By Karen Rubin, Travel Features Syndicate, goingplacesfarandnear.com
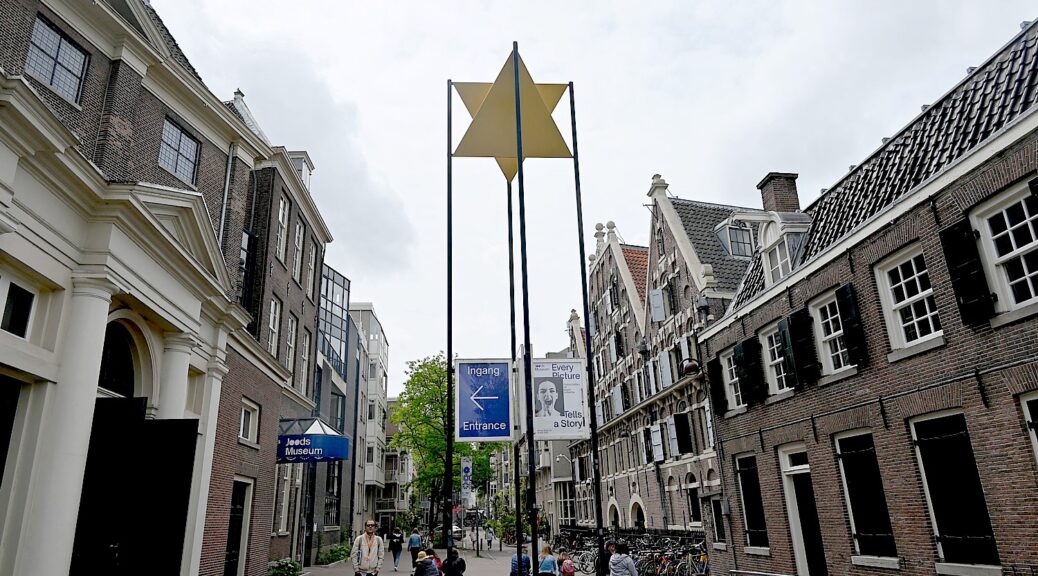
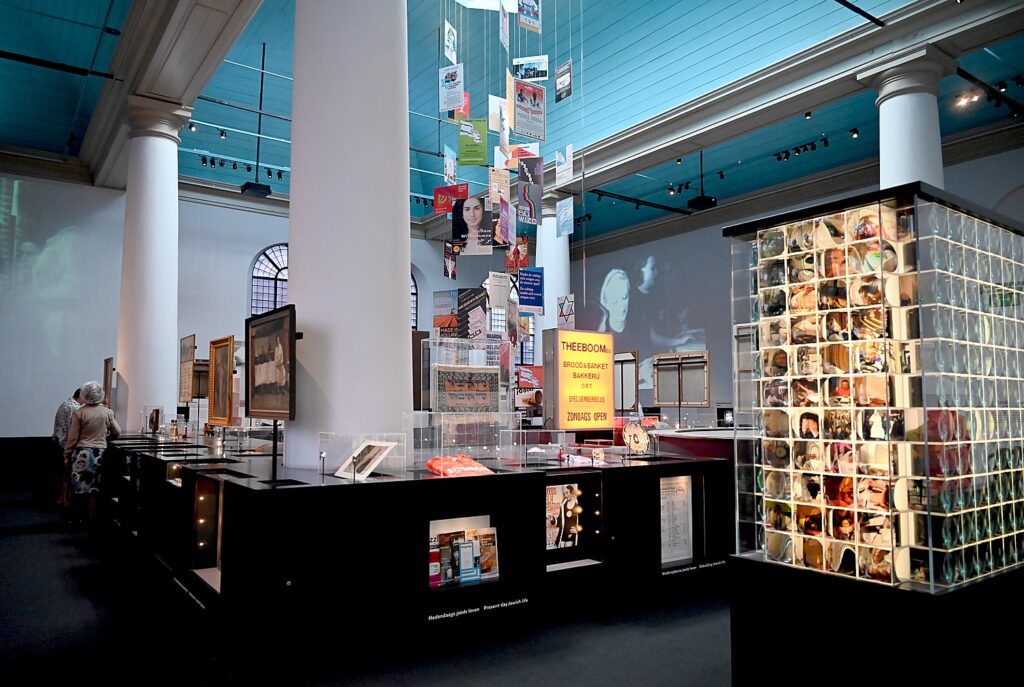
At the Jewish Museum in Amsterdam, I pick up a sheet detailing a walking tour through the Jewish Cultural Quarter which features 37 points (Rembrandthuis and the Waterlooplein flea market are included) and 12 museums, monuments and memorials. It is supposed to take about 90 minutes.
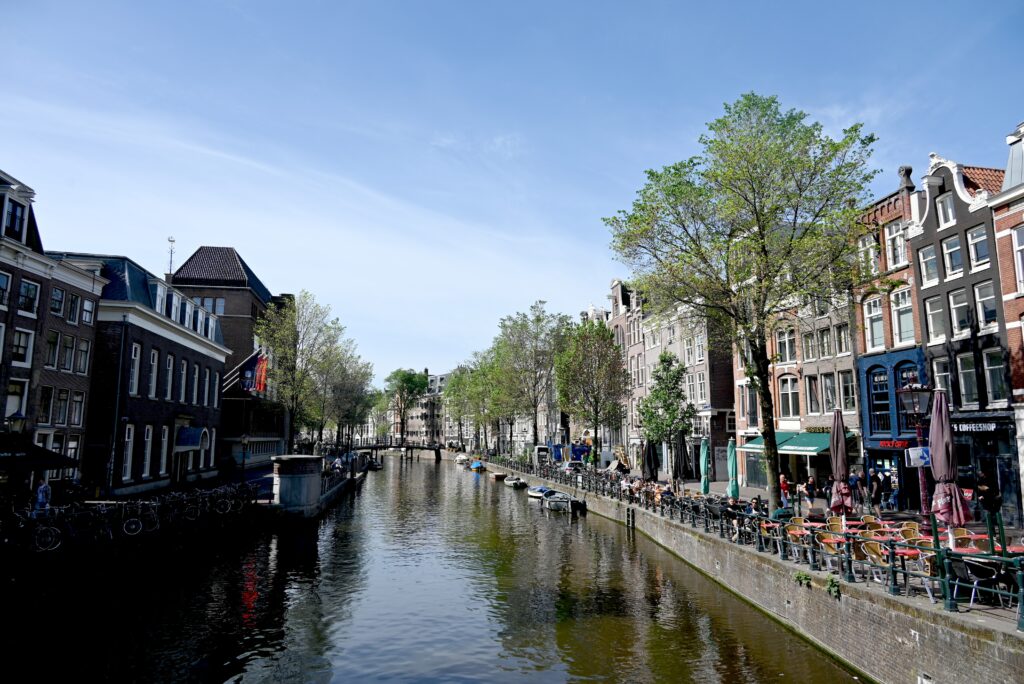
I go off to follow much of the list – which is most interesting because you go into this historic neighborhood where you almost hear the voices of the people who lived there, certainly feel their presence. It feels a bit like time travel.
