation on Fort George Island near Jacksonville, Florida which stuck in my mind, “What if…”.)
You also can see a fascinating display of archeological artifacts from the late 1700s that were uncovered at the site of the National Constitution Center between 2000 and 2003, only two blocks from Independence Hall where the Constitution was drafted. These historic treasures illuminate daily life in Philadelphia as a new nation was being born.
The Central Ring through the main gallery explores how the constitutional system works through a series of immersive, interactive exhibits designed with families and school groups in mind. Visitors have the opportunity to learn about the great rites of democracy, such as serving on a jury or voting.
Role-playing is a key component of the central path. In one of the most popular displays, you can stand behind a presidential podium and take the oath of office. You can try on a judge’s robe, sit at a replica of the Supreme Court bench, and decide landmark cases selected to illustrate the broad range of constitutional issues that come before the court: Katz v. United States is a wiretap case involving the Fourth Amendment and issues of privacy; Texas v. Johnson, the flag-burning case, tested the protection of the First Amendment; United States v. Nixon, the Watergate tapes case, involved separation of powers and executive privilege.
The American National Tree, another prominent exhibit, tells the stories of 100 Americans – a few of them well known, but most of them unheralded. By selecting their faces streaming by on touch screens, you can read and hear how these noteworthy Americans have shaped constitutional history.
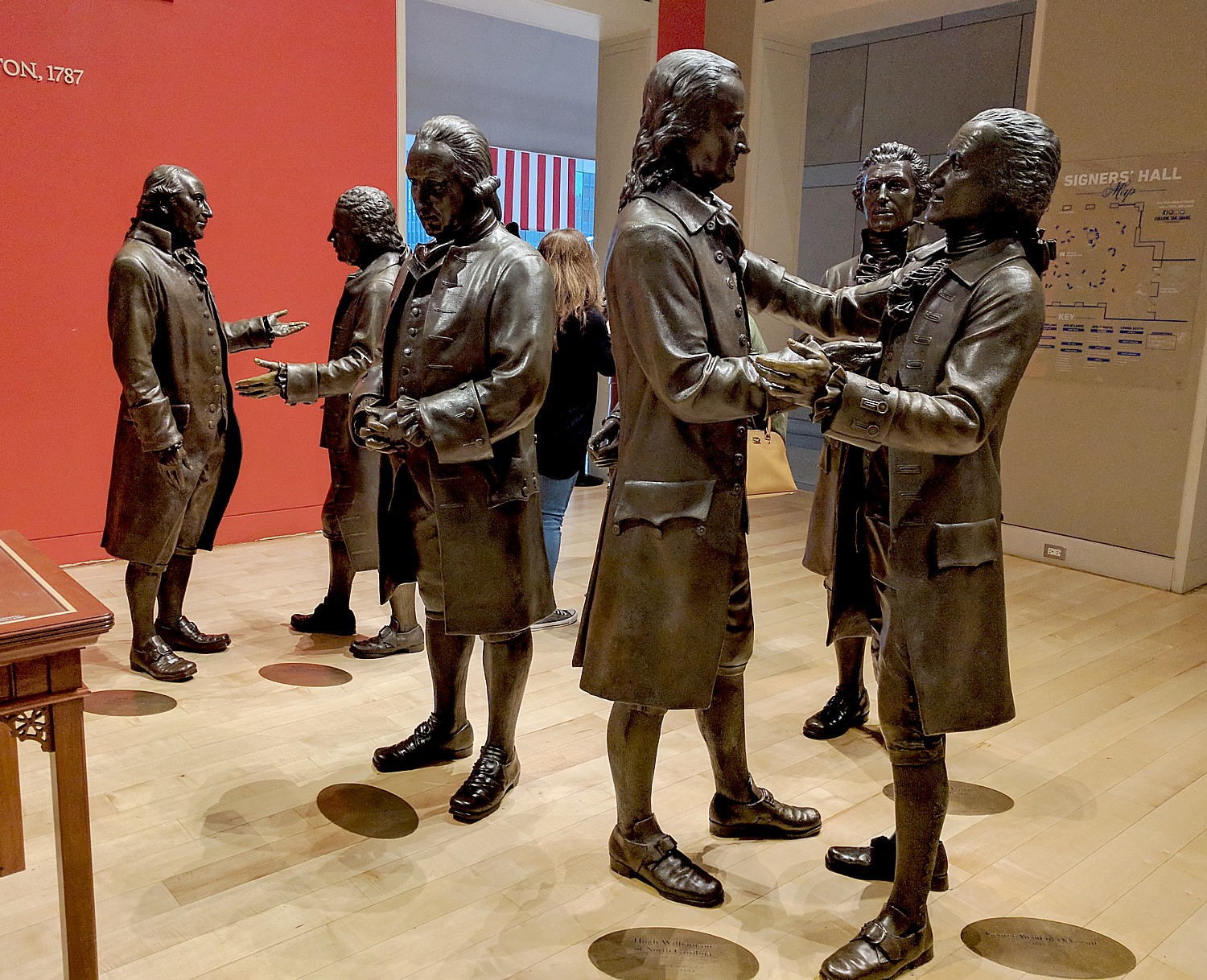

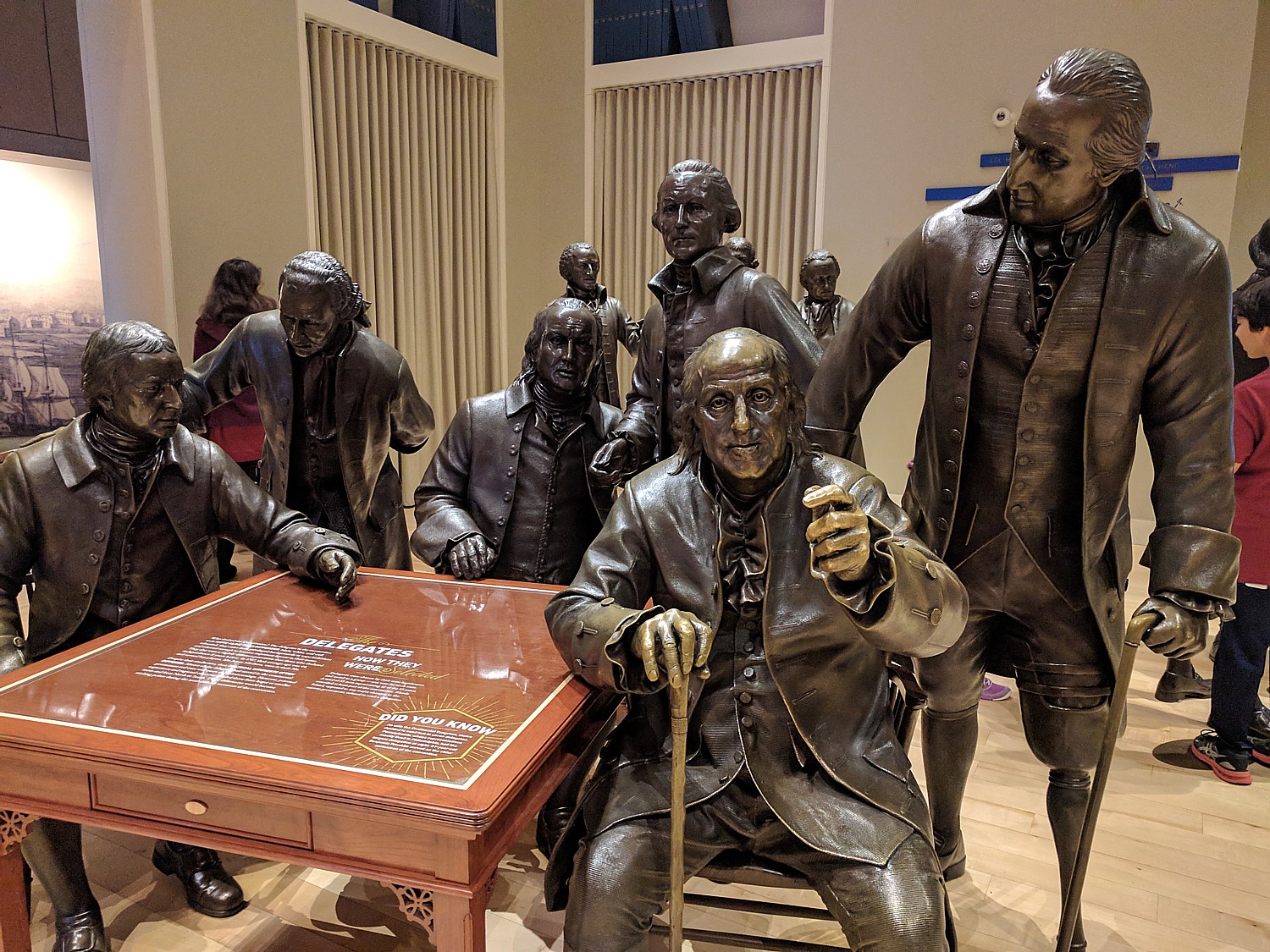
