by Karen Rubin, Travel Features Syndicate, goingplacesfarandnear.com
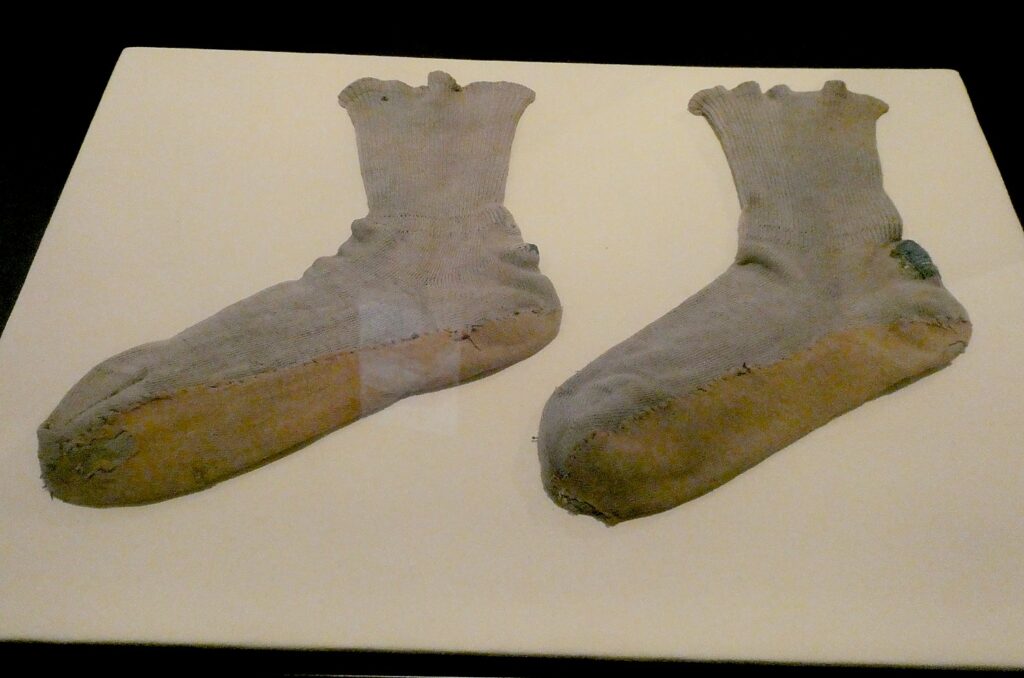
Out of 1200 artifacts, photos, video testimonies, it comes down to one: a tiny, well-worn leather child’s shoe, the sock still hanging out of it. Was it taken off in anticipation the child was just going to a shower, or was the child ferociously pulled out of the shoe and sock?
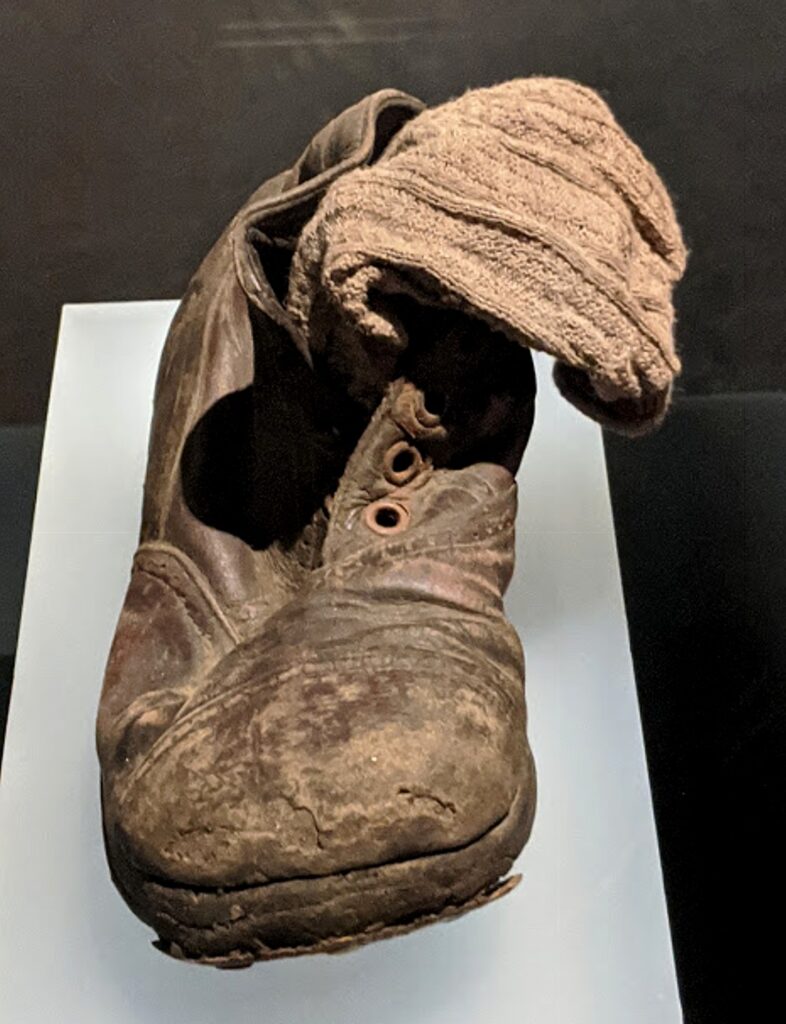

Shoes take on special significance at the “Auschwitz: Not so long ago. Not far away.” landmark exhibit at the Museum of Jewish Heritage in downtown Manhattan, which has been extended through August 30, 2020 before touring to other cities.
