By Karen Rubin, Travel Features Syndicate, goingplacesfarandnear.com
New-York Historical Society’s exhibition “I’ll Have What She’s Having”: The Jewish Deli, is a fascinating exploration of the rich history of the Jewish immigrant experience that made the delicatessen so integral to New York and American culture. On view through April 2, 2023, the mouth-watering and culturally significant exhibition, organized by the Skirball Cultural Center in Los Angeles (where it is on view through September 18), examines how Jewish immigrants, mostly from Central and Eastern Europe, imported and adapted traditions to create a cuisine that became a cornerstone of popular culture with worldwide influence.
The exhibition explores the food of immigrants; the heyday of the deli in the interwar period; delis in the New York Theater District; stories of Holocaust survivors and war refugees who found community in delis; the shifting and shrinking landscapes of delis across the country; and delis in popular culture. You get to see iconic neon signs, menus, advertisements, and deli workers’ uniforms alongside film clips depicting delis in popular culture and video documentaries.
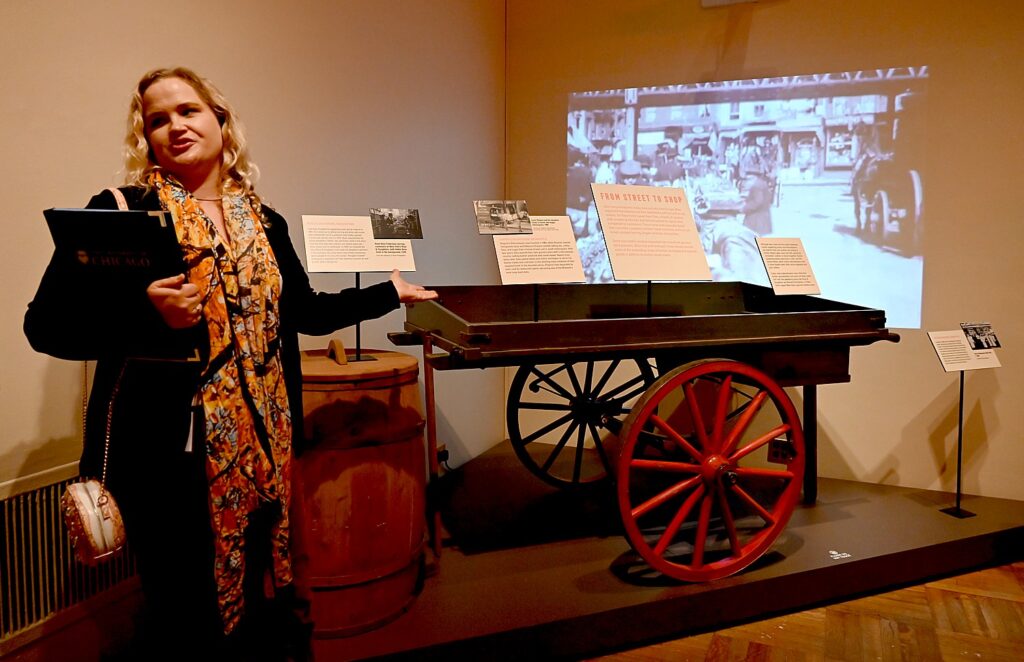

Some 2 million Jews came from Eastern and Central Europe to the United States between 1880 and 1924, when nativist anti-immigrant furor shut down immigration (there is a display showing some of the anti-immigrant propaganda). New York was a stopover but also a destination for millions and they brought with them their food culture, which, of necessity, was adapted.
“Why make a museum show out of the Jewish deli – which is a specific and unusual topic? The ‘deli’ allowed us to explore themes of how people of different backgrounds relate to one another” in such a melting pot as New York, said Laura Mart, one of the curators. “It shows how Jewish-American culture was created and maintained through generations. And it is also about joy, more important than ever. Museums are a place for joyful learning.”
“It’s a story of tradition and change, adaptation and resilience,” said Lara Rabinovitch.