People really enjoyed Signers’ Hall, where you walk into a stylized evocation of the Assembly Room in the Pennsylvania State House, known today as Independence Hall, where the delegates to the Constitutional Convention met in Philadelphia during the summer of 1787. The room is “peopled” with life-sized bronze statues of 42 men: the 39 delegates who signed as well as the three present on September 17, 1787, who refused to sign. We are encouraged to walk among them and to consider them as real people, imaging the dilemma they faced in creating the framework for a new nation founded on “We the People” – choices that still impact the nation, the oldest continuously surviving democratic republic. You also can add your name to a digital version of the Constitution alongside the Founding Fathers’ signatures.
Notably, Thomas Jefferson and John Adams, signers of the Declaration of Independence, are not represented in Signers Hall because they were both serving as ambassadors overseas (Jefferson in France and Adams in England) during the Constitutional Convention. Several other famous Founding Fathers who were not signers of the Constitution include John Hancock, Samuel Adams and Patrick Henry.
The statues in Signers’ Hall were created by some 50 artists – sculptors, designers, costumers, mold makers – at Studio EIS in Brooklyn, who used numerous historical sources, including portraits and written descriptions, to create the most accurate likenesses possible. The project began in early 2001 and was completed in May 2003.
Unanswered Questions: How Democratic are We?
I come away with a few new insights, but few answers to long-lingering questions I have harbored:
Everything George Washington does as president sets a precedent, including doing the unimaginable of stepping down after two terms when many wanted him to be president for life. (But having visited the Museum of the American Revolution, I wonder what would have happened if Washington had been younger and not so anxious to retire to Mount Vernon, if he would have been so interested in giving up presidency.)
We learn that slander and scandals have always been a part of the political process: A Federalist called Jefferson “a Godless man whose election would lead to reign of terror, like France.” Republicans claimed John Adams was “a British-led tyrant bent on enslaving us.”
The Supreme Court’s infamous Dred Scott Decision was based on a ruling which found that Congress in its 1820 Compromise deprived slaveholders of their 5th Amendment property rights.
I learn that 1824 was the first presidential election that counted the popular vote (though I don’t really understand what that means, to “count” the popular vote.) On the other hand, it renews a question that I had ever since visiting the Women’s Rights National Monument in Seneca Falls, NY: Without any change in the Constitution that gave voting rights only to “white men with property,” suddenly, in that election, white men without property were allowed to vote. And yet, it took the 15th amendment in 1870 to give Black men the vote, and the 19th amendment in 1920 to finally give women the vote. I’ve never seen anyone question how without any change in the Constitution, all of a sudden, white men were allowed to vote, and it enabled –Andrew Jackson, who lost in 1824 to John Quincy Adams, to win his election in 1828.
When freed black men also turned up to vote, states passed laws restricting voting to “white men over 21”.