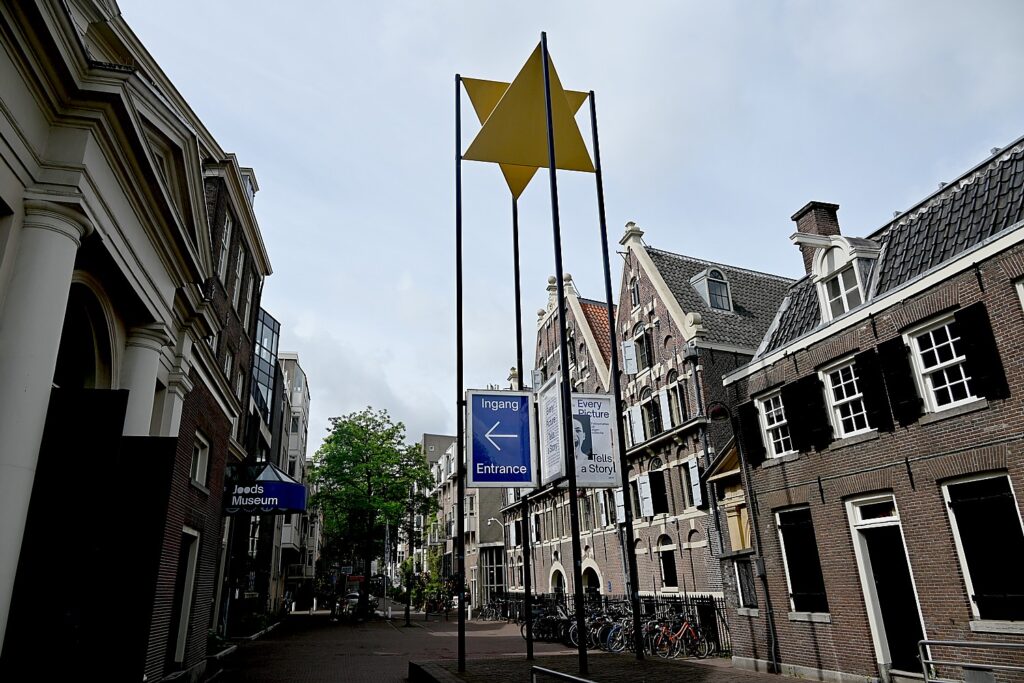
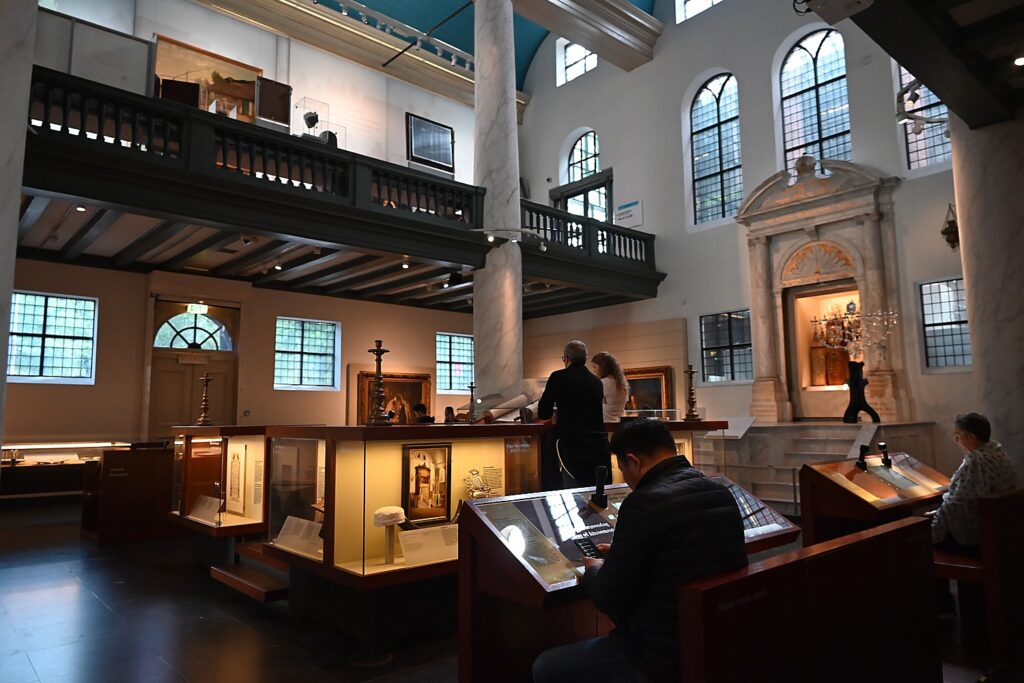
Across the street from the Jewish Museum, which is housed in four former synagogues including the Great Synagogue, is one of the most beautiful and grandest synagogues of the world, the Portuguese Synagogue. Dating from 1675 (just four years after the Great Synagogue which is across the street), this Sephardic synagogue is in fact a whole religious complex with the synagogue, archives, a mortuary, and a library.
Known as The Esnoga, the Portuguese Synagogue was designed by Elias Bouman, who had also helped design the Great Synagogue of the Ashkenazim across the road. Elias Bouman later became the city’s chief architect. The colossal building dominated its surroundings then, as it still does today. When finished, it was the largest synagogue in the world. And even centuries ago, was a tourist attraction. (Mr. Visserplein 3, jck.nl/en/longread/portuguese-synagogue)
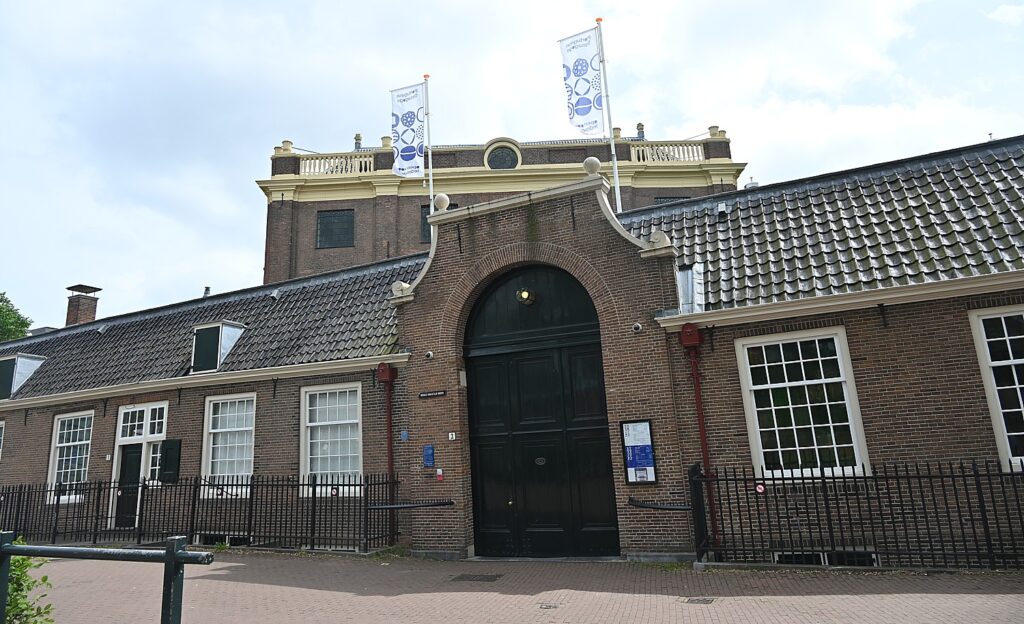

The Portuguese Synagogue is still used for religious services (it’s Saturday so I don’t get to go inside), but on most days you can buy a ticket to see inside. It is renowned for its exquisite 17th century interior. There are also smaller buildings in the complex where there are “treasure chambers” displaying ceremonial objects of silver, gold, brocade and silk. The synagogue also hosts frequent candlelight concerts. (I experienced an extraordinary concert at the Spanish Synagogue in Prague at the start of my European odyssey.)
