
By Karen Rubin, Travel Features Syndicate, goingplacesfarandnear.com
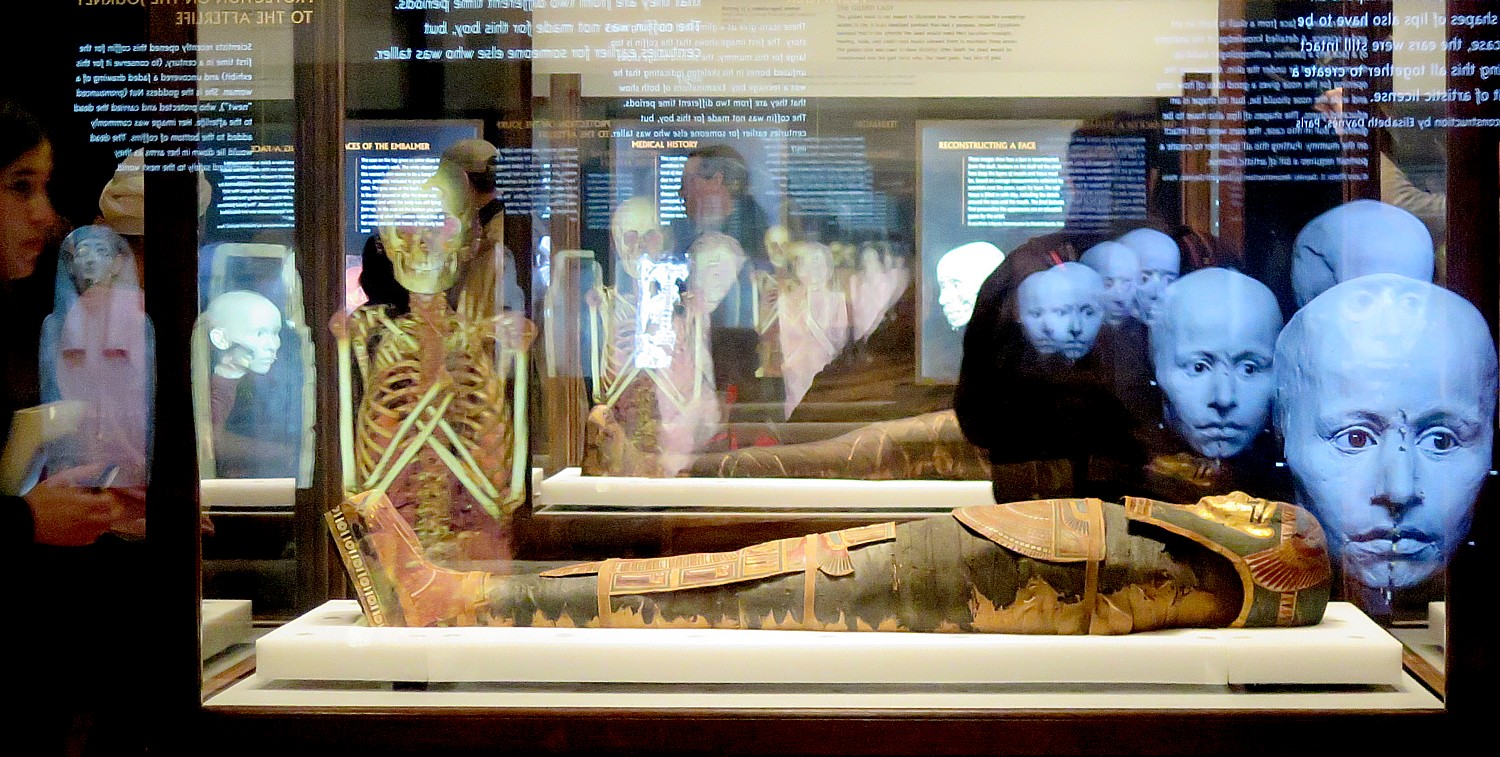
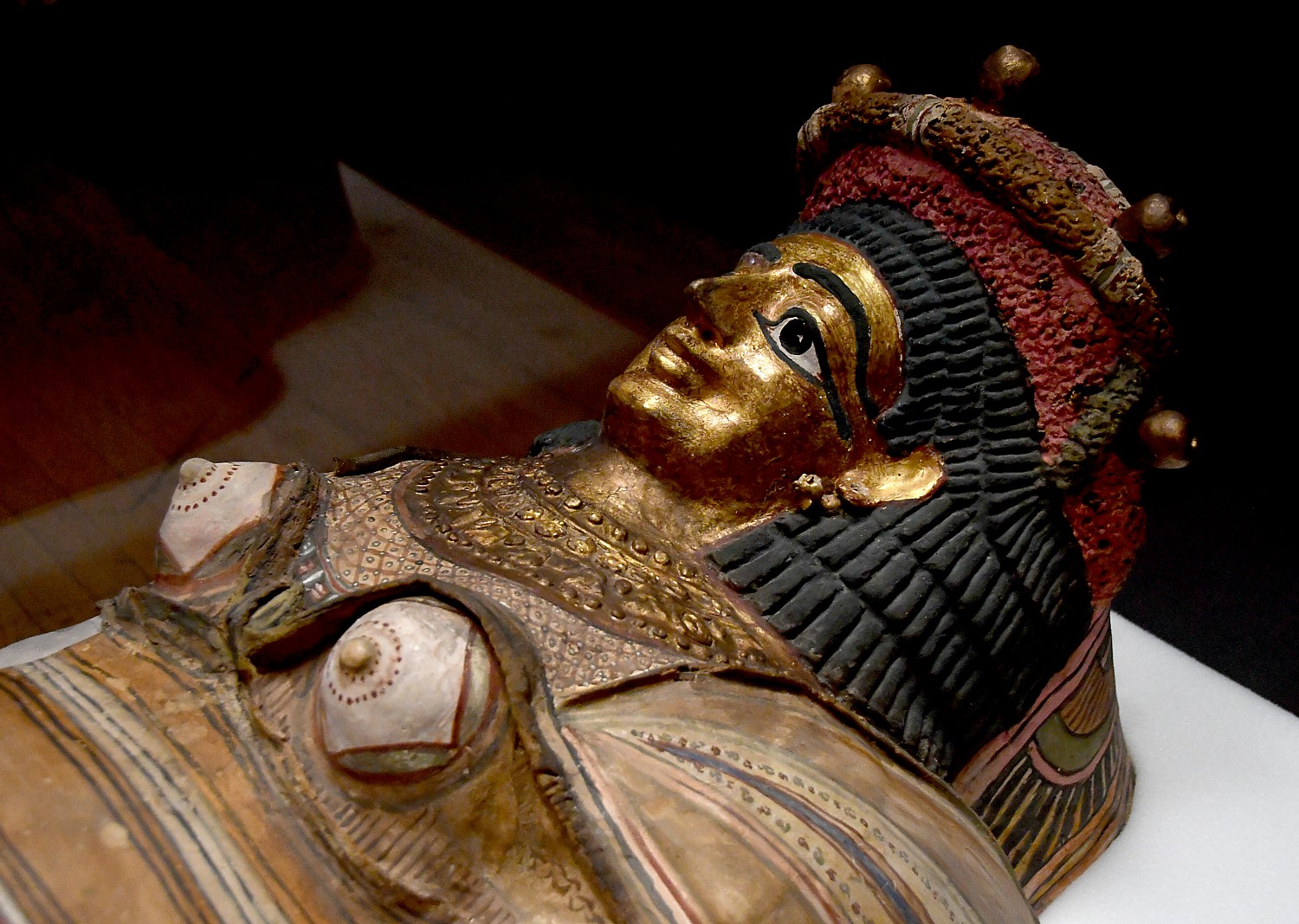
The Gilded Lady seems to be resting peacefully, her painted visage staring up to the sky. But inside this container are the remains of a real woman who lived nearly 2000 years ago, and for the first time, the ancient coalesces with 21st century scientific techniques: we actually get to peer inside, probing down layer by layer to her mortal remains, and then, at a digitally reconstructed, 3-D image of her as she lived: this middle-aged woman was beautiful.