“It’s our great pleasure to present an exhibition on a topic so near and dear to the hearts of New Yorkers of all backgrounds,” said Dr. Louise Mirrer, president and CEO of New-York Historical. ‘I’ll Have What She’s Having’: The Jewish Deli tells a deeply moving story about the American experience of immigration—how immigrants adapted their cuisine to create a new culture that both retained and transcended their own traditions. I hope visitors come away with a newfound appreciation for the Jewish deli, and, with it, the story of the United States.”
“Whether you grew up eating matzo ball soup or are learning about lox for the first time, this exhibition demonstrates how Jewish food became a cultural touchstone, familiar to Americans across ethnic backgrounds,” said co-curators Cate Thurston and Laura Mart. “This exhibition reveals facets of the lives of Central and Eastern European Jewish immigrants in the late 19th and early 20th centuries that echo in contemporary immigrant experiences. It shows how people adapt and transform their own cultural traditions over time, resulting in a living style of cooking, eating, and sharing community that is at once deeply rooted in their own heritage and continuously changing.”
I’ll Have What She’s Having is co-curated by Skirball curators Cate Thurston and Laura Mart along with Lara Rabinovitch, renowned writer, producer, and specialist in immigrant food cultures. It is coordinated at New-York Historical by Cristian Petru Panaite, curator of exhibitions. The exhibition explores topics including deli culture, the proliferation of delis alongside the expansion of New York’s Jewish communities, kosher meat manufacturing, shortages during World War II, and advertising campaigns that helped popularize Jewish foods throughout the city.
As is typical of New-York Historical’s exhibits, expanded presentation from its own collection and local twist includes additional artwork, artifacts, photographs of local establishments, and objects from deli owners, as well as costumes from The Marvelous Mrs. Maisel, a mouthwatering interactive, and a Bloomberg Connects audio tour.

Highlights include a letter in New-York Historical’s Patricia D. Klingenstein Library collection from a soldier fighting in Italy during World War II writing to his fiancée that he “had some tasty Jewish dishes just like home” thanks to the salami his mother had sent—confirmation of the success of a famous “Send a Salami to Your Boy in the Army” campaign. (Panaite painstakingly poured over a huge collection of World War II letters, one by one, to find it.)
There are photos of politicians and other notable figures eating and campaigning in delis, including then-US Senate candidate Hillary Clinton at Ben’s delicatessen in Greenvale, Long Island. Movie clips and film stills include the iconic scene in Nora Ephron’s romantic comedy When Harry Met Sally…, which inspired the exhibition title. This and other movie scenes underscore the prominent role of Jewish delis in American popular culture.
Special to New-York Historical’s presentation is a closer look at the expansion of Jewish communities at the turn of the 20th century, not just on the Lower East Side but also in Brooklyn, Queens, and the Bronx. In the 1930s, some 3,000 delis operated in the city; today, only about a dozen remain.

The exhibition gives special attention to dairy restaurants, which offered a safe meatless eating experience; a portion of the neon sign from the Famous Dairy Restaurant on the Upper West Side is on display. Salvaged artifacts, like the 2nd Avenue Delicatessen storefront sign and vintage meat slicers and scales from other delis, are also on view, along with costumes by Emmy Award-winning costume designer Donna Zakowska from the popular Prime Video series The Marvelous Mrs. Maisel.
Visitors are invited to build their own sandwiches named after celebrities, such as Milton Berle, Sophie Tucker, Frank Sinatra, Ethel Merman, and Sammy Davis Jr., in a digital interactive inspired by menu items from Reuben’s Deli and Stage Deli (the menus are on display).

On the Bloomberg Connects app, exhibition goers can enjoy popular songs like “Hot Dogs and Knishes” from the 1920s, along with clips of Mayor Fiorello La Guardia discussing kosher meat pricing, 1950s radio ads, and interviews with deli owners forced to close during the pandemic lockdown.
It’s a trip down memory lane for so many of us native New Yorkers – with the neon signs from popular delis and suppliers (Hebrew National), menus (there is one from Reubens, the home of the Reubens sandwich, which was a very popular venue for my family).
The roots for Jewish Deli cuisine were the fermentation, the types of foods, the technology of food, that originated in Europe, but the hallmarks of the Jewish Deli culture go beyond the food – to the booths, the waiters, the zeitgeist of the deli. We learn that that ambiance evolved – first from pushcarts on the streets of the Lower East Side (street food), to stools, to counter-style take-away shops, to finally having seating in full-fledged restaurants.
Case in point: Joel Russ founded his appetizing store out of a barrel in 1907 in Manhattan. He moved up to selling herring and other salt-cured and smoked fish out of a pushcart and finally opened a brick-and-mortar store in 1914.His daughters, Hattie, Ida, and Anne, worked in the store from the time they were 11 and 12. In 1935, he renamed the store Russ & Daughters, and are known as the “Sturgeon Queens.”
The delis introduced Americans to borscht (Slavic), gefilte fish, kishke (Slavic), vereniki (Ukrainian), kasha varnishkes (Russian), herring and chopped liver (“What am I, chopped liver?”). Also latkes (Ashkenazi), blintzes, knishes, rugelach and babka. Cheesecake is actually an American innovation.