The Great Synagogue was destroyed in the Holocaust (it was restored and turned into a museum in 1961), but the Portuguese Synagogue was saved apparently because Hitler wanted to leave a trace of the vanished nation (I was told much the same about how Prague’s Jewish Quarter managed to survive.)
The world’s oldest functioning Jewish library, Ets Haim Livraria Montezinos, which is on UNESCO’s World Heritage List, is also here in the Portuguese Synagogue (Mr. Visserplein 3). The library has more than 25.000 books and 560 manuscripts in Hebrew, Spanish, Portuguese, Latin, Greek, Arabic and Yiddish in its collection. Some of the manuscripts date to13th C. (An appointment is required to visit: for a guided tour phone: +31 20 531 03 80; researchers call +31 20 531 03 98).
Outside the Portuguese Synagogue is the Jonas Daniel Meijerplain, a square named for Jonas Daniel Meijer who in 1796 became the first Dutch Jew to receive a doctoral degree. He was a leader in the Jewish struggle for emancipation and equal rights (which was won in 1796). There are Stolpersteine (small memorial plaques) in front of houses that are along the square (nos. 13, 15, 19) that bear the names of Jews who lived there and were murdered by the Nazis. (I saw these Stolpersteines in Dordrecht, as well.)
In the square is the February Protest Monument commemorating the strike of the Amsterdam dock workers on February 24, 1941, to protest persecution of Jews. The strike has been followed by protest actions all over the city: in public transport, schools and in some companies. Strike actions also took place in several cities around Amsterdam and in Utrecht. Although the Nazi administration, which invaded the Netherlands in 1940, managed to suppress the strike within just a few days, killing nine of the protesters, injuring many and perpetuating several other ruthless actions, the open protest against the Nazis had the symbolic importance for all people in the Netherlands. The monument represents a striking worker called “De Dokwerker”. The sculpture is by Mari Andriessen, a sculptor who during the war refused membership of the Nazi-led artist union and hid Jewish friends at his home to save them from death.