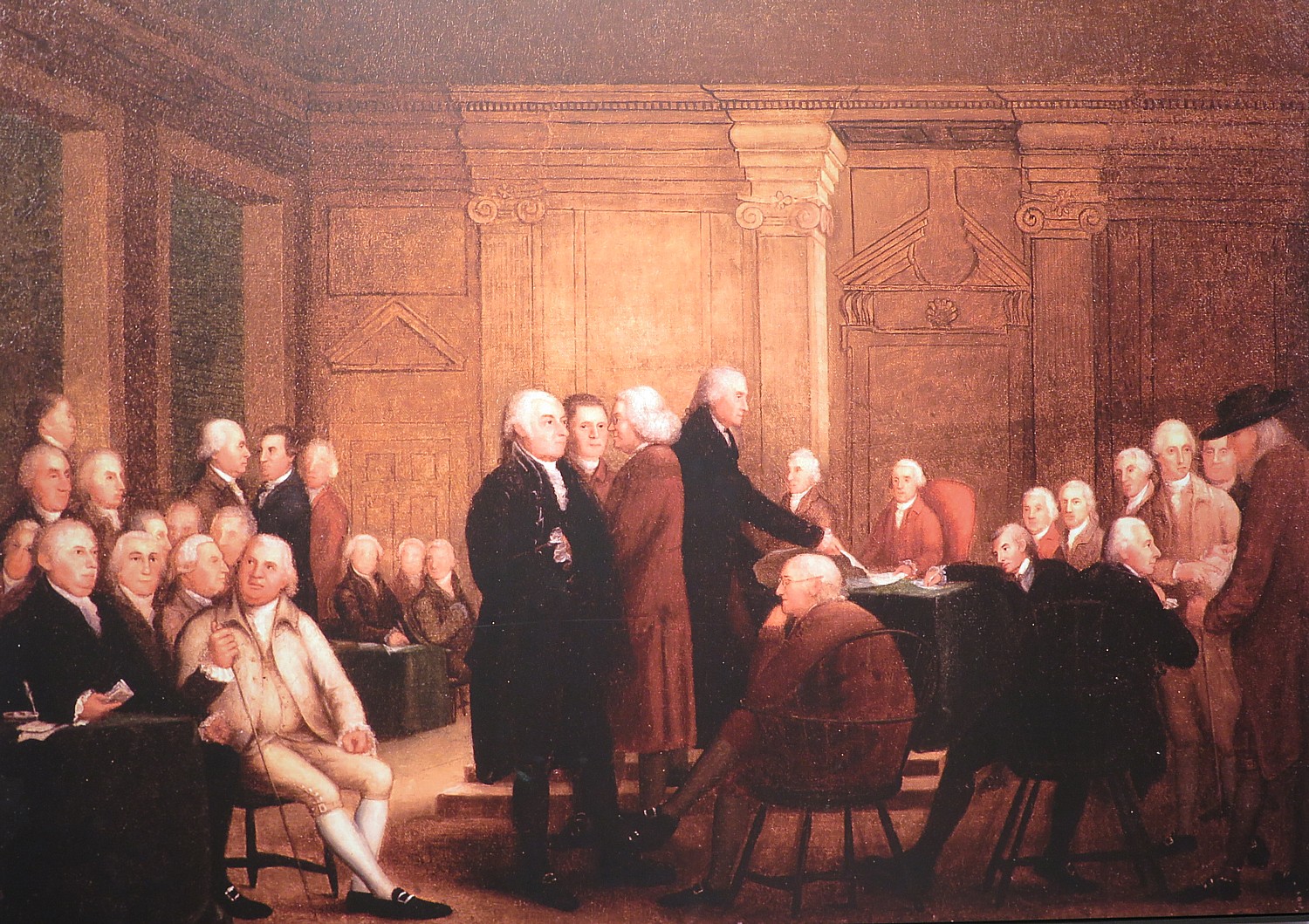

I learn that the Bill of Rights, adopted in 1791 (itself a compromise because there were states that would not ratify the Constitution without a Bill of Rights, which are the first 10 amendments) only applied to federal law. In recent decisions, the Court ruled that their protections apply to states because certain rights are so fundamental, they are incorporated in amendment guarantee of due process.