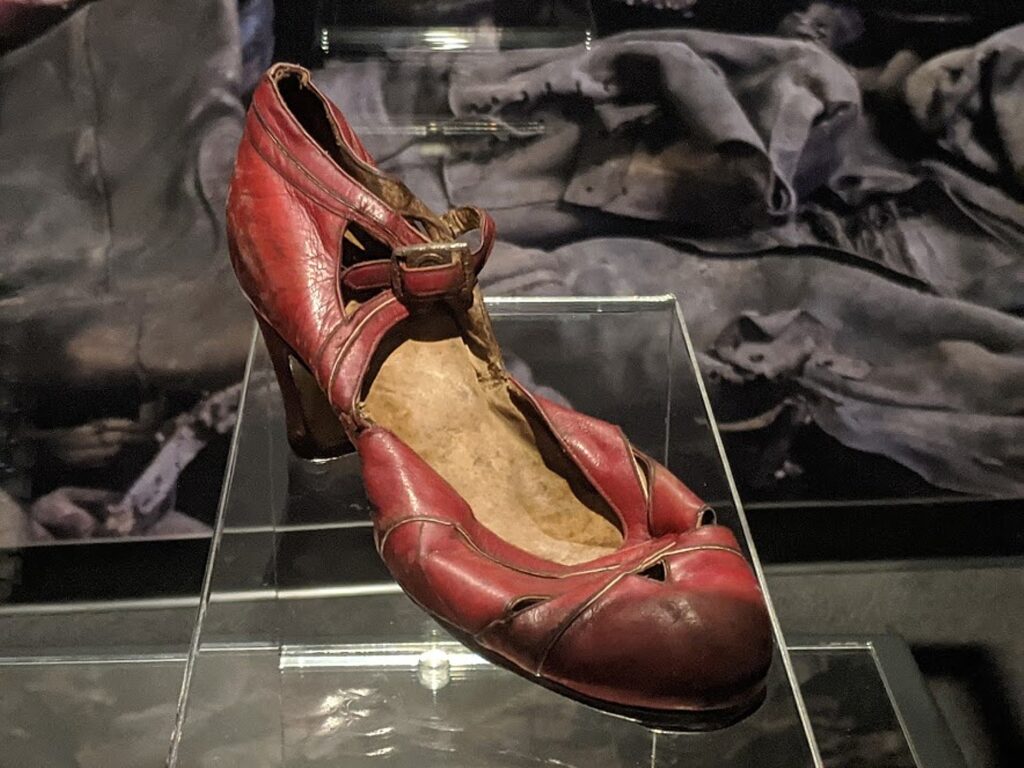
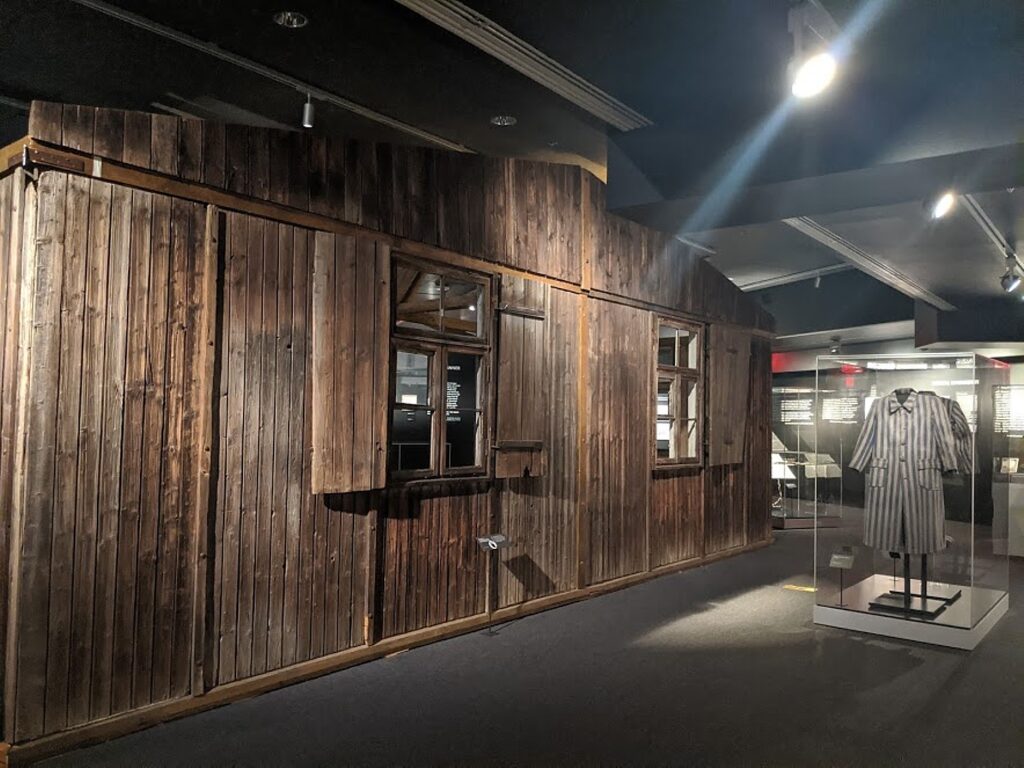
As you first walk in, there is a single red shoe in a glass case that perversely sparks an image of the ruby slippers in “Wizard of Oz.” set against a grey-toned wall-mural sized photo of piles of shoes. Further on as you walk through the three-floors of exhibits, there is the pair of hardened leather clog-looking shoes in a case with a prison uniform so rough and raw they would irritate, then infect and swell the feet, a death sentence for the hapless prisoner.

Another display case in the “Selection” section contains shiny leather boots, much like those that the prisoners would see Mengele wearing as they were forced out of the freight cars minutes after being unloaded at Auschwitz, beneath the sign that said. ‘Work Sets You Free.” He was the doctor who selected out twin children for his medical experiments. The rest of the children – 200,000 of them – were immediately sent to the gas chamber along with their mother, aunt, sister, grandmother or friendly stranger who had accompanied them on their journey. The tiny leather shoe with the sock still in it is the only evidence this child existed at all, his life extinguished.
800,000 more Jews were immediately sent to their deaths in the gas chambers, 2000 at a time, their bodies thrown into crematoria that worked 24/7 to keep up with the factory-scale exterminations, their ashes thrown into a river.
Out of the 1.1 million “deported” to Auschwitz, the largest of the Nazi killing camps, only 200,000 were “selected” not for immediate death but to become slave labor in the concentration camp. They too were immediately marched into showers, their hair shaved, their arms tattooed, their bodies stripped of any dignity or humanness. Few lived more than a month or two under the atrocious conditions – dying of starvation, disease, overwork, beatings or simply shot on the spot. Some became so infirm, they settled into their fate, and welcomed being carried by stretcher to end their daily terror and pain. Others, packed six to a wooden plank in the barracks, would wake up to find a dead person next to them.

“Auschwitz: Not long ago. Not far away.” offers a different perspective on the Holocaust, a horror on a scale that is incomprehensible, by focusing down to the most personal elements.
This exhibit, which focuses down to one “tiny dot” on a map that was the largest killing camp in the Nazi’s network – makes it as personal as is possible. You walk in their shoes. And yet, as well as they show the faces, the horrors, the personal objects, the testimonials of survivors, the drawings and photos, an actual freight car and an actual barracks, even so, it is still hard to comprehend.