My walking tour takes me to what was the Ashkenazi Jewish Girls Orphanage, which from 1863-1943 was where these orphaned girls received religious education. In the Holocaust, 80 were deported to concentration camps.
The Plancius/Resistance museum, was where the Jewish choral society, Oxfening Baart Kunst (Practice Makes Perfect) was established in 1876; it has been the site of the Dutch Resistance Museum since 1999.
The De Castro Pharmacy is Amsterdam’s oldest apothecary (1832). Daniel Henriques de Castro was not only an apothecary but also an administrator of the Portuguese Synagogue and a glass engraver.
The Pinto House (Sint Antoniebreestraat 69), was built in 1603, bought by the wealthy Jewish merchant Isaac de Pinto in 1651 and rebuilt by his son David Emanuel in 1686 with the broad classical facade. Devastated in 20th C. and saved from a demolition, it is a public library today.
I go to the Walter Suskind Bridge – fairly nondescript – named for Walter Suskind (1906-1945) who was the head of Jewish staff of the Hollandsche Schauwburg and in this capacity saved hundreds of Jewish children from deportation and murder.
(Gassan Diamonds is also here in the Jewish Quarter and had an important role in the Jewish community. I book a free tour for the next morning at its website, https://www.gassan.com/en/tours/gassan-historical-tour)
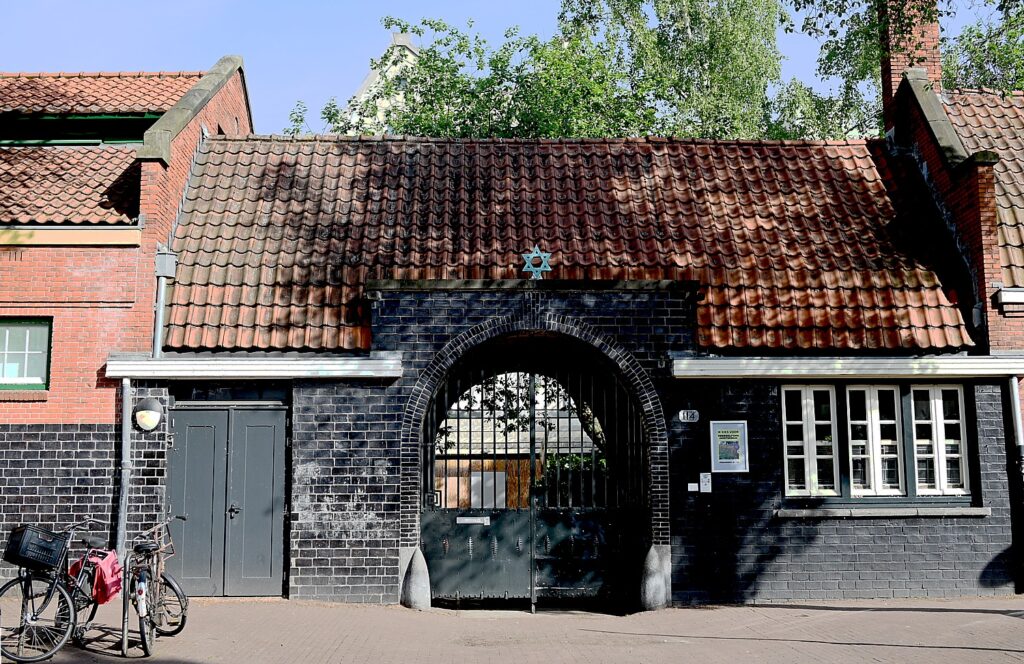

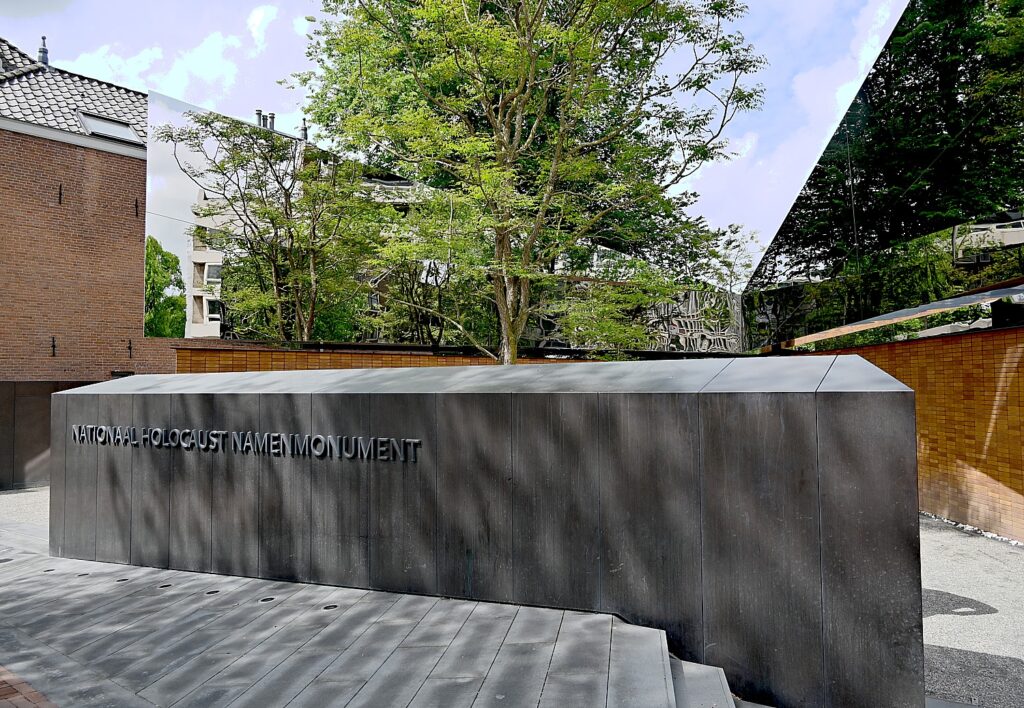
I visit as many of the sites as I can, and finally come to the National Holocaust Memorial, which only opened in September 2021. It’s the first in the Netherlands to name all 102,000 Dutch Jews, Sinti and Roma who were killed by the Nazis during World War II. Designed by Polish-American architect Daniel Liebeskind, the 102,000 bricks, each bearing the name of a victim, form the shape of four Hebrew letters meaning “in memory of.”
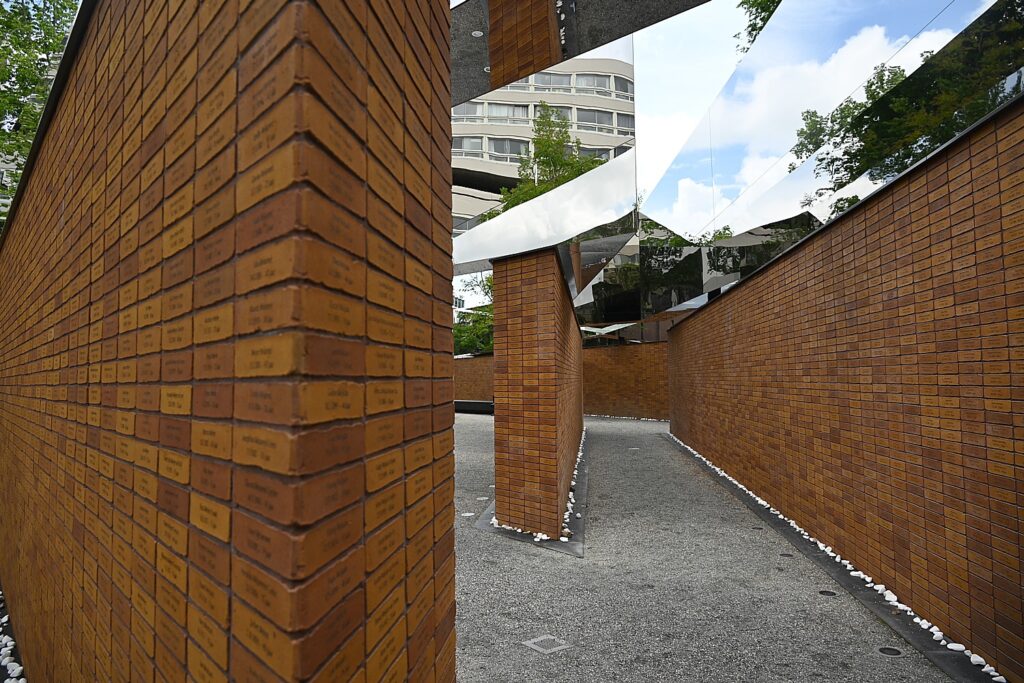

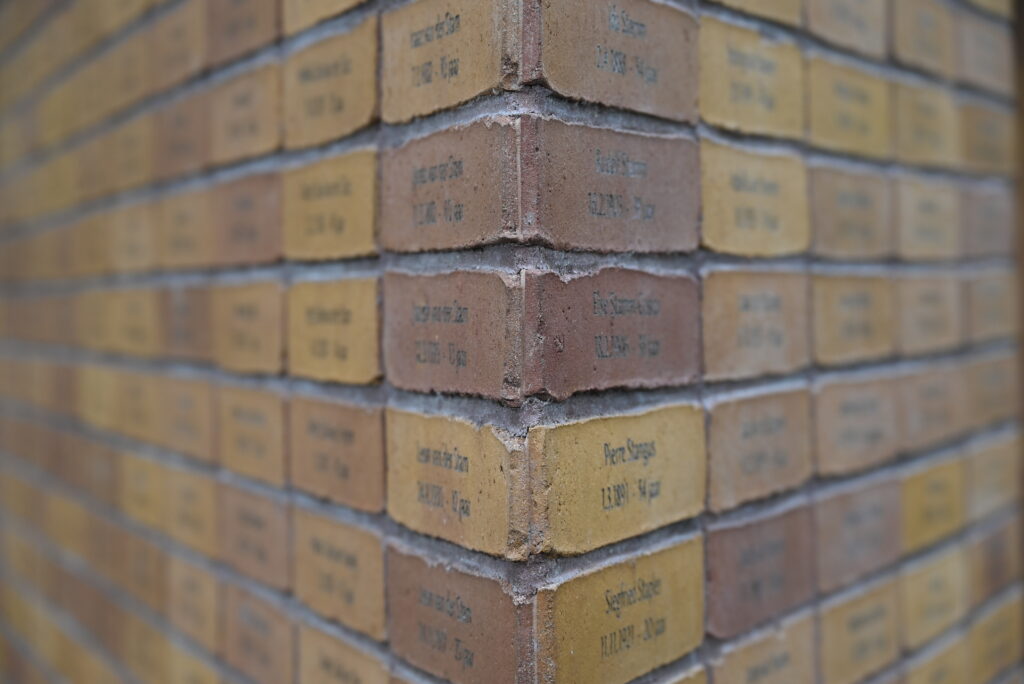
I estimate there are 32 rows of 50 bricks just named DeVries. I note some of the names: Frouwkevn Mandenburg Gosschalk, Rooje van Maagdenburg-Frank, Maas, Magtige, Maij – very Dutch, with some of these families I would bet having lived in Amsterdam for hundreds of years. The name plaques seem to go on forever.