She has already traveled from Chicago where she lives at the Field Museum, to Los Angeles, Minneapolis, Denver and now she is reposing here in New York as part of Mummies, an extraordinary exhibit featuring one of the largest collections of mummies housed in North America that just opened at the American Museum of Natural History through January 7, 2018.

The exhibit provides an unparalleled glimpse into the lives and traditions of people from ancient cultures. It puts us face to face, head to head with people who lived their lives thousands of years ago, in Egypt and in Peru – two of the many cultures that practiced mummification. The contrasts and the similarities are striking, and just as their similarities speak to a unity of humanity, this extraordinary way of connecting past to present connects us as human beings. (And to bring about an even broader connection, increasing the span from thousands to 100s of thousands of years ago, be sure to visit the AMNH’s Human Evolution wing.)

“Mummies have long been fascinating, and now the intersection of these ancient relics and cutting-edge technology is revealing new and intriguing secrets,” said Ellen V. Futter, President of the American Museum of Natural History. “For generations, the Museum has studied and presented the diverse cultures of humanity, past and present, to help us better understand one another and ourselves. Today, when such understanding is more important than ever, Mummies invites us all to consider both what may be distinct among cultures and what is universal in the human condition.”
On a special, limited tour from the collections of The Field Museum in Chicago — and presented for the first time on the East Coast (the traveling exhibition has already been on view in Los Angeles, Minneapolis and Denver), Mummies showcases the ritually preserved remains of 18 individuals from ancient Egypt and pre-Columbian Peru. The Peruvian mummies that are on display have not been seen since they were exhibited at the 1893 Chicago World’s Fair.
Significantly, you get to discover how modern imaging techniques have transformed the study of mummification by letting researchers peer inside centuries-old mummies without disturbing or damaging them. Digital touchscreens let you “virtually” peer into Peruvian mummy bundles, layer by layer from the skin to the bones, as well as animal mummies buried as offerings to Egyptian gods. You also get to handle 3D-printed figurines of burial goods that were encased within mummy wrappings for millennia and only recently revealed.
“You may think you know mummies,” Futter said at a press preview, pointing to the most popular representations in horror movies. “That’s not what this show is about. This is serious business that simultaneously offers a window to the past – two different ancient worlds – and into the latest technology and study. You get a glimpse of actual people entombed – who they were, what their lives were like, what they looked like.”
“They are like messages from a different time – they are our sisters and brothers in a shared humanity. It may not be as sensational as a [horror] movie, but more amazing than you would have imagined.”
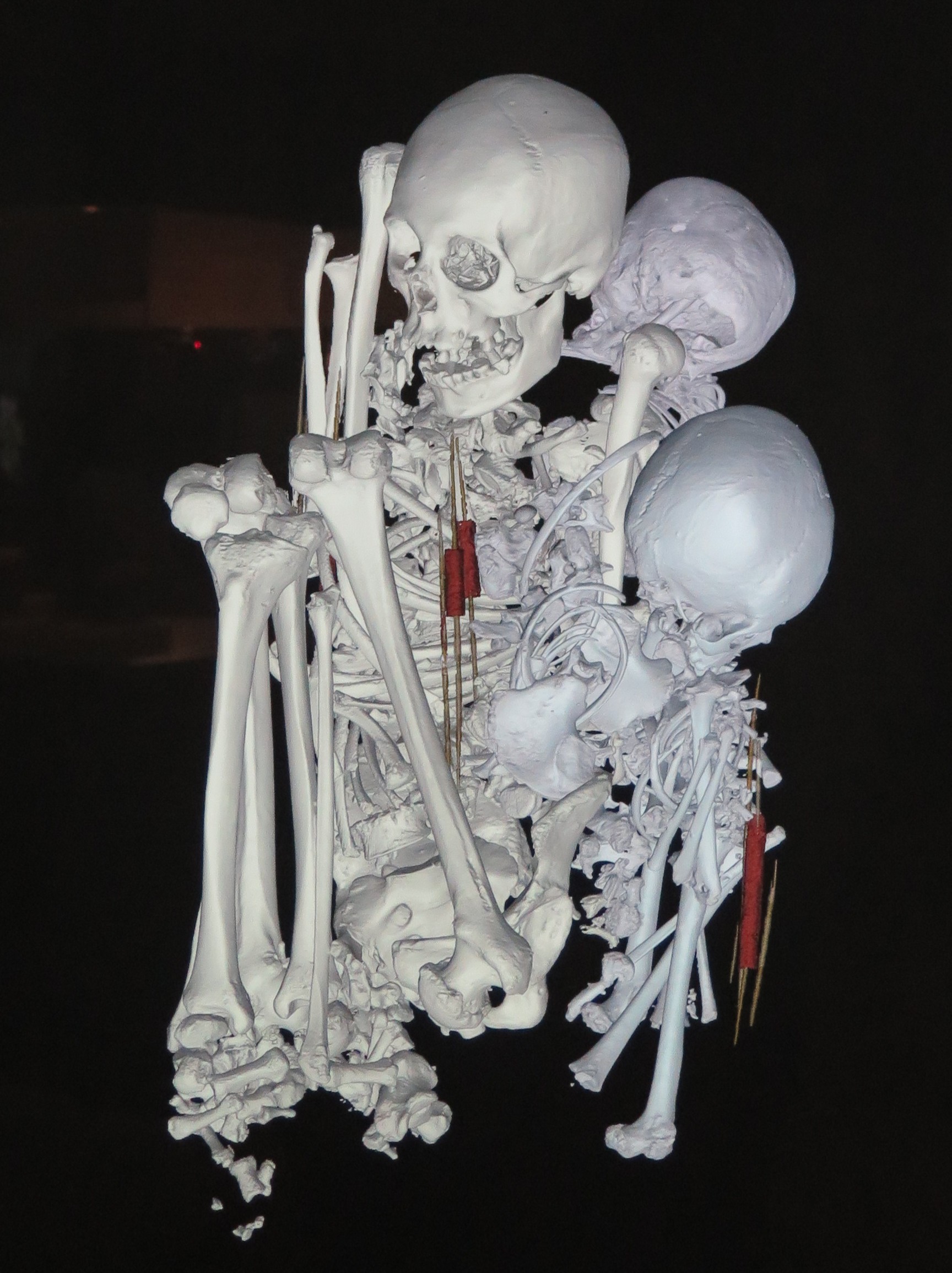
Indeed, most people – especially young people – have never actually seen a dead body before. The most profound experience in the exhibit is seeing the remains of a woman who lived 5500 years ago, whose bundled body was left in the Egyptian desert where it naturally mummified.