Interestingly, the rise of industrial food processing and cattle production (which mass produced beef and discouraged pork consumption) actually increased the desirability of Kosher food – certified as meeting religious standards, hence the Hebrew National slogan, “We answer to a higher authority.”
Jewish entrepreneurs in Chicago capitalized on the opportunity to produce kosher beef, but ultimately, what became the Jewish Delicatessen was American.

“Meat was expensive in Europe. Jews couldn’t own land and meat was a luxury. But in the United States, meat became central to deli food.” At first, there was strict separation between deli restaurants like Katz’ and dairy restaurants, like Ratner’s – because Koshruth forbids the mixing of meat and milk – but over time, and with assimilation, even delis would offer items like cheesecake as dessert after a corned beef sandwich.
We learn about the Vienna Beef factory, founded in 1893 by Jewish Austro-Hungarian immigrants Emil Reichel and Sam Ladany. They first sold frankfurters at the 1893 World’s Columbia Exposition in Chicago, then expanded to include Vienna sausages, pastrami, corned beef and salami.

Katz’s Delicatessen, likely the oldest continuously operating deli in the US, was founded in 1888 by two brothers named Iceland. The Katz family became business partners and by 1917, bought out the brothers. At a time when most deli food was being sold from carts and barrels on the street, Katz’s was a brick-and-mortar delicatessen.
In 1916 on Coney Island, Polish immigrant Nathan Handwerker began building his empire by selling franks for five cents and undercutting his competition, Feltman’s.
And then there is this intrigue: fraud and corruption became pervasive in the kosher meat industry. In 1925, an estimated 40 percent of meat sold as “kosher” was non-kosher. In 1933, the NYC Department of Health and US Department of Agriculture raided Jacob Branfman & Son, one of the city’s main kosher delicatessen manufacturers, and seized over 1,400 pounds of nonkosher beef briskets. The owner was sentenced to 30 days in the infamous city workhouse.

During World War II, Jewish delis promoted a campaign to “Senda Salami to Your Boy in the Army” (the slogan was developed by Sixth Avenue Delicatessen waiter Louis Schwartz) and used by delis including Katz’s. The slogan became so popular that comedian Jerry Lewis used it in the film, “At War with the Army” (1950).
Louis G. Schwartz, aka “Louie the Waiter,” helped raise more than $9 million in war bonds – that paid for 66 P-47 Thunderbolt fighter planes, each which bore the moniker, “Louie the Waiter.” Schwartz developed a rhyme to inspire patrons to buy the bonds, “you’ll buy war bonds sooner or later, so get them from Louis the Waiter!”