“Like the preamble of Declaration of Independence, the Bill of Rights at the time of ratification was largely a promissory note. It was not until the 20th century when the Supreme Court vigorously applied the Bill of Rights against the states that the document becomes centerpiece of the contemporary struggle over liberty and equality. It defends the majority against an overreaching federal government but also against overreach by the state.”
What you appreciate, though, is that through all of American history, there have been “firsts” – challenges or unsettled issues of the Constitution. It was never fixed or complete. The Founders designed the Constitution to be a “living” document. So-called “originalists” who pretend to divine what was in the mind of the Founders are just that: pretenders.
A new display is an “Interactive Constitution”, where you can click on the freedoms of the Bill of Rights to see the documents that were used.
There are hands-on materials. For example, you can try on a black robe of a Supreme Court justice.
When I am visiting, I am lucky enough to see an original copy of the Bill of Rights on view in the George H.W. Bush Gallery before it was sent back to New York. It is one of 12 original copies that survive. (North Carolina’s was stolen during the Civil War but was returned in 2003 with the help of the National Constitution Center, which informed the FBI after being told they could have it back for $4 million ransom). This copy, is shared by New York and Pennsylvania which alternates every three years (it now has gone back to New York, where you can see it on camera).
There is also a first-edition Stone Engraving of the Declaration of Independence and an original copy of the US Constitution.

I’m not sure that what I came away with was the message that the Center intended: Instead of assurances that the Framers created mechanisms – fool-proof checks-and-balances – to insure a democratic republic would withstand every challenge, I am shaken by the realization of how wrong those in power, with the ability to set laws, decide laws and implement laws, have been (think Dred Scott, Citizens United). It seems that it has been a matter of luck that has let us survive this long, but one wonders how would we survive a “perfect storm” of various levers breaking down against threats that the Framers could never have foreseen, like an election that was stolen by a foreign adversary, or a president who used his office to personally profit, who sold favors to a foreign government and then defied a subpoena. Andrew Jackson defied the Supreme Court’s ruling that his Indian Removal Act was unconstitutional, daring the court to bring its army to force him to do its bidding.
I went in wondering if it would address some of the questions that I have long harbored: did the Salem Witch Trials play any part in the Founders’ interest in preserving Religious Freedom? What role did the Iroquois Confederacy play in the writing of the Constitution? How does the notion of “originalism” – the pretense of knowing what the Founders intended – carry sway since the Constitution was clearly not perfect, the Founders were not omniscient and could not predict technology of today, were not Gods, knew their own human fallibilities in devising a system of government that had never been seen before, as well as the need to compromise on such issues as slavery in order to forge a union and the fact we have already adopted 27 amendments?
The Constitution already has provision for impeachment (for “high crimes and misdemeanors”), already has an Emoluments clause, more recently adopted a 25th Amendment to provide for a President who is “unable” or unfit, but what provision is there to “re-do” (or nullify) an election that is stolen – votes literally being switched in an e-ballot box – using the advanced technology of today? I wonder about the changes that need to be made in light of expanded population and new technologies, but that are resisted.
For example, the Founders never imagined the powerful role that political parties would play – indeed, had to immediately change the procedure for “electing” the President and Vice President – but the present system almost guarantees a President elected by a minority of voters. The Electoral College, which functions mostly by tradition and not by law, but was created as a check against populism at a time when communications were slow, voting confined to a small elite, has already been demonstrated to be obsolete in its function by twice selecting as President a candidate who lost the popular vote, not to mention that it nullifies the ideal of “one person-one vote” because it gives so much unequal representation to small-population states over high-population states (as does the Senate). The Founders never imagined the fire power of an assault weapon at a time when the most sophisticated personal weapon was a single-ball musket.