Of the 107,000 deported to concentration camps, only 5200 Jews and 30 Santi and Roma survived.
“A warning for all generations, all over the world and in the future,” a plaque reads.

According to reporting of the event, the memorial was unveiled by King Willem-Alexander and Dutch Prime Minister Mark Rutte.
“Last year marked the first time an official in the Netherlands publicly apologized on behalf of the government for the war-time persecution of Jews, after Rutte admitted little was done to protect them from the atrocities committed by Nazi Germany.” (https://www.dw.com/en/dutch-holocaust-memorial-opens-after-years-long-legal-deadlock/a-59231217)

Tickets to all the Jewish Cultural Quarter exhibits may be purchased at any of the participating institutions. Adults – € 12 ; young people age 13 -17, students, Stadspas – € 6 ; children age up to 13; free admission is provided with the Amsterdam Holland Pass, iAmsterdam Pass, Museum Card, Friends of The Jewish Historical Museum, ICOM, Rembrandt Association. Tickets to the Jewish Historical Quarter are valid 1 month for a multiple access to all exhibits. Tickets to concerts at the Portuguese Synagogue: € 13.50.
You can also sign up for a walking tour with a knowledgeable, personal guide (see www.amsterdam.info/jewish/).
“Night Watch” at Rijksmuseum
By now, it is time for me to walk over to the Rijksmuseum for my timed ticket, which brings me through more of the neighborhoods that seem so far removed in time and place from what I had just experienced.
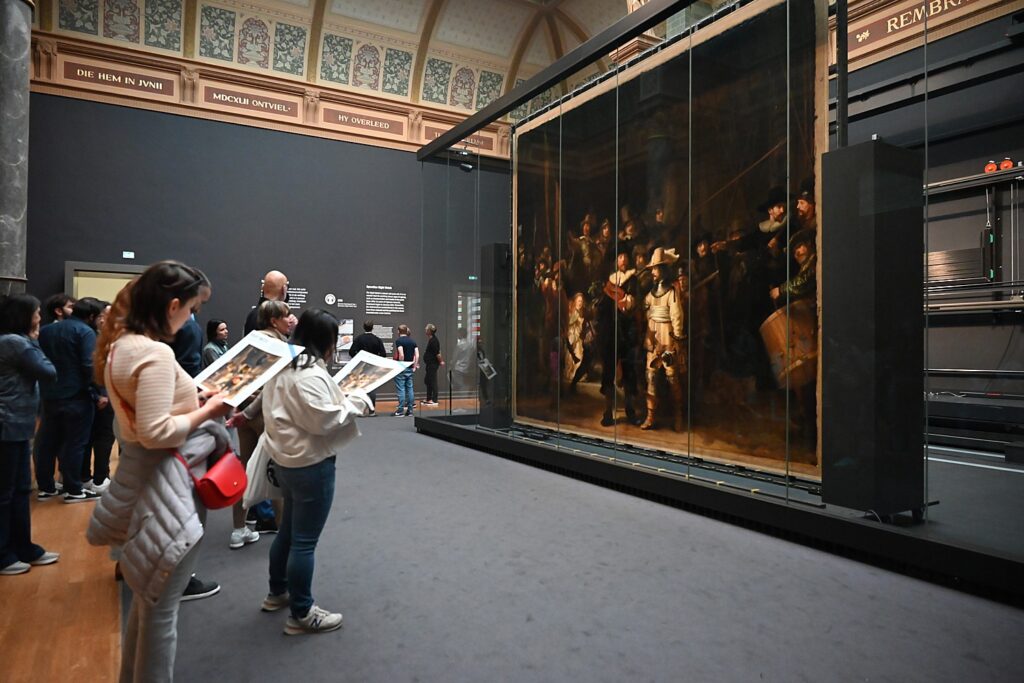

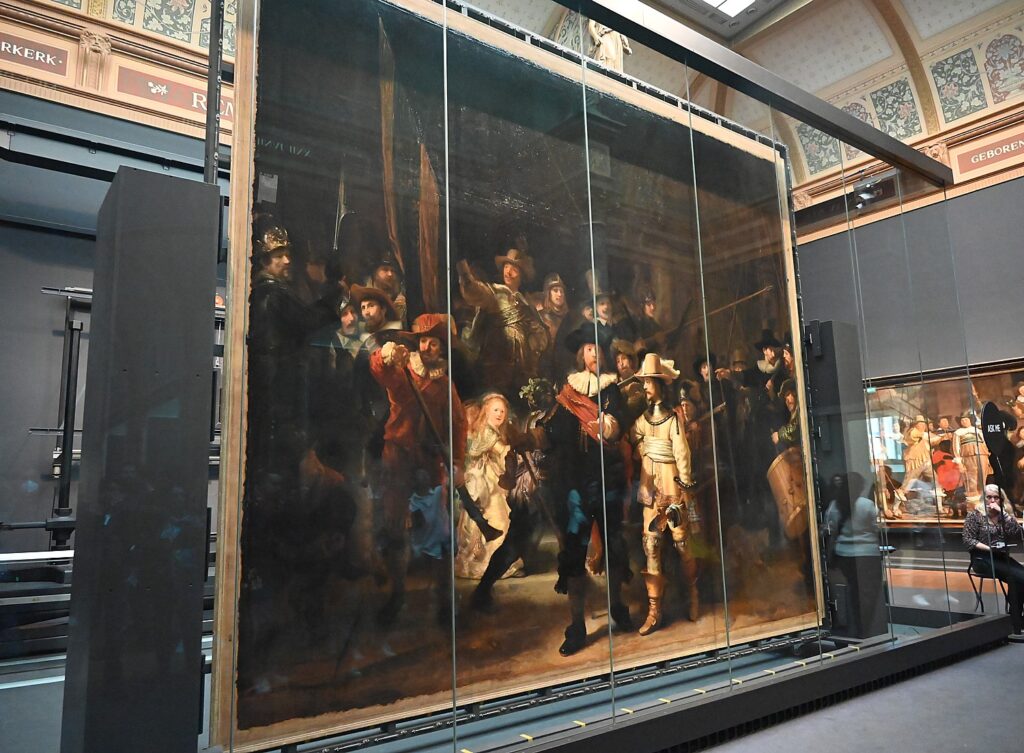
The big attraction at the Rijksmuseum (I only have two hours before closing) is Rembrandt’s famous “Night Watch” painting (I hadn’t realized it is the size of an entire wall), and you get to see it as it is being conserved, behind a glass-enclosed studio. A docent is there to answer questions about it.