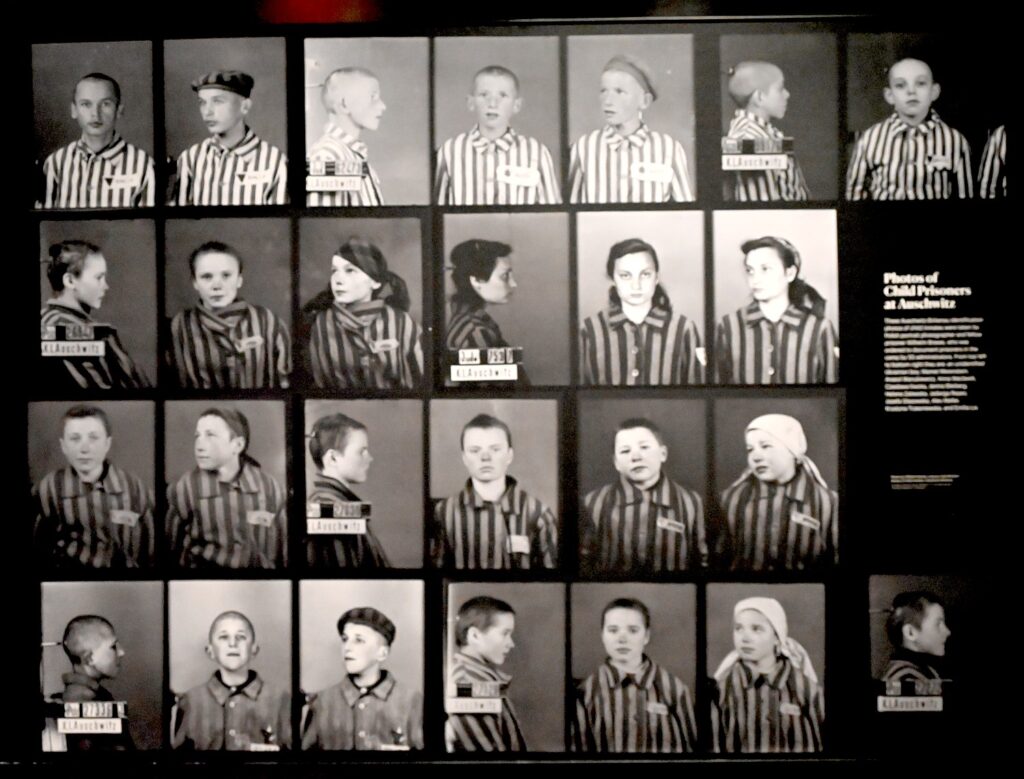
Most interesting is to learn about some of the people who found refuge in the delis – as owners or workers. Paula Weissman, born in present-day Ukraine, survived Auschwitz and Bergen-Belsen concentration camps. She arrived in New York in 1948 with two dollars. After working in a Brooklyn girdle factory, she was hired as a temporary waitress at Fine & Schapiro Kosher Delicatessen on West 72nd Street. The 7-day temp job turned into 30 years.”In her black uniform and white shoes, Paula took the orders of Zero Mostel, Molly Picon, Rita Moreno and many other Broadway stars.”
Rena Drexler was liberated from Auschwitz in 1945 and moved to Munich, Germany, where she and her husband, Harry, began their new lives working in a deli. The couple moved to Los Angeles in 1951 and opened Drexler’s Deli on Burbank Boulevard in 1957, selling kosher meals and products for the Orthodox Jews who settled in the neighborhood.

The original owner of the Second Avenue Deli, Abe Lebewohl, was a Holocaust refugee. Upon arriving in America and not even speaking the language, he took his first job in a Coney Island deli as a soda jerk, graduating to counterman and over the next few years, learning the secrets of superb pastrami and other traditional Jewish delicacies. In 1954, with a few thousand dollars he managed to set aside, Abe took over a tiny 10-seat luncheonette on East Tenth Street—the nucleus of the 2nd Ave Deli. Working around the clock for years—often filling in as cook, counterman, waiter, and even busboy—he put all his time and energy into making a success of his tiny establishment. “He never turned anyone away for lack of funds, he fed striking workers, homeless.” In 1996, he was robbed and murdered when making a bank deposit; the case unsolved.
In a nostalgic tribute to departed delis that continue to hold a place in the hearts of many New Yorkers, photographs show restaurants that closed in recent years. Eateries include the Upper West Side’s Fine & Schapiro Kosher Delicatessen, Jay & Lloyd’s Kosher Delicatessen in Brooklyn, and Loeser’s Kosher Deli in the Bronx. An exuberant hot dog-shaped sign from Jay & Lloyds Delicatessen, which closed in May 2020, and folk artist Harry Glaubach’s monumental carved and painted signage for Ben’s Best Kosher Delicatessen in Queens, also pay tribute to beloved establishments. The exhibition concludes on a hopeful note, highlighting new delis that have opened their doors in the past decade, such as Mile End and Frankel’s, both in Brooklyn, and USA Brooklyn Delicatessen, located steps from the site of the former Carnegie and Stage Delis in Manhattan.

Ben’s, still a force on Long Island and Manhattan is illustrative of the changes in the Jewish Deli that followed changes in the lives of American Jews. To be blunt, in the mid-20th century, restrictive covenants that barred Jews (and Blacks) from living in certain neighborhoods were lifted, and American Jews were flocking to the suburbs. The delis followed.
What I found fascinating was that the Jewish deli grew up as the American industrialized cattle industry grew – displacing home-grown pork – making beef plentiful and giving rise to the sky-high thick pastrami and corned beef sandwiches that would never have been available to Jews in their European shtetls, where meat would have been a cherished rarity.