I don’t find the answers to my questions.
Constitution Heritage Act
A permanent memorial to the Constitution was first proposed around the celebration of the centennial of the Constitution in 1887. It did not begin to take shape until the idea was proposed again 100 years later during the document’s bicentennial celebration in 1987.
President Ronald Reagan signed the Constitution Heritage Act of 1988 on September 16, 1988. The act directed the establishment of the National Constitution Center, an institution “within or in close proximity to the Independence National Historical Park” that “shall disseminate information about the United States Constitution on a nonpartisan basis in order to increase awareness and understanding of the Constitution among the American people.”
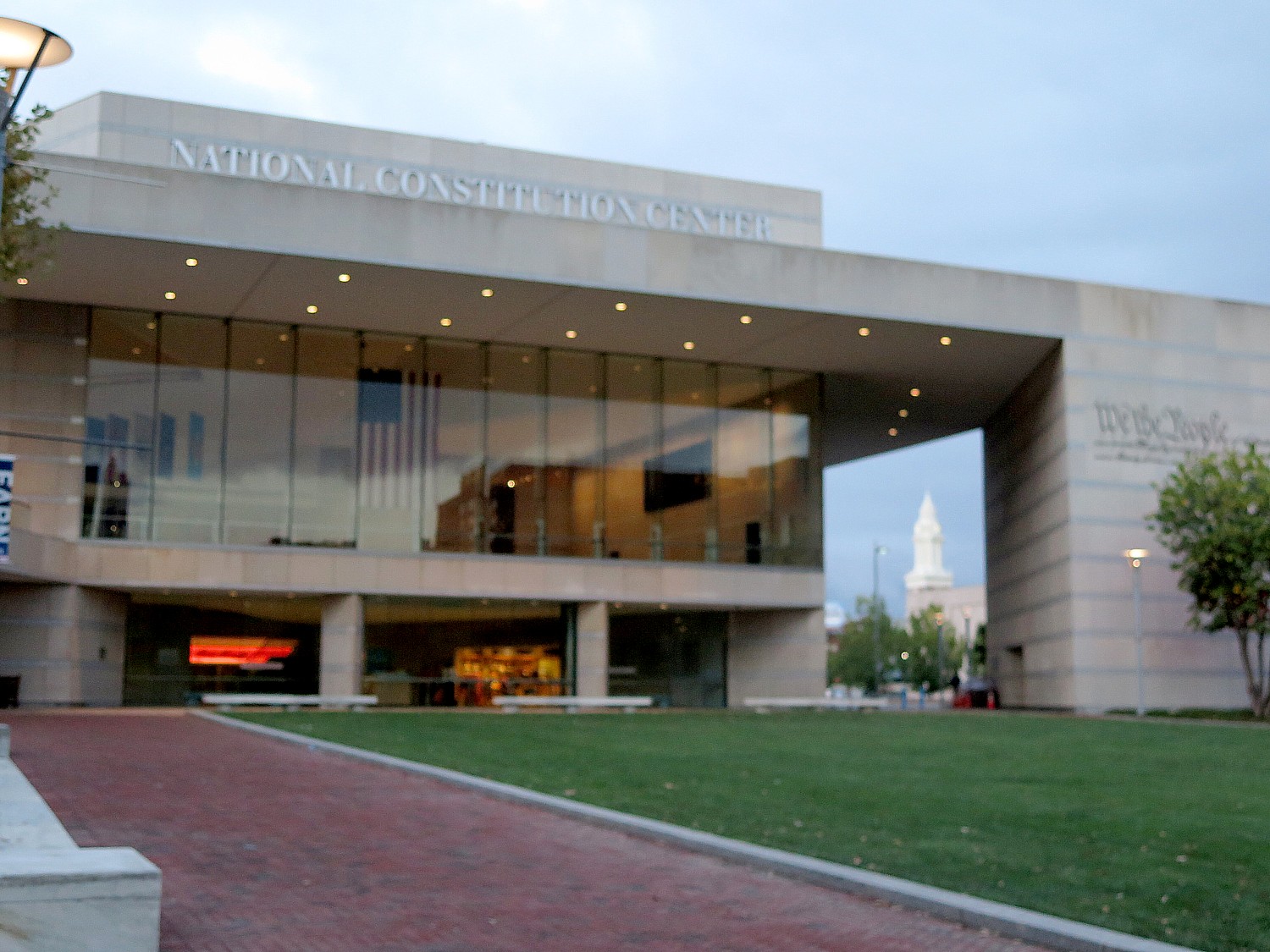

The Center opened on July 4, 2003, at 525 Arch Street (the date itself was significant, translating to May 25, 5/25, the date that the Constitutional Convention began in Philadelphia in 1787) in Philadelphia’s Independence National Historical Park, “America’s most historic square mile.” Designed by the architectural firm Pei Cobb Freed & Partners, the building is made of American products, including 85,000 square feet of Indiana limestone, 2.6 million pounds of steel, and a half-million cubic feet of concrete. The limestone used in the building is from the same quarry as the Empire State Building’s materials.