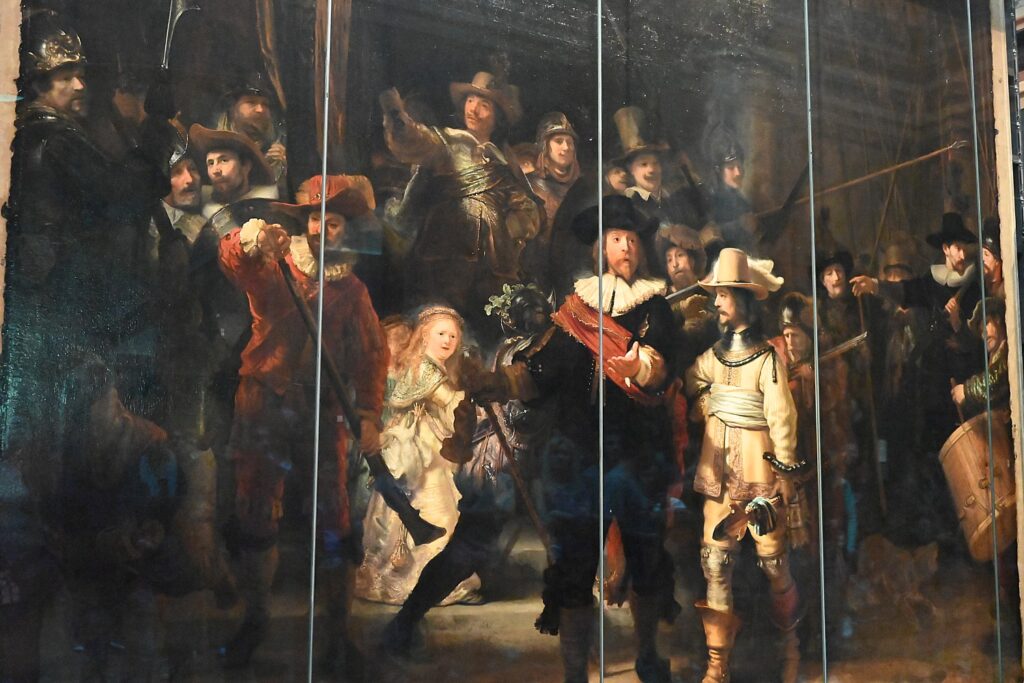

At the Rembrandthuis, I was told that this painting was one of the reasons that Rembrandt went bankrupt – the three benefactors who paid the most for the painting are not shown prominently, and they conveyed their discontent so that Rembrandt lost commissions. The docent disputes this and points out that was a decade between the painting and his bankruptcy.

By now, I have to get to my COVID19 test that I scheduled, so I get to discover more neighborhoods. As it turns out, the clinic is across the way from Amsterdam’s science museum, along the boulevard that would go to the Central Station. The process is extremely efficient (shortly after, the United States halted requiring COVID tests within 24 hours of entering the country.)
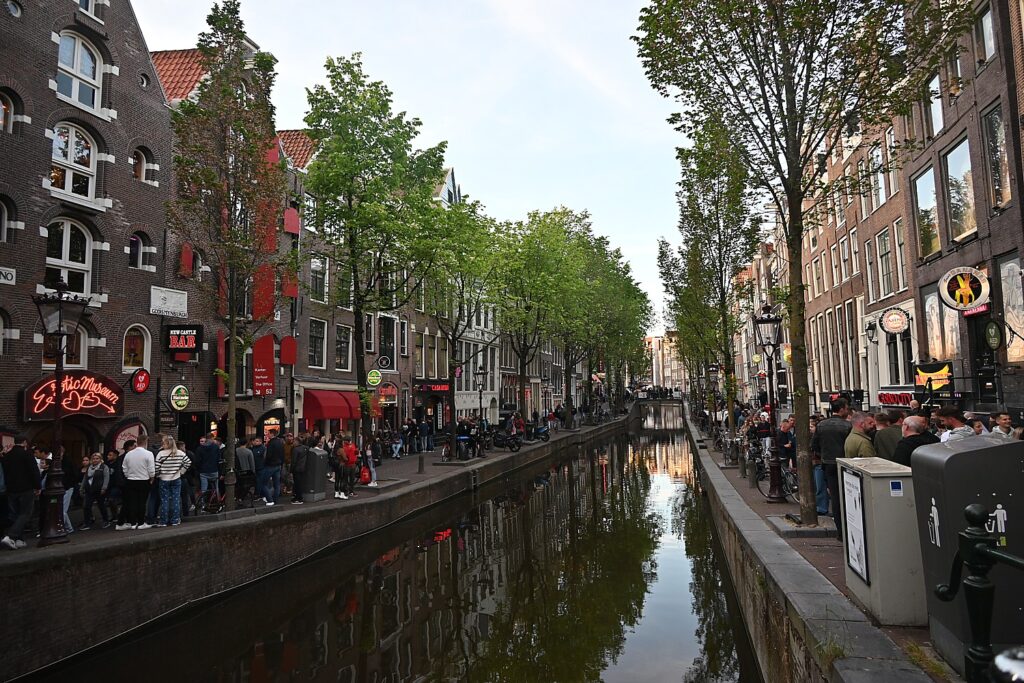
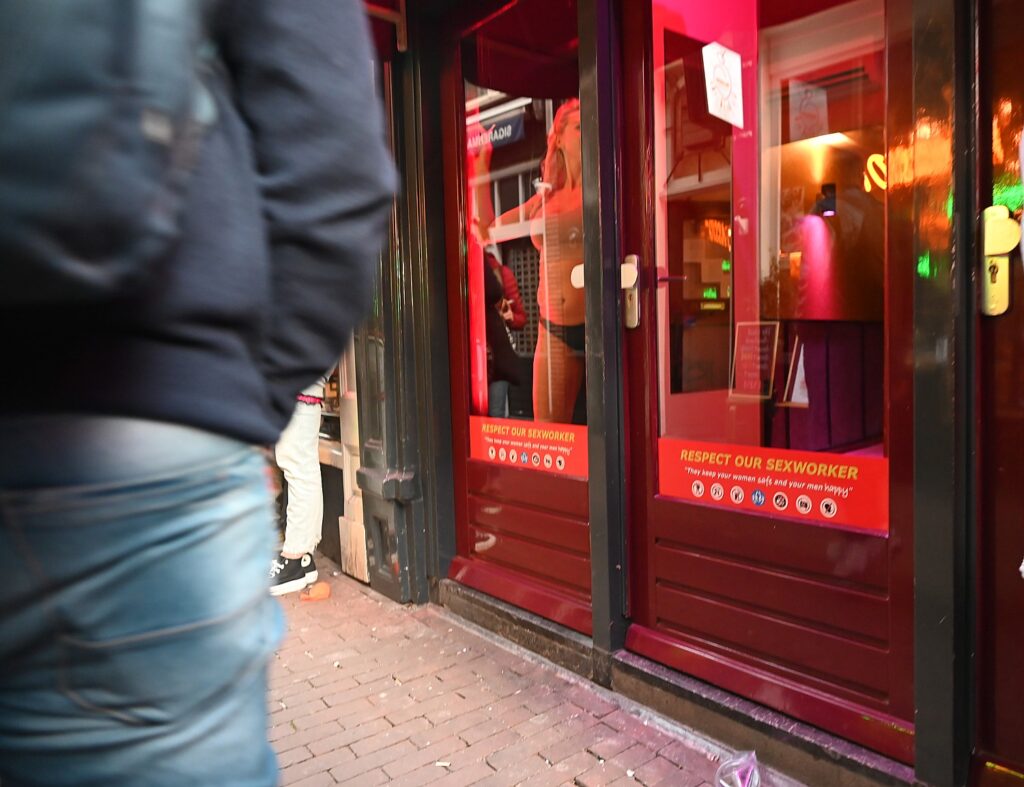
On the way back to Sofitel Legend Grand Amsterdam Hotel, I find myself walking through the Red Light District, jam-packed with people. Here you can also visit museums to Erotica, Prostitution, assorted peep shows and museums devoted to Hash, Marijuana and Hemp . Even the public toilet is titillatingly called the “Sexy Loo.”