Indeed, it wasn’t just pharaohs and their spouses and other royal figures who were mummified, though their tombs and the possessions that were left with them reflected their station. This was the common practice – as people were lower and lower down the economic totem pole, the possessions that they would have been buried with were more and more modest.
In Egyptian society, it was also common for animals to be mummified and buried – there is a baboon and a crocodile in the exhibit. Cats were actually popular and David Hurst Thomas, the co-curator of the exhibit, said that archaeologists found cemeteries of a million mummified cats, manufactured for sale to be entombed with the loved one.

It is fascinating to have this view to contrast the Peruvian mummies (I’m betting few people have even realized that pre-Colombian Peruvian peoples practiced mummification), with the Egyptian burial practices. The two civilizations never interacted – mummification developed independently, indeed, on every continent but Antarctica, Dr. David Hurst Thomas, curator of North American archaeology, division of Anthropology and co-Curator of the Mummies exhibit, said at a press preview of the exhibit.
In Peru, mummification was intended to enable the living to stay connected with their loved ones. The body was carefully prepared and wrapped and then a mask was placed on top the canvas.
One of the scans of a bundle reveals that it is a woman with two children. The scans also show artifacts that have been buried with the individual.
The ancient Egyptians, in contrast, mummified their dead so that they could live on – their limbs intact – in the next world. The earliest mummies, like the 5500-year old woman, were not buried in elaborate pyramids or tombs, but were put into a pit grave. Over the centuries, the mummification process became more and more elaborate – organs were preserved in canopic jars and bodies placed in magnificently painted coffins with gilded masks.
By using these new technologies – most that have come from medicine – the scientists have been able to see artifacts that were buried with them, how a mother is buried with her two children (how did they die?).
“They have so much to teach us – medical infirmities, migration, interaction of societies,”
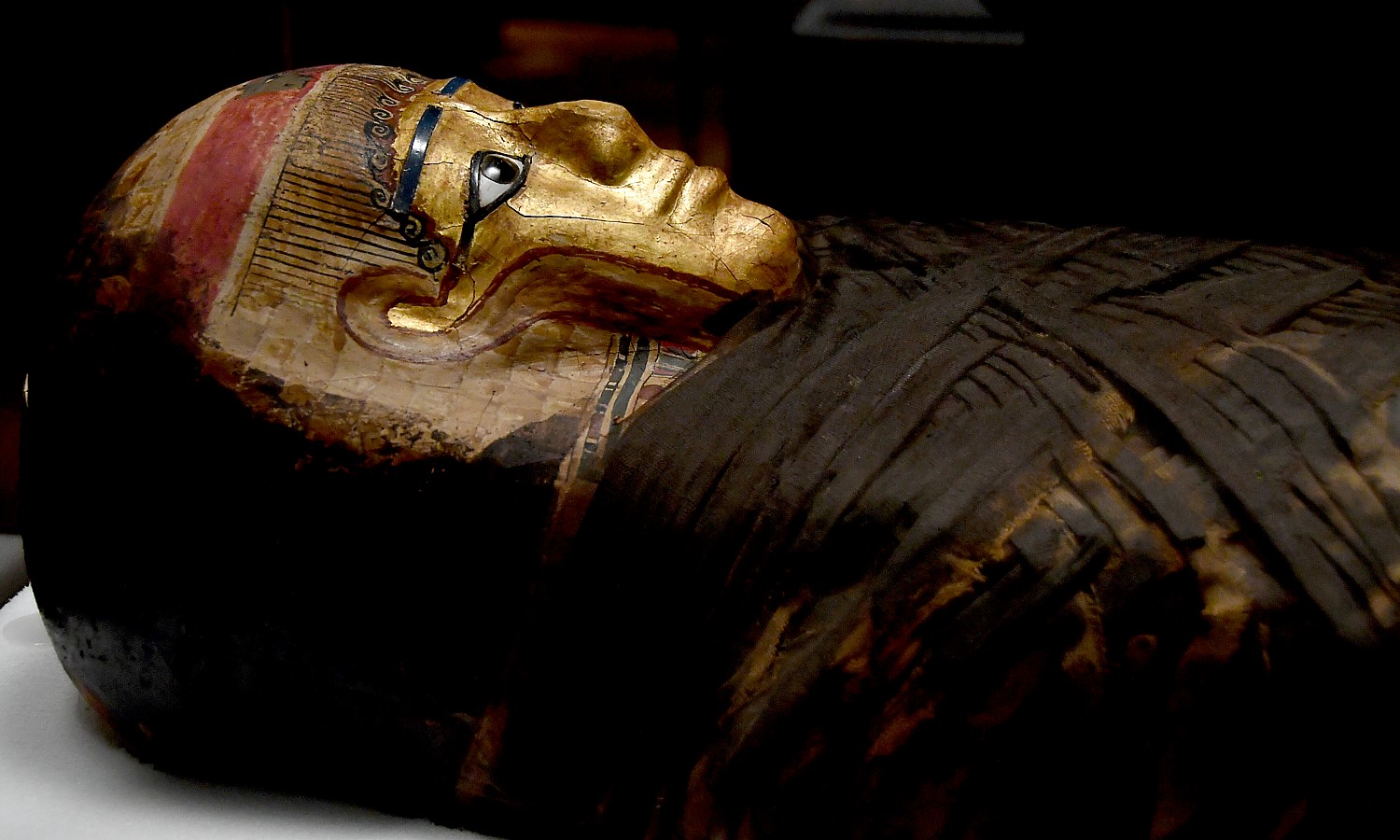
The Gilded Lady, for example, is utterly fascinating – you see her in her magnificently decorated coffin, and on the wall are the slides that show how her hair was curled, had a damaged spine, possibly as a result of tuberculosis. Based on the scan of her skull, they made a 3-D reconstruction using a 3-D printer, and from that, like a forensic scientist, re-created what she likely looked like in life – all of this in one view.