The exhibit ponders how it was, why it was that Jewish deli became so much a part of American pop culture.
“There is no definitive answer as to why the deli has inspired generations of Jewish filmmakers, comedians, musicians and writers. Perhaps it is because so many Jewish creatives got their start in New York City, where they frequented Jewish delis and later infused these experiences into their work. Or maybe it is because the Jewish deli is one of the most public secular environments in Jewish American life. It is a place where characters can demonstrate or celebrate their Jewish identity outside of private or religious spheres. Whatever the reason, the deli continues to have significant influence on Jewish artists.”
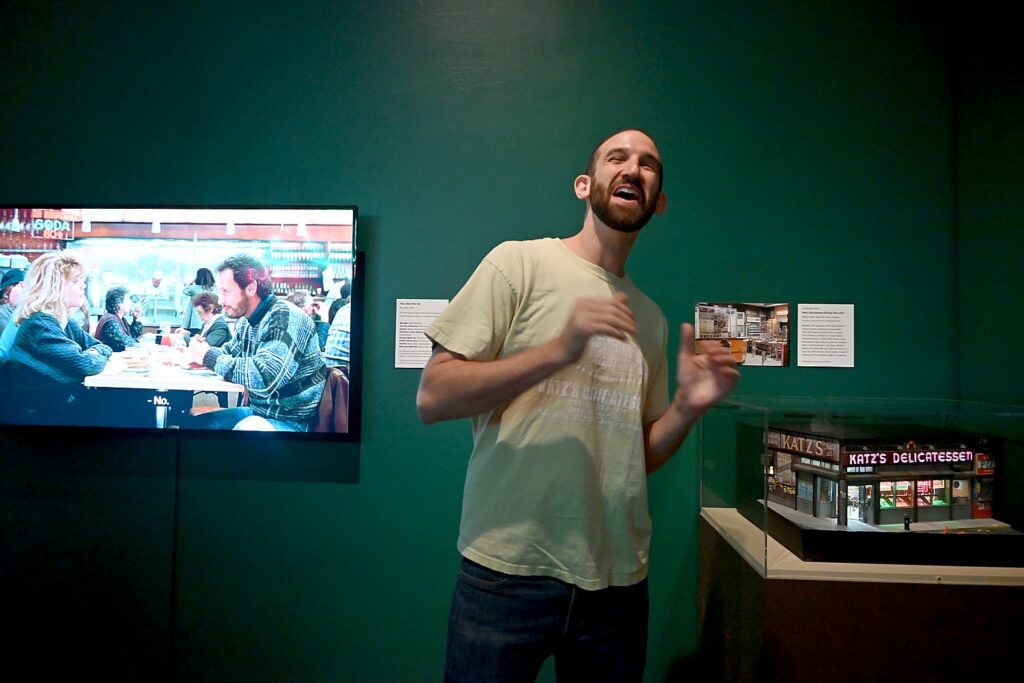