Indeed, the incomprehensibility of the horror was key to its success – along with secrecy and deception. People could not imagine the level of brutality, cruelty, savageness. So they packed up what they could in suitcases, expecting they were being resettled to places free of anti-Semitism, where they could work and live out their lives.
It is also the danger that such dehumanization, genocide, industrial-scale killing can happen again. Indeed, Auschwitz was not that long ago, nor that far away.
“Auschwitz” isn’t just a look back with graphic evidence to plant a marker in the history books that others are working so hard to erase . It is a look at now, a look at where the trajectory can lead. That is what is embodied in the phrase. “Never Again.”

I had been steeling myself to visit the Auschwitz exhibit at the Museum of Jewish Heritage. I recognized that I had an obligation, a responsibility to be a witness to the extent possible. A NYC-Arts special on PBS helped enormously because I could visualize, know what to expect and better prepare for the horror – unlike the millions who were sent to the killing camps. Then there was that television screening of the story of Irena Sendler, a Warsaw nurse who smuggled 2,500 children out of the Ghetto to safety – the film so graphic, her courage and nobility so palpable. Surely I could summon the courage to face the past. To Remember. Never Forget.
If you thought you knew about the Holocaust and the Nazis’ Final Solution that exterminated 6 million Jews and too many (40% of adults and 65% of young people) don’t know anything at all, this rare exhibit, with artifacts gathered from 20 institutions around the world, focuses just on Auschwitz – from how a simple Polish village, Oswiecim where half the population was made up of Jewish families who had lived there for centuries, was turned into the largest of six killing factories in Poland. Original artifacts – documents, personal items, posters, photos – show the roots of anti-Semitism and how being Jewish was converted from a religion to “an inferior race,” a sub-human species, stripped of legal, political, property and professional rights. That’s the first floor.
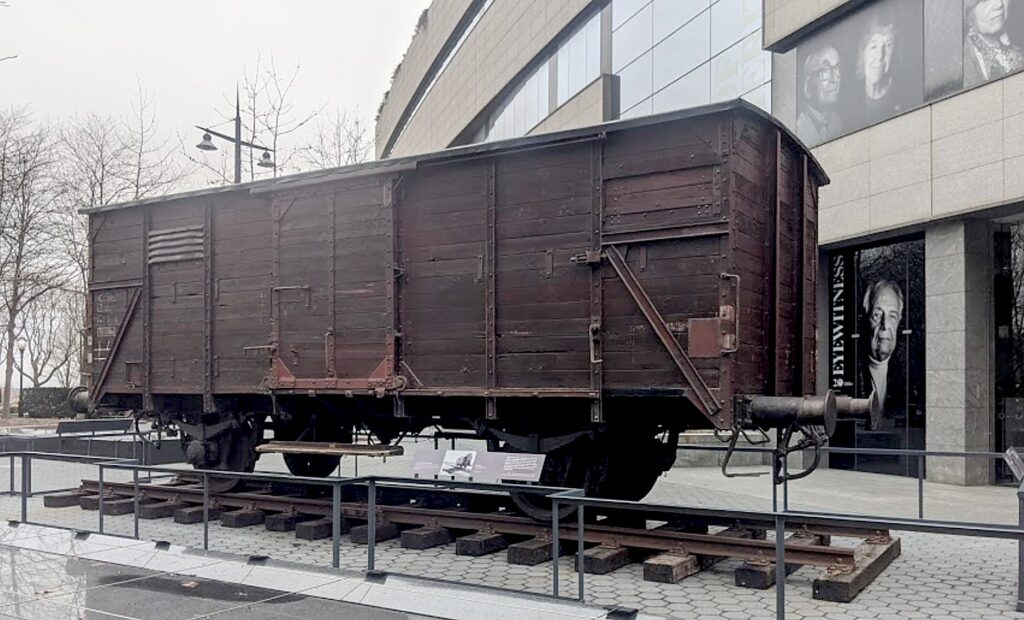
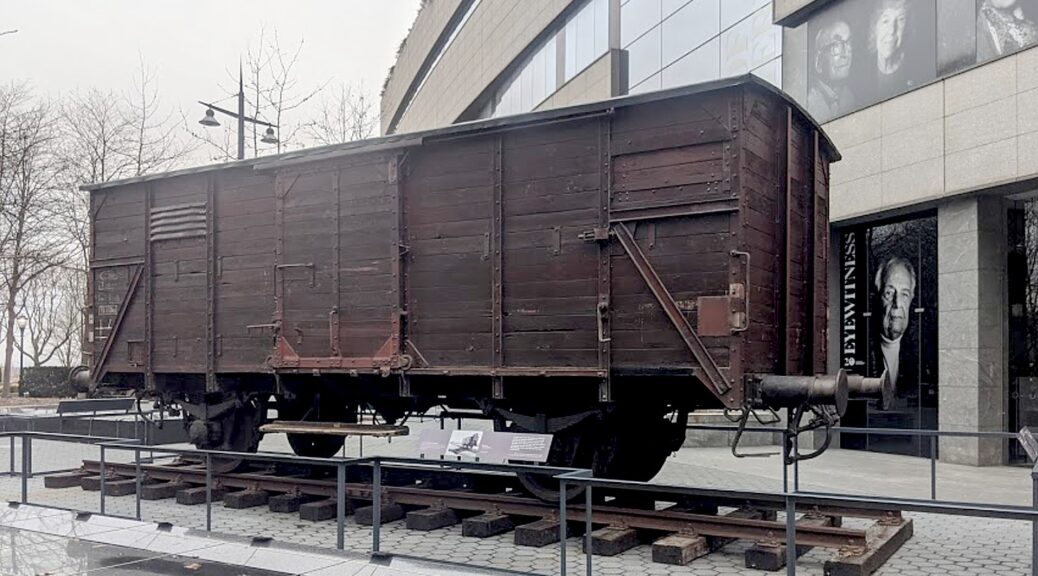
You see and hear from survivors how families were stuffed 100, 150 into a box car (like the one outside the museum), with the ploy of telling them they were being resettled to a better place free of anti-Semitism, then locked in with just one pail as a toilet and one pail for water, so crowded, one had to stand up in order for someone to sit down. And then they arrive on the “ramp”, where they are “selected,” crossing under a wrought iron sign that said, “Work Makes You Free.” That’s just the middle of the second floor.
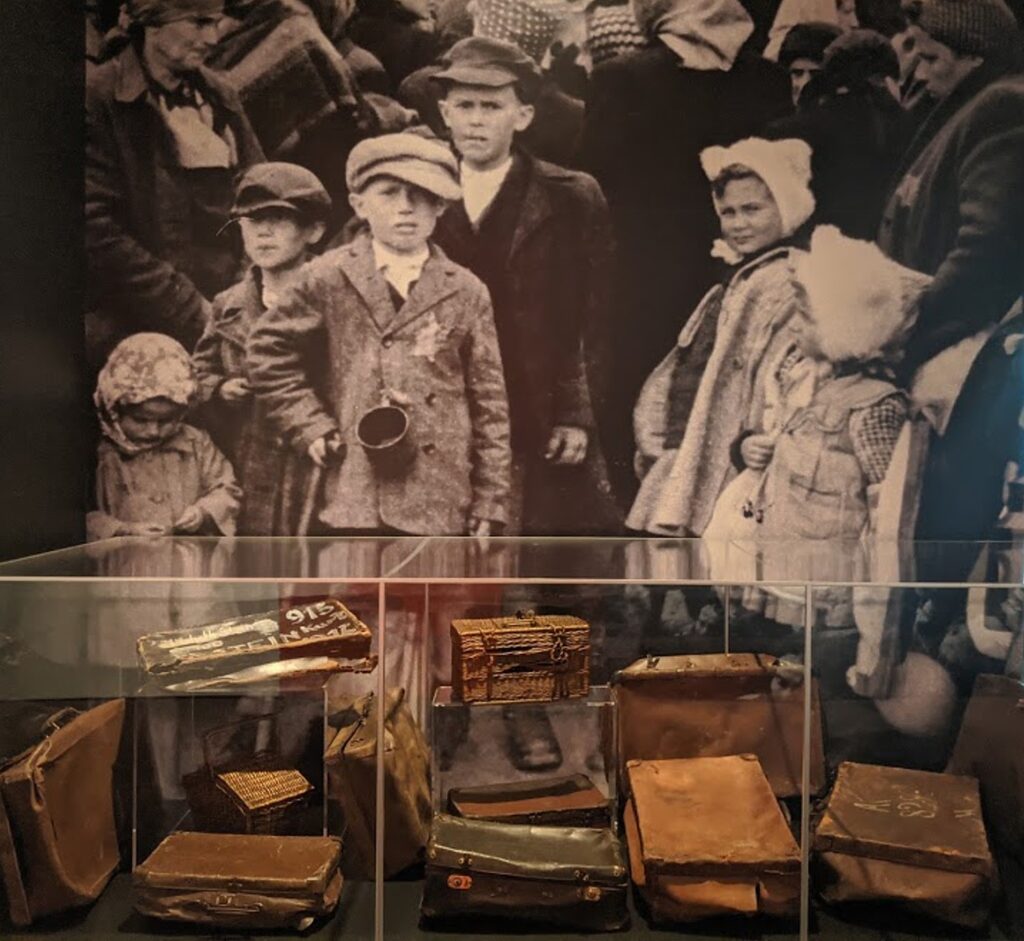

Here you see stacks of suitcases, a pram (a rare artifact) that eerily reminds you of the display as you enter Ellis Island, the gateway for millions of immigrants into the United States. But here, it shows how unwitting the victims were. Because they were only moments away from being sent to their death. And because access to safe harbors like the United States were shut off to them.