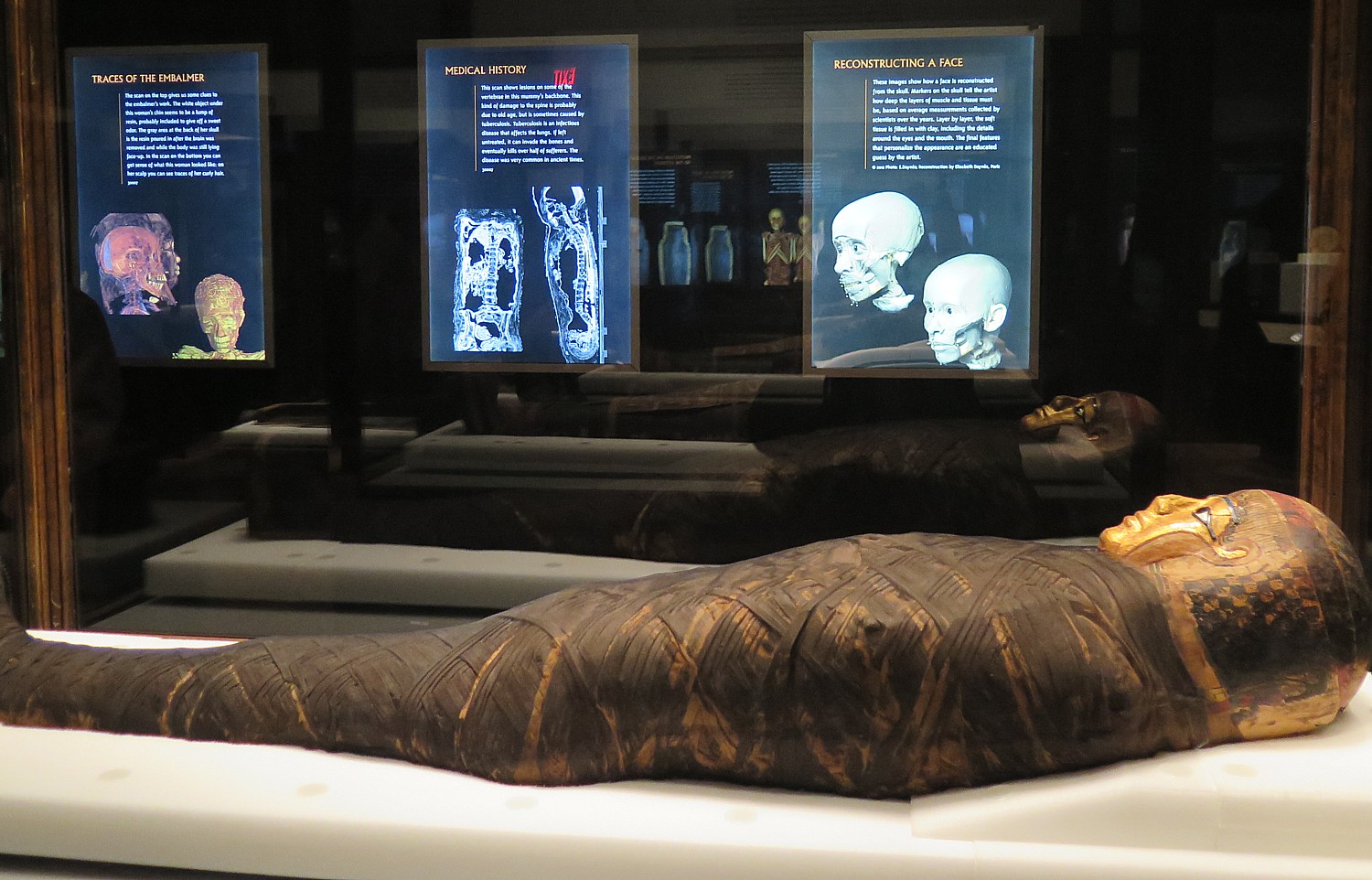
The gilded mask that we see was not meant to illustrate how the woman looked in life, but was an idealized portrait that had a purpose: the Ancient Egyptians believed that in the afterlife, the dead would need their faculties – eyesight, hearing, taste and smell. The masks allowed them to maintain these senses. The golden skin was used to show divinity: after death, the dead would be transformed into the god Osiris, who, like most gods, had skin of gold.
The Gilded Lady lays across the room from another mummy, named Minirdis according to the hieroglyphs on the coffin. The coffin was opened for the first time in a century for this exhibition. In examining the remains, researchers discovered the teenaged boy inside was mummified around 250 BC, or 200 years after the coffin was made, construction of the coffin, indicating that the mummified individual wasn’t Minirdis after all, and confirming that coffins were occasionally recycled (though might not the inscription have been added when the boy was buried?)
The hieroglyphs on the coffin say the name of the mummy who is supposed to go inside it – Minirdis, son of a priest. Preserving the person’s name was essential for their soul to reach the afterlife. Minirdis means “Min is the one who gave him,” and Min was a god of fertility. The inscription also says that Minirdis’ father, Inaros was a priest, in charge of purifying and clothing the god’s statue. The only problem was that the boy inside was mummified around 250 BC, or 200 years after the coffin was made, indicating that the mummified individual wasn’t Minirdis after all, but also confirming that coffins were occasionally recycled.
The scans of the body show that the coffin was too large for the body inside and the bones hadn’t fused, indicating that the body was a teenage boy.