The National Constitution Center owns a rare, original copy of the first public printing of the Constitution. This printing was published in a newspaper, The Pennsylvania Packet and Daily Advertiser, on September 19, 1787—two days after the Constitution was signed. Since the Constitutional Convention was conducted under an oath of secrecy, this printing represents the first time that Americans (“We the People”) saw the Constitution. (The original signed, handwritten Constitution is at the National Archives in Washington, D.C.)
Now is an especially exciting time for visitors because the Center is displaying the rarest handwritten drafts of the U.S. Constitution through 2019.
In addition to exhibits, visitors can enrich their visit with daily museum programs or a Living News performance.
In Living News, today’s headlines are brought to life in a dynamic performance incorporating video, contemporary music, and current news broadcasts. Featuring three engaging actors who play multiple roles, Living News introduces controversial constitutional issues and encourages audience members to explore their own points of view during a post-show discussion.
Visitor amenities include The Delegates’ Cafe, a glass-enclosed restaurant providing the backdrop of historic Independence Mall, as well as a Museum Store, offering a wide range of gifts, books, apparel, jewelry, and toys.
The National Constitution Center also houses the Annenberg Center for Education and Outreach, the national hub for constitutional education, which offers cutting-edge civic education resources both onsite and online.
Constitution Daily Blog: constitutioncenter.org/blog
We the People Podcast: constitutioncenter.org/podcasts
America’s Town Hall Programs Live: constitutioncenter.org/live
The National Constitution Center is located steps from Independence Hall, where the Constitution and the Declaration of Independence were signed.
You need a minimum of 1 hour to visit, but more likely will spend at least two to three hours.
General Admission to the museum and daily programming: Adults $14.50; Youth (6-18) $11; Students w/ID, Seniors $13. Members, active military personnel, and children ages 5 and under admitted free.
The National Constitution Center, Independence Mall, 525 Arch Street, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19106, 215-409- 6700, constitutioncenter.org.
Visit Philadelphia provides excellent trip planning tools, including hotel packages, itineraries, events listings: 30 S 17th Street, Philadelphia PA 19103, 215-599-0776, visitphilly.com.
See also:
National Museum of American Jewish History is Unexpected Revelation in Philadelphia
Philadelphia’s New Museum Immerses You into Drama of America’s Revolutionary War
72 Hours in Philadelphia: Meet Betsy Ross: A Thoroughly Modern Woman
_____________________________
© 2018 Travel Features Syndicate, a division of Workstyles, Inc. All rights reserved. Visit goingplacesfarandnear.com, www.huffingtonpost.com/author/karen-rubin , and travelwritersmagazine.com/TravelFeaturesSyndicate/. Blogging at goingplacesnearandfar.wordpress.com and moralcompasstravel.info. Send comments or questions to [email protected]. Tweet @TravelFeatures. ‘Like’ us at facebook.com/NewsPhotoFeatures