Turn the corner in a room shrouded in darkness and you come upon a white door of a gas chamber, a metal mesh chimney down which the Zykon B poison was sent, a gas mask. In another case, one of the innocuous looking showerheads that survived the fire the Nazis set to destroy evidence of their Final Solution. Extraordinarily powerful and horrifying drawings by survivor Alfred Kantor depict how women and children were told to undress and hang up their clothes on a numbered hook so they would find them again – “Remember your number.” And then they would be locked into the gas chamber.
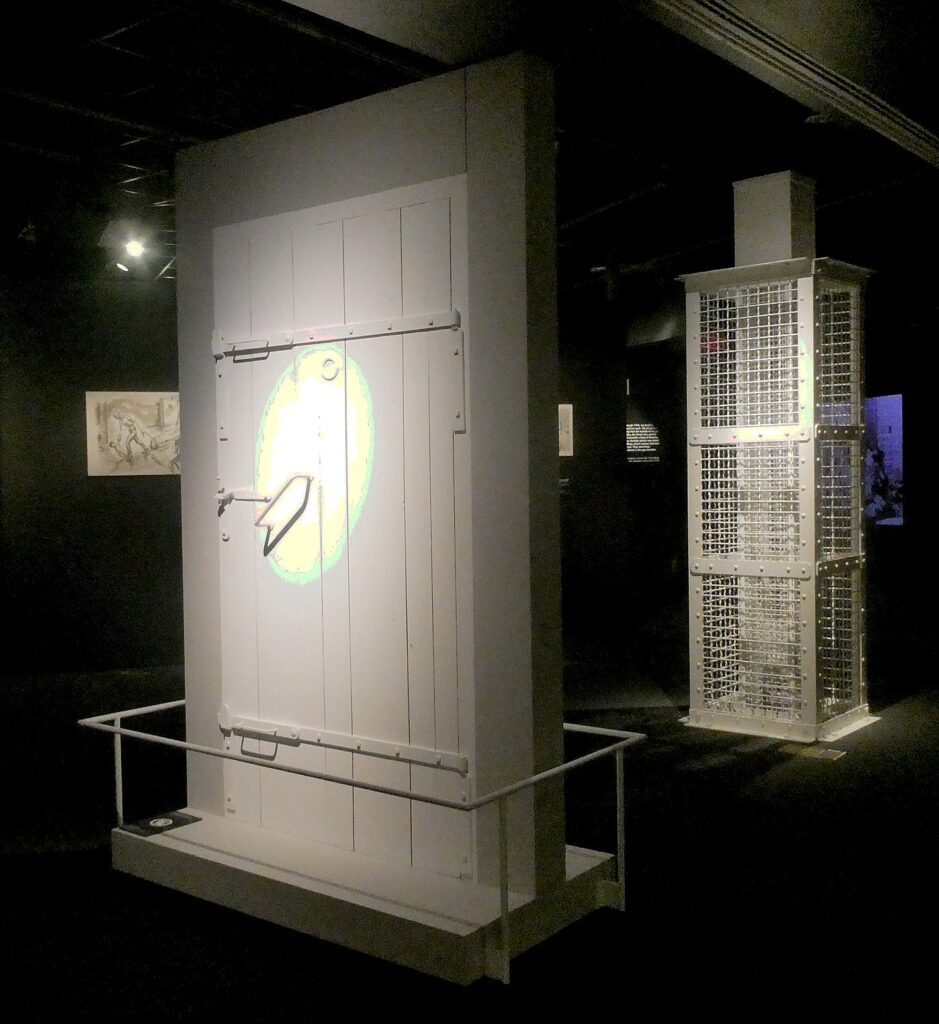
They, too, were told they were going to shower to be de-loused. The Nazis made a show of having them undress in a changing room, have them put their clothes on numbered hooks so they could find them again. They were shoved 1000 at a time into a shower room, the doors clanked shut, and Zykon B poison pumped in. It took barely 15 minutes to exterminate them all.