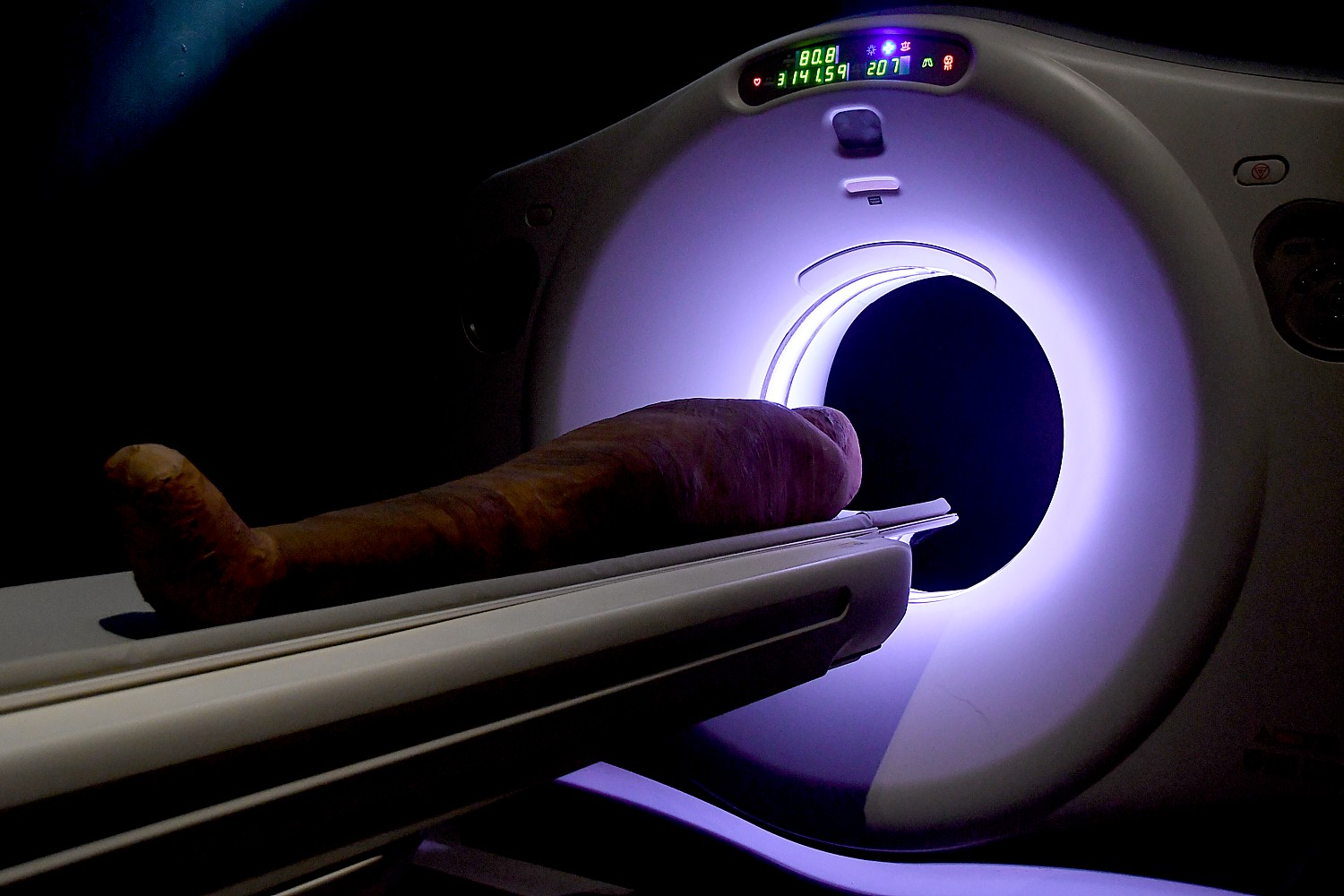
The CT scans enabled scientists to generate 3D-printed skull reconstructions of both the “Gilded Lady” and Minirdis. Then, artist Elisabeth Daynès studied the replicas and built facial muscles and skin layer by layer. The hyper-realistic portraits in 3D. we meet at the end of the exhibit let us come face-to-face with these ancient people, seeing them as they may have looked in life —while their mummified remains sleep peacefully.
Peruvian Mummies On View for the First Time in a Century
We are much more familiar with Egyptian mummies, particularly with the sensational exhibits of King Tut and the artifacts uncovered from his tomb in the Valley of Kings, as well as the scientific analysis of his mummified remains. But this exhibit goes much further in its exploration of the cultural significance of the burial practice.
The first part of the exhibit focuses on the collection of Peruvian Mummies, which had not been seen in public since they were on display in the 1893 Chicago World’s Fair.
People living along the Pacific coast of South America in what is now Peru began to mummify their dead more than 5,000 years ago. Scholars think that the Chinchorro culture (5,000–2,000 BC)—the world’s first practitioners of mummification—prepared the bodies of their loved ones personally, removing the deceased’s skin, de-fleshing the bones, and removing the organs before reinforcing the skeleton with reeds and clay and reattaching the skin. The mummy was then painted black or red and given a wig and an individualized clay portrait of the deceased.
In addition to the Chinchorro, dozens of societies in the region mummified their dead to remember and remain connected with the departed.
As we walk through the Mummies exhibit, we encounter a number of Peruvian mummy bundles, including the mummified remains of three children from the Chancay culture (AD 1000–1400), which placed their dead into a sitting position and wrapped them in layers of cloth.
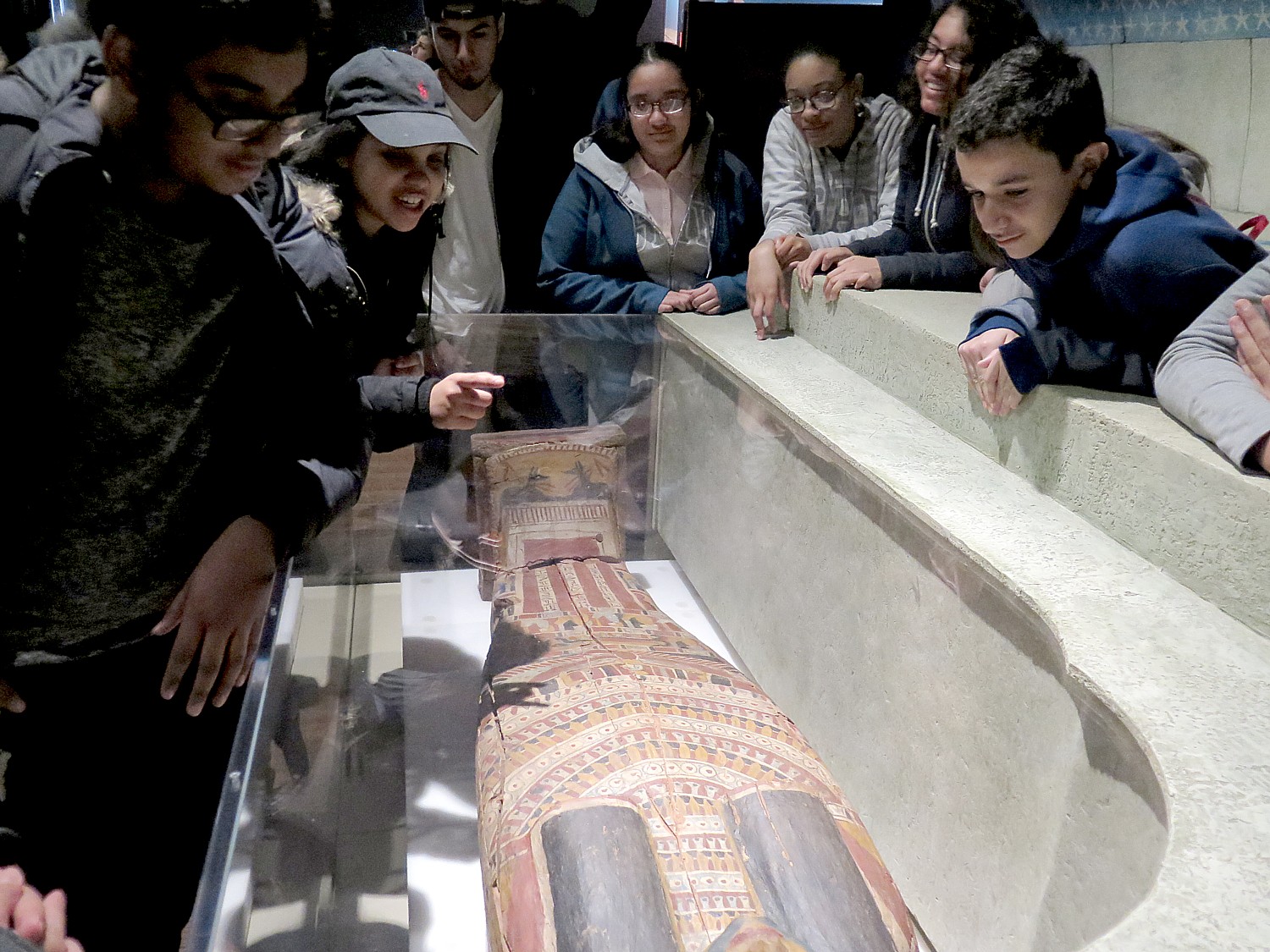
The exhibit is very much hands-on, interactive, if you can believe it, because you get to do what scientists do, in penetrating the layers of scans to reveal the body contained in the wrappings, through the skin layer, to the bones.