Here you find posters on the bridges warning of fines for peeing in the canal or taking alcohol out of the district, and as the evening grows later, more and more police presence.


Diamonds!
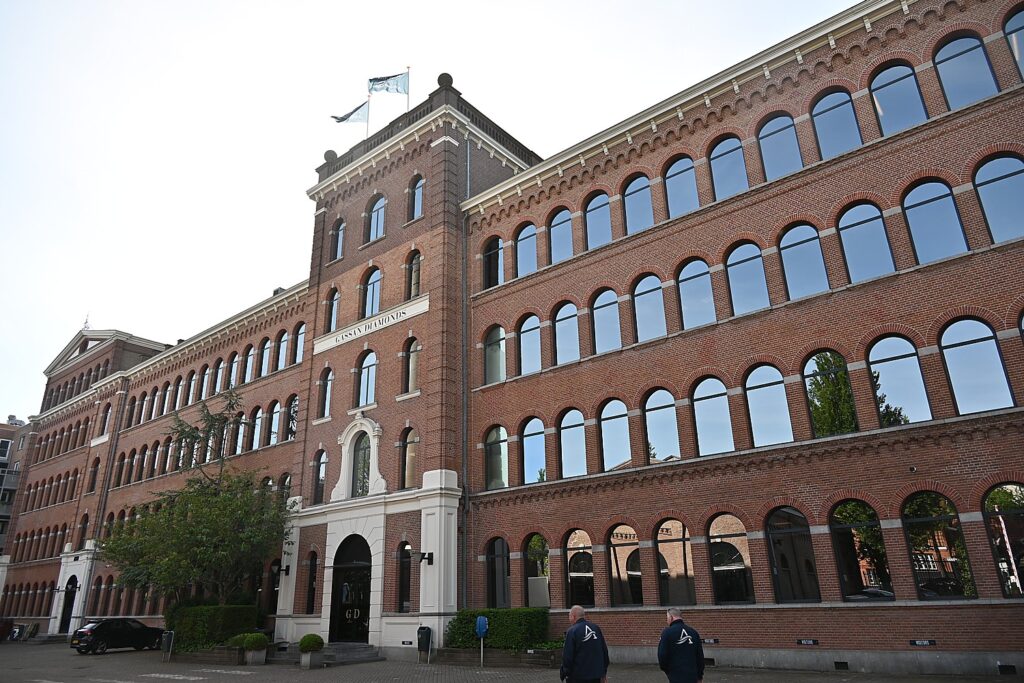
The next morning, before I have to get to the airport (and after enjoying a terrific breakfast at the Sofitel Legend the Grand Amsterdam Hotel), I tour the Gassan Diamonds, a historic place which had great importance in the Jewish Quarter.

Initially, Jews were not permitted into Amsterdam’s guilds, so the only occupations that were open to them were street trading (hence the giant flea market at Waterlooplein), financing, book printing and diamond cutting. In the 19th century many Jews worked in the flourishing diamond trade and industry.
Amsterdam has been famous for its diamonds since the 16th century, and after 400 years, the city is still regarded as a diamond trading center of the world. The popular brilliant-cut with 57 facets which was developed in Amsterdam is known as the “Amsterdam-cut”.
There are about a dozen diamond factories in Amsterdam left, five which offer guided tours.
Gassan Diamonds has played a pivotal role in Amsterdam’s diamond history, as well as in Jewish life in Amsterdam. The diamond factory was built in 1879 by the Boas brothers, and at the time was the largest diamond factory in Europe. It was shut down during World War II, and resurrected by Samuel Gassan, whose father actually worked there as a diamond cutter.
Samuel Gassan stayed in Switzerland until the end of the war, became a captain in the British Army. Working in the repatriation service, he helped children of diamond workers who had lost their parents and who had been held captive in Bergen-Belsen, return to the Netherlands.
In October 1945, having returned to Amsterdam, Samuel, now 35, opened his own diamond trading company, Firma Gassan, in the Diamond Exchange on the Wesperplein. He traveled all over Europe selling his diamonds. Five years later he owned his own diamond cutting factory on the Zwanenburgerstraat.
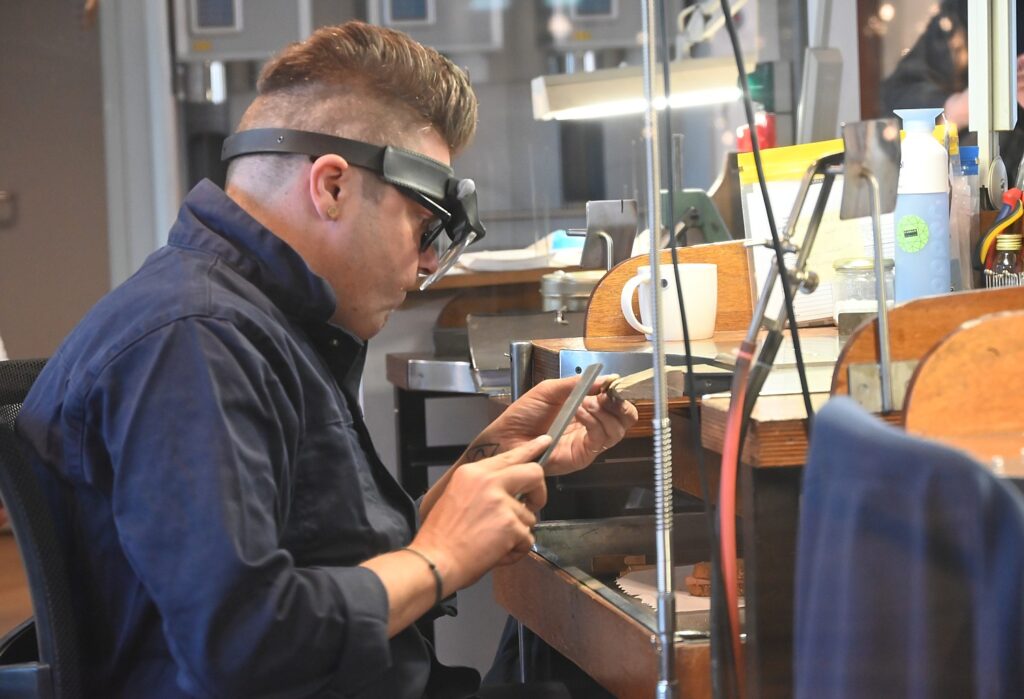

On the tour, we get to see the diamond polishers at their craft, while a guide explains how they turn rough diamonds into dazzling brilliants. And Gassan has taken the “Amsterdam cut” to a new level, patenting the technique of the Gassan 121 diamond – a diamond cut with 121 facets to dazzling effect.