The better question has to do with how Jewish cuisine has become as integrated into in American culture as bagels (with or without lox). And that’s because so many of the creatives – in Broadway theater, film – were Jewish.
But Jewish delis, themselves, are struggling today, particularly after the coronavirus pandemic, but also because of changing economics – the cost of that two-inch high pastrami on rye, the rent. The sandwich that used to cost $1.95 (see the Reubens menu), now costs $25. The fifth generation “Katz,” Jake Dell, on hand at the press preview, spoke of the changing economics, he said that they don’t even make a profit on a $25 pastrami sandwich. “The profit is in the soup.”
Programming: Private group tours can be arranged throughout the run of “I’ll Have What She’s Having”: The Jewish Deli. Family programming includes a food-focused family day celebrating foodways brought to New York City by immigrants from around the world. Living History programs bring to life the stories of proprietors, patrons, and staff of New York City’s Jewish delis. Visit nyhistory.org for dates and details.
“Confronting Hate 1937-1952”
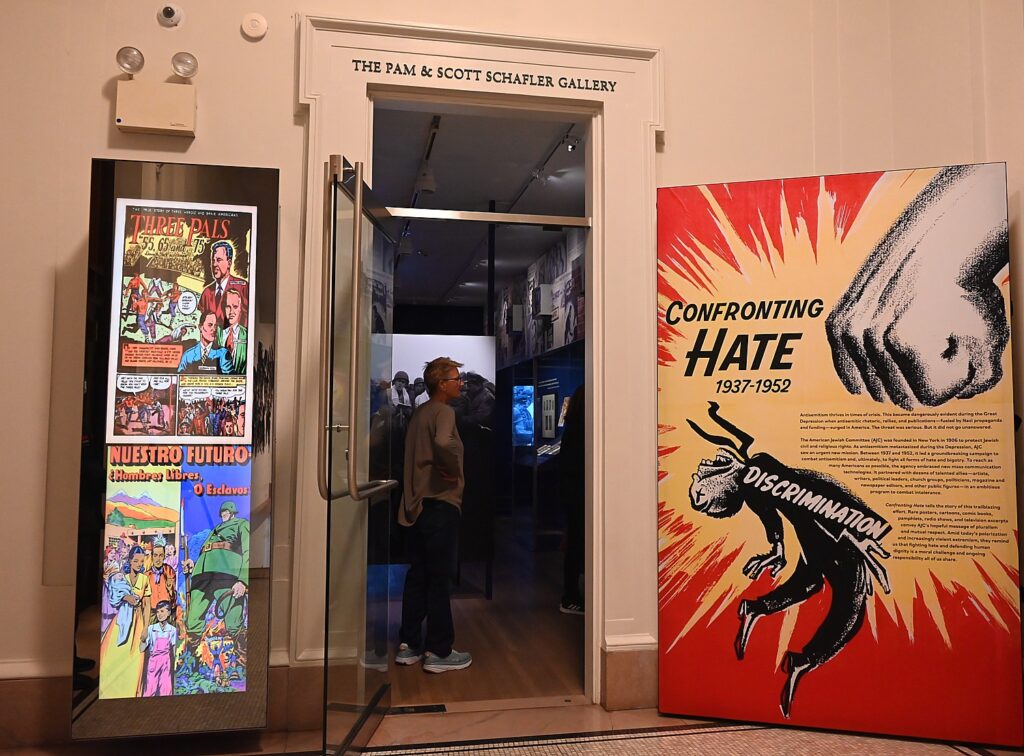

After enjoying the joyful “I’ll Have What She’s Having,” go up to the second floor of the historical society for another, more serious, exhibition that is so timely in the here and now: “Confronting Hate 1937-1952” about the American Jewish Committee’s groundbreaking campaign to combat anti-Semitism and ultimately to fight all forms of hate and bigotry. To reach as many Americans as possible in the period leading up to the Holocaust, World War II and the aftermath, the agency embraced new mass communication technologies and partnered with talented allies – artists, writers, political leaders, church groups, politicians, magazine and newspaper editors. They produced comic books, ads, articles. Among the celebrities who joined a “Speaking for America” poster campaign in 1946: Bob Hope, Frank Sinatra, Judy Garland and Danny Kaye, plus President Harry Truman and Admiral Chester Nimitz.
New-York Historical Society, New York’s First Museum
At the New-York Historical Society, New York’s first museum, you experience 400 years of history through groundbreaking exhibitions, immersive films, and thought-provoking conversations among renowned historians and public figures. A great destination for history since 1804, the Museum and the Patricia D. Klingenstein Library convey the stories of the city and nation’s diverse populations, expanding our understanding of who we are as Americans and how we came to be. Ever-rising to the challenge of bringing little or unknown histories to light, New-York Historical will soon inaugurate a new annex housing its Academy for American Democracy as well as the American LGBTQ+ Museum. These latest efforts to help forge the future by documenting the past join New-York Historical’s DiMenna Children’s History Museum and Center for Women’s History.
Digital exhibitions, apps, and For the Ages podcast make it possible for visitors everywhere to dive more deeply into history. Connect at nyhistory.org or at @nyhistory on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, YouTube, and Tumblr.
The New-York Historical Society is located at 170 Central Park West at Richard Gilder Way (77th Street), New York, NY 10024, 212-873-3400, nyhistory.org.
__________________
© 2022 Travel Features Syndicate, a division of Workstyles, Inc. All rights reserved. Visit goingplacesfarandnear.com, www.huffingtonpost.com/author/karen-rubin, and travelwritersmagazine.com/TravelFeaturesSyndicate/. Blogging at goingplacesnearandfar.wordpress.com and moralcompasstravel.info. Visit instagram.com/going_places_far_and_near and instagram.com/bigbackpacktraveler/ Send comments or questions to [email protected]. Tweet @TravelFeatures. ‘Like’ us at facebook.com/NewsPhotoFeatures