There are digital touchscreens, where you can examine composite CT scans of these mummies and virtually “unwrap” them to reveal figurines and other burial offerings that are contained within, becoming surprised as surely the scientists were, when a scan reveals a mother with two children bundled together, or seeing the objects that were personal or prized which reveal so much about who they were in life.
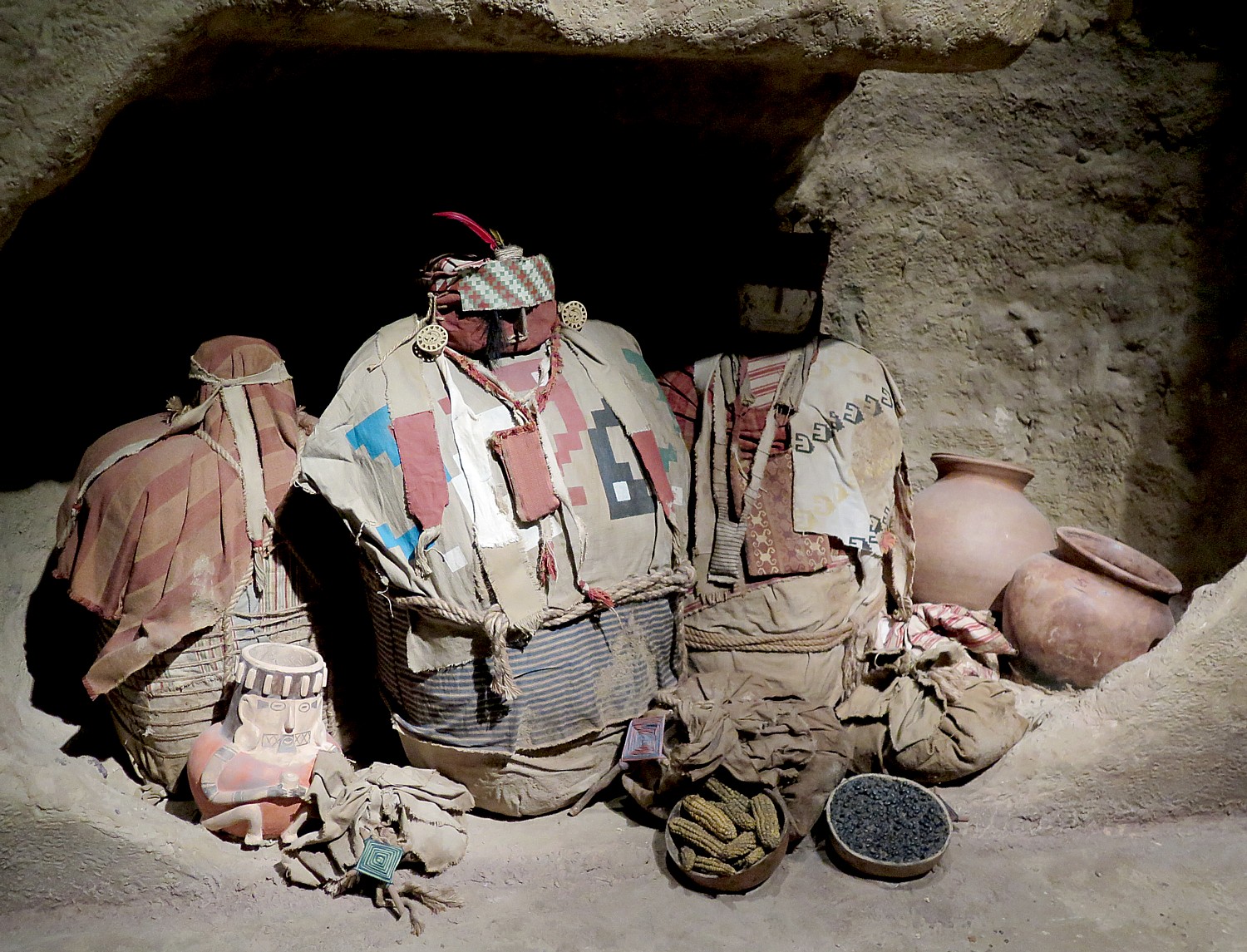

A life-sized diorama of a Chancay pit burial demonstrates the common practice of interring members of an extended family together. These burial pits were accessible to living family members, allowing relatives to bring food or drink to their loved ones’ graves, or even to remove mummies to take them to festivals or other special events. We see examples of real burial offerings such as chicha (corn beer) pots.
Jim Phillips, curator of The Field Museum, tells me that the Peruvian mummies were uncovered on expeditions in the 1880s and 1890. This means they would have been recent finds – the most modern discoveries – when they were displayed at the 1893 Chicago World’s Fair.

Egyptian Mummies of the Nile Valley
Unlike people in Peru, ancient Egyptians believed the dead could live on in the next world if provided with a physical home, preferably within the body itself. This belief made it essential to preserve the corpse, and Egyptians used an elaborate process of mummification to halt the natural process of decay. Scholars posit that natural mummification—an example of which can be seen in the remains of a woman whose preservation occurred naturally in the hot, dry sand about 5,500 years ago—gave Egyptians the idea for artificial mummification.