I am taken into a room where, even though it is Sunday morning, there are a couple of people polishing diamonds. My guide explains the three-step process: cutting (phosphorous blade, rotates 6400/min, coated with olive oil and diamond dust because only a diamond can cut diamond; shaping and elevating sharp edges (not sparkling yet); and third, polishing with olive oil and diamond dust to make facet. Facets are what make the diamond clear and sparkling.
It takes 3 to 4 working days to prepare one diamond.
A brilliant cut has 57 facets (33 on top, 24 on bottom), which originated in Amsterdam and is known as the “Amsterdam cut.” But, she explains, Gassan (pioneered and patented) a 121-facet diamond with exponentially more refraction (no one else can sell 121 facets)
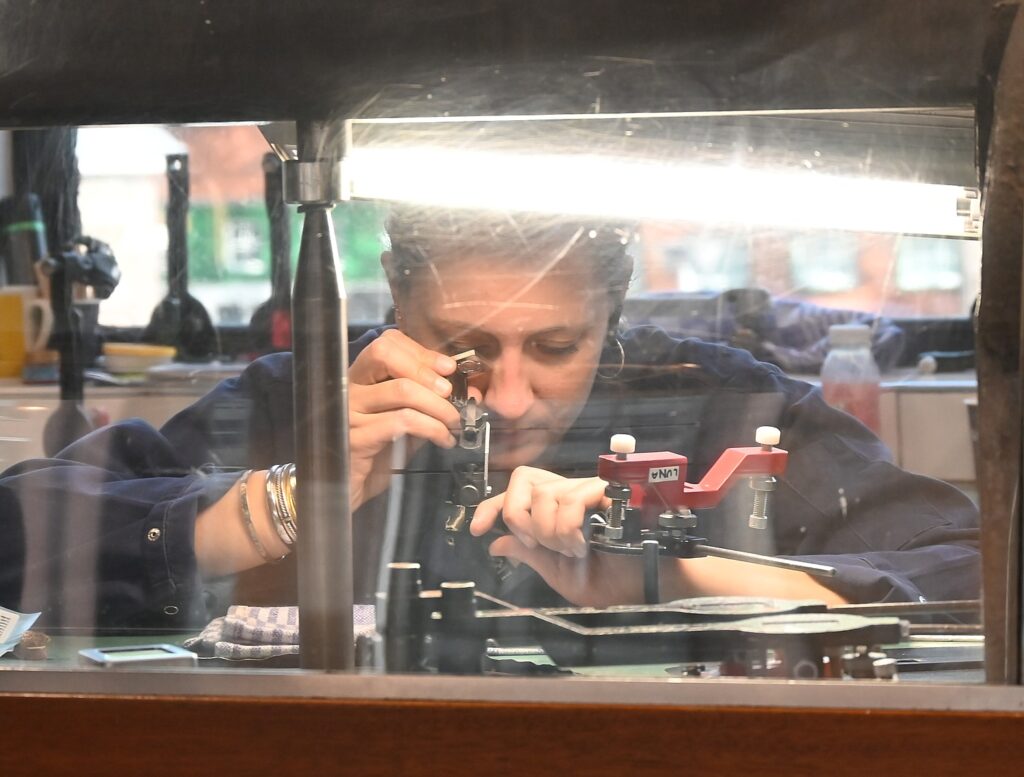

Luna, who I watch polishing a diamond, has had 3 years experience (it takes two years to learn basics, 10-20 years to perfect, and by the time you are ready to retire, you are a master). A half carat is the biggest diamond she has worked on, she tells me.
All the rough diamonds that come to the Antwerp bourse must have a certificate that they are not conflict diamonds. Diamonds come from all over the world and are found everywhere but Australia, Canada, India, and China, she tells me.
This 1879 building is long and narrow because it was built before electricity, so the workers were dependent upon natural light, and used steam system (you can see the pipes).
In a display case are old pieces of glass with names etched with diamond into it. “This was a Jewish neighborhood and a Jewish company,” she tells me. “A lot of Jews worked here. During World War II, most were killed, so we keep the glass with their names. Gassan’s own father was a diamond worker in the factory here. After the war, Samuel acquired the old factory.
My guide takes me into a small room to explains the different elements that go into the quality (and price) of a diamond – carats, colors, clarity, cuts and, of course, the ultimate Gassan 121- and fortunately, you can buy here at factory price (and get the 16% tax refunded at airport). ”You can choose a diamond today, choose setting and it will be ready within 30 to 60 minutes – ring, necklace, earrings.” You can also peruse the jewelry store, filled with luxury items.
Gassan also offers a VIP tour through the diamond factory and the in-house Rolex boutique which includes a glass of champagne, a goodie bag and the chance to chat with a certified Rolex watchmaker. Or you can take a seat behind the grinder yourself with the Diamond Polishing Experience, where you can apply the final facets to your own diamond!
Gassan Diamonds, Nieuwe Uilenburgerstraat 173-175, www.gassan.com/en/tours/gassan-historical-tour
I time it so I get back to the Sofitel Legend Grand Amsterdam hotel so I can take the tour of this fascinating place that played such an important role in Holland’s history, and still have time for one last walk through the historic district to Amsterdam’s Central Station. It’s a hop-skip-jump on the train to Schiphol Airport (2nd class ticket does just fine), all of about 15 minutes ride.

Pre-purchase the I AmsterdamCity Card, which provides access to the city’s major highlights and more than 70 museums, city-wide public transport, a canal cruise and bicycle rental. You also get discounts at restaurants, attractions and concerts. https://www.iamsterdam.com/en/i-am/i-amsterdam-city-card iamsterdam.com.
Plan your visit at www.iamsterdam.com/en.
See also:
Sofitel Legend The Grand Amsterdam: Historic Hotel that Played Major Role in History
36 Hours in Amsterdam: Time-Traveling in the Jewish Quarter
36 Hours in Amsterdam: Time-Traveling Through Amsterdam’s Jewish Quarter
__________________
© 2022 Travel Features Syndicate, a division of Workstyles, Inc. All rights reserved. Visit goingplacesfarandnear.com, www.huffingtonpost.com/author/karen-rubin, and travelwritersmagazine.com/TravelFeaturesSyndicate/. Blogging at goingplacesnearandfar.wordpress.com and moralcompasstravel.info. Visit instagram.com/going_places_far_and_near and instagram.com/bigbackpacktraveler/ Send comments or questions to FamTravLtr@aol.com. Tweet @TravelFeatures. ‘Like’ us at facebook.com/NewsPhotoFeatures
