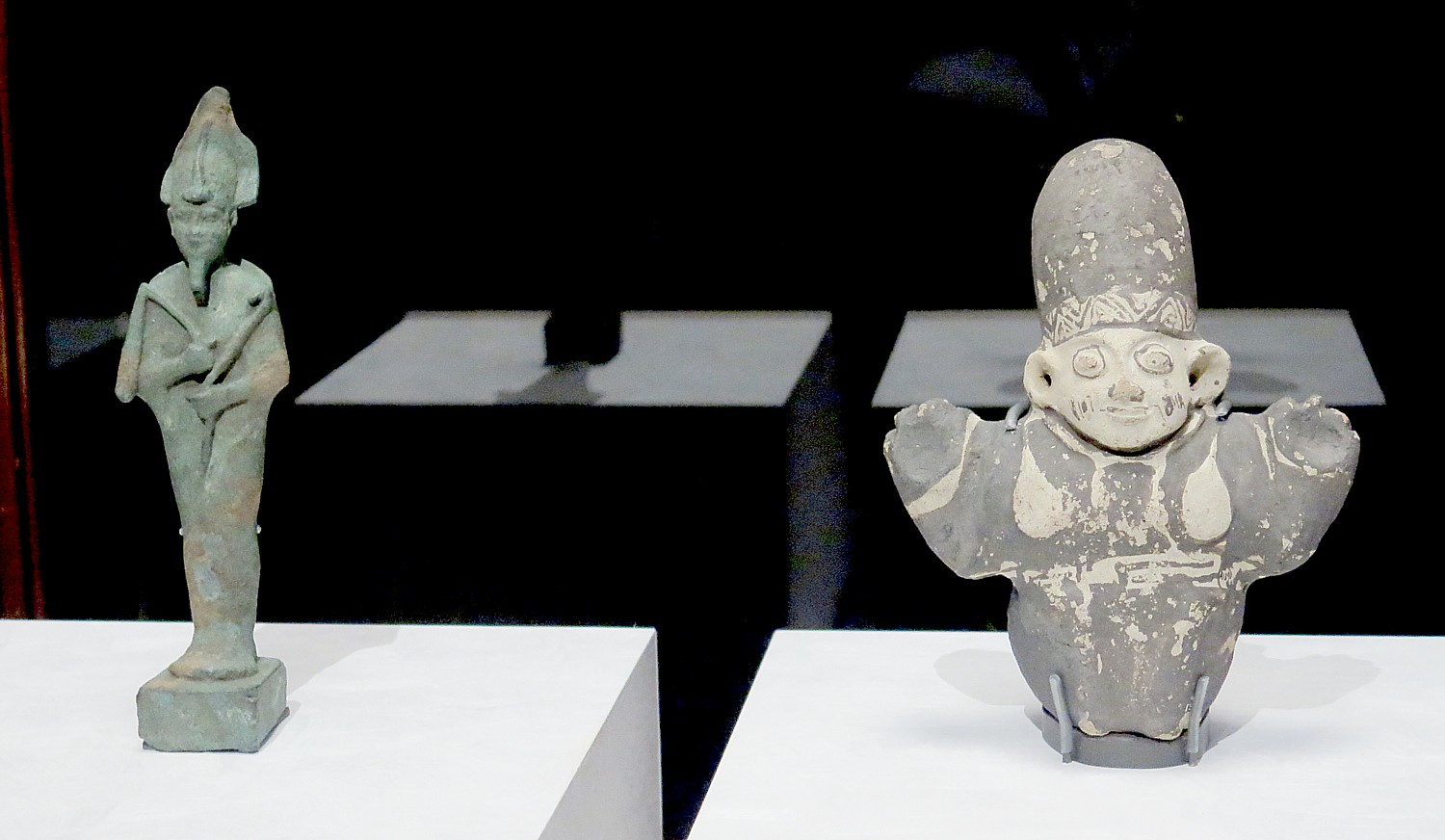

Within centuries, ritual burial in Egypt evolved into a complex practice that included elaborate embalming, brilliantly decorated sarcophagi, and grandiose tombs designed to deter grave-robbers (we see magnificent limestone busts from sarcophagi that were an added layer of security to those who could afford this extra protection and would have weighed thousands of pounds). Organs that would hasten decay—the liver, lungs, intestines, and stomach—were removed, preserved, wrapped, and housed in separate containers. The heart—thought to be the source of emotion and intellect—often stayed in place, since it would be necessary in the afterlife, while the brain, thought to have no use, was removed through the nose. Forty days in salt desiccated the body, and embalmers then used resins, oils, and padding to restore its appearance before wrapping it in linen. Artifacts on view include a Ptolemaic Period mummy (332-30 BC) along with canopic jars containing the person’s organs. Here, there are stations where you can handle 3D-printed burial figurines that depict ancient Egyptian gods provide visitors with an opportunity to explore the hidden artifacts within its wrappings.

The objects found in Egyptian tombs were meant to provide for the deceased in the afterlife. Burials of wealthy Egyptians include their servants, represented by figurines called shawabti; ideally there would be 365 of these, one for each day of the year, with 36 overseers, one for each week in the Egyptian calendar. Even mummified animals were included in tombs, and archaeologists have uncovered cemeteries containing millions of animal mummies, including cats, baboons, gazelles, birds and even crocodiles, some of which are on view. Grave-robbing was rampant in ancient Egypt, and an Egyptian tomb diorama represents a type of crypt that Egyptians with rank or wealth constructed to guard against such thefts. Within the tomb, a plain stone sarcophagus contains a smaller stone sarcophagus and a wooden coffin from the Late Period (525-343 BC) covered in hieroglyphs. Most of the imagery on the coffin was inspired by scenes in The Book of the Dead, a collection of funerary texts believed to assist a person’s journey into the afterlife.
Dr. Thomas says the Gilded Lady steals the show, and indeed she does. She was mummified during the Roman Period (30 BC-AD 395), a period when we see in the exhibit the most magnificently painted coffins. There is one of a woman whose coffin is a stunning piece of artwork – it has a magnificent gilded mask and the body had pronounced breasts. Why? The anthropologists could not say, showing that there is still so much more to be learned.

Mummies is on view in New York through January 7, 2018. The exhibition is co-curated at the American Museum of Natural History by David Hurst Thomas, Curator of North American Archaeology in the Division of Anthropology, and John J. Flynn, Frick Curator of Fossil Mammals in the Division of Paleontology.
Mummies was developed by The Field Museum, Chicago, and will go back there for an exhibition after its New York showing.
Explorer
Mummies is featured in the Museum’s recently re-launched Explorer app, developed with support from Bloomberg Philanthropies, which lets visitors think like an explorer by personalizing their onsite experience using cutting-edge location-aware technology that provides unique journeys through the Museum’s 45 permanent halls.
More information about the exhibit is available at amnh.org/mummies.
A Major Scientific Research Institution
When we see these fantastic exhibits, we don’t necessarily see behind them, to the fact that the American Museum of Natural History, founded in 1869, is one of the world’s preeminent scientific, educational, and cultural institutions, whose research has contributed not only to their discovery, but to the understanding of what is displayed.
Indeed, the press tour takes us behind the scenes to the institution’s Microscopy and Imaging Facility – the technology that would have been used to scan the mummies. The equipment is shared by all five departments of the institution, whether AMNH scientists are studying fossils, cultural artifacts, planets or solar systems, the cutting-edge imaging technologies in the facility make it possible to examine details that were previously unobservable. While earlier studies often required unwrapping mummies – which could have damaged them – tools like high-resolution computerized tomography (CT) scanner provide scientists with non-invasive methods to examine them. MIF technician Morgan Hill walked us through the process, along with Zachary Calamari, a Ph.D. student in comparative biology program at the Museum’s Richard Gilder Graduate School, who showed us how the scans help in research of two naturally-mummified newborn wooly mammoths – one who was mummified by being frozen and the other who was “pickled.”
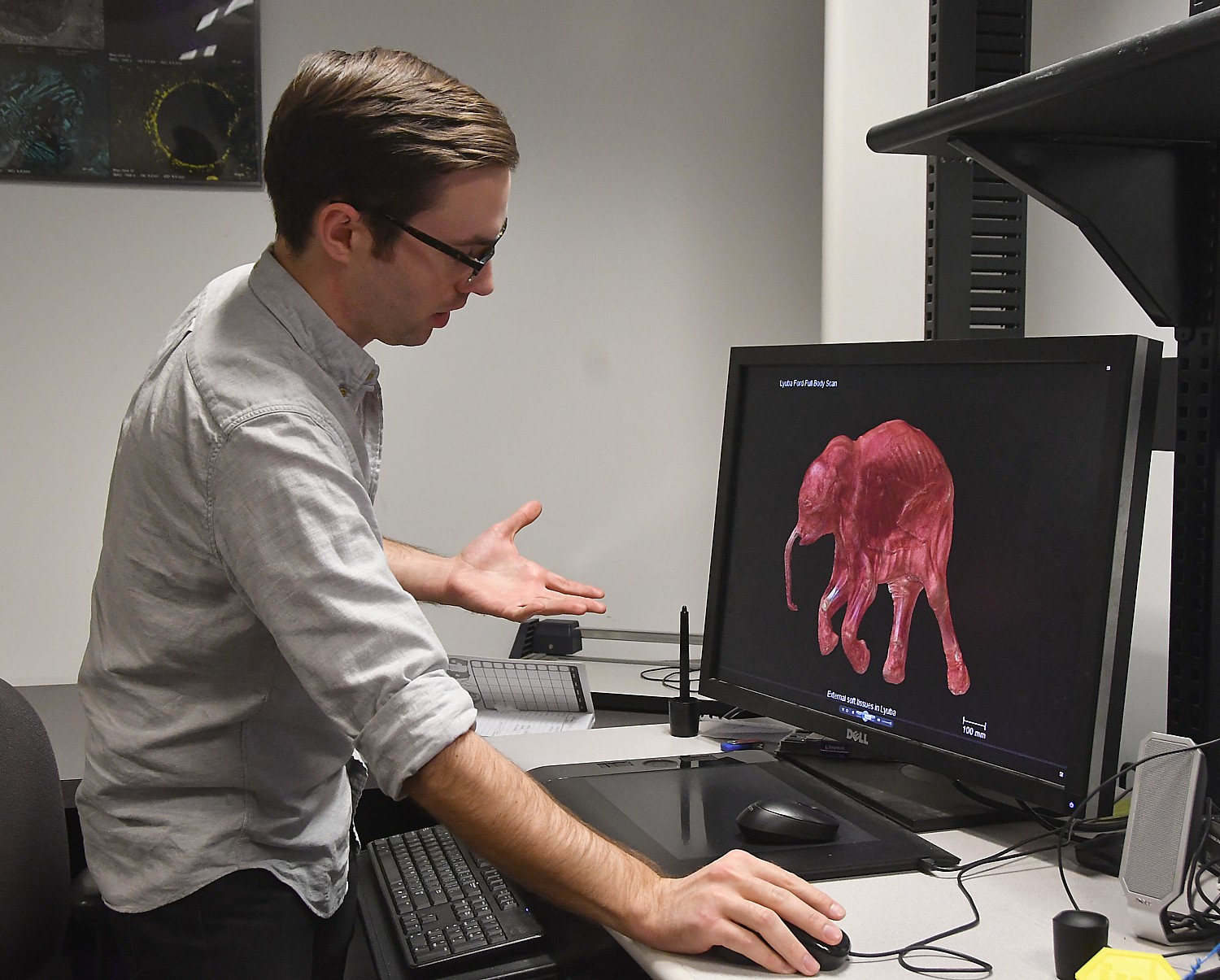

During our visit, the CT scanner is doing an image of a rabbit. It is this ability to understand the internal aspects of dinosaurs and fossils that have led scientists to rejigger Evolution’s schema, to redefine who is related to who and what is connected to what.
The Museum’s five active research divisions and three cross-disciplinary centers support approximately 200 scientists, whose work draws on a world-class permanent collection of more than 33 million specimens and artifacts, as well as specialized collections for frozen tissue and genomic and astrophysical data, and one of the largest natural history libraries in the world. Through its Richard Gilder Graduate School, it is the only American museum authorized to grant the Ph.D. degree and the Master of Arts in Teaching degree.
The Museum encompasses 45 permanent exhibition halls, including the Rose Center for Earth and Space and the Hayden Planetarium, as well as galleries for temporary exhibitions. It is home to the Theodore Roosevelt Memorial, New York State’s official memorial to its 33rd governor and the nation’s 26th president, and a tribute to Roosevelt’s enduring legacy of conservation.
The museum gets 5 million visitors a year and the Museum’s exhibitions and Space Shows can be seen in venues on five continents. The Museum’s website and apps for mobile devices extend its collections, exhibitions, and educational programs to millions more beyond its walls.
American Museum of Natural History, Central Park West at 79th Street, New York, NY 10024-5192, 212-769-5100. Open daily from 10 am-5:45 pm except on Thanksgiving and Christmas. Visit amnh.org for more information.
Become a fan of the American Museum of Natural History on Facebook at facebook.com/naturalhistory, follow us on Instagram at @AMNH, Tumblr at amnhnyc, or Twitter at twitter.com/AMNH.
____________________
© 2017 Travel Features Syndicate, a division of Workstyles, Inc. All rights reserved. Visit goingplacesfarandnear.com, www.huffingtonpost.com/author/karen-rubin , and travelwritersmagazine.com/TravelFeaturesSyndicate/. Blogging at goingplacesnearandfar.wordpress.com and moralcompasstravel.info. Send comments or questions to FamTravLtr@aol.com. Tweet @TravelFeatures. ‘Like’ us at facebook.com/NewsPhotoFeatures