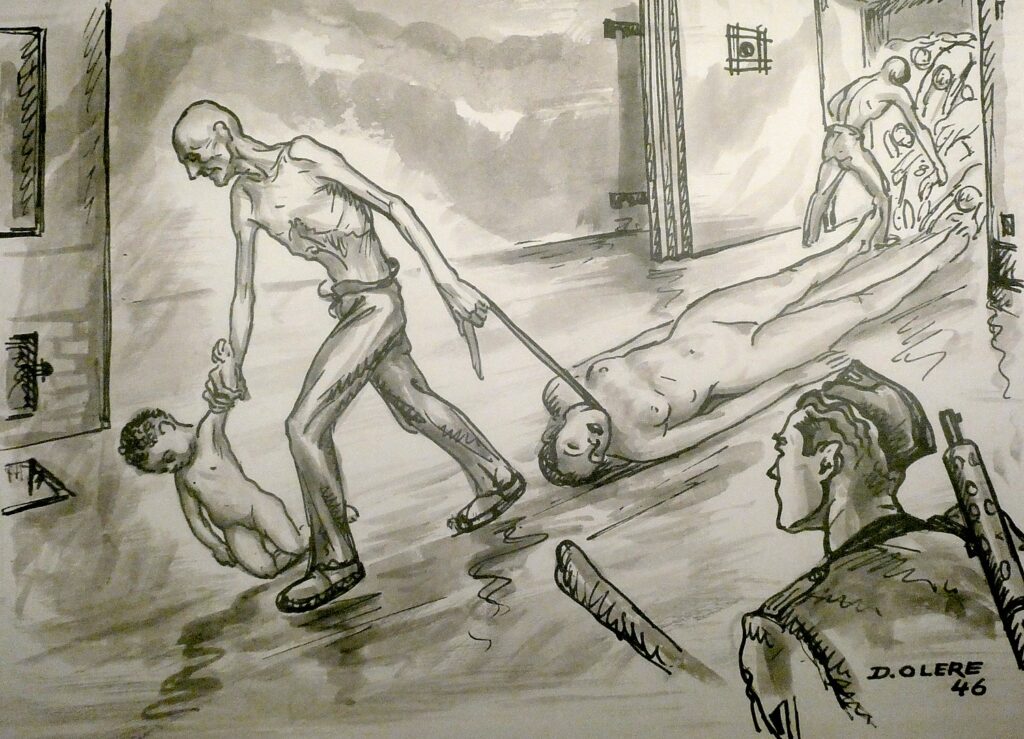
The door would open at the other end and a group of Jewish prisoners, called Sonderkommandos, would pull the bodies out one by one, drag them to a dumbwaiter to the crematoria. To keep the secret safe, the Sonderkommandos were kept isolated from the rest of the camp, living in barracks above the crematoria. A rabbi among them, a Hungarian, took each child and said Kaddish before placing the small body in the crematorium.

But one of the Sonderkommandos, working with Polish resistance, smuggled a camera and film and took photos of bodies being burned in vast fields with the overflow that couldn’t be handled in the crematoria, working night and day. There are four of these photos on display.
The Nazis harvested their victims. As the bodies were pulled from the gas chamber, a Sonderkommando designated “The Dentist” would pull out their gold teeth. Their clothes and meager belongings had already been plundered and sent to “Kanada” – vast warehouses named for a country that was considered rich but out of reach. Between the various business enterprises that the Nazis used their slave labor and the looting, it is estimated that each prisoner returned $794 in profit to the SS.

How were the Nazis able to lead 11 million including 6 million Jews to slaughter like sheep? The secret is how they kept such a massive killing secret, and who could have imagined such diabolical cruelty, such grotesque brutality, who could have imagined a Final Solution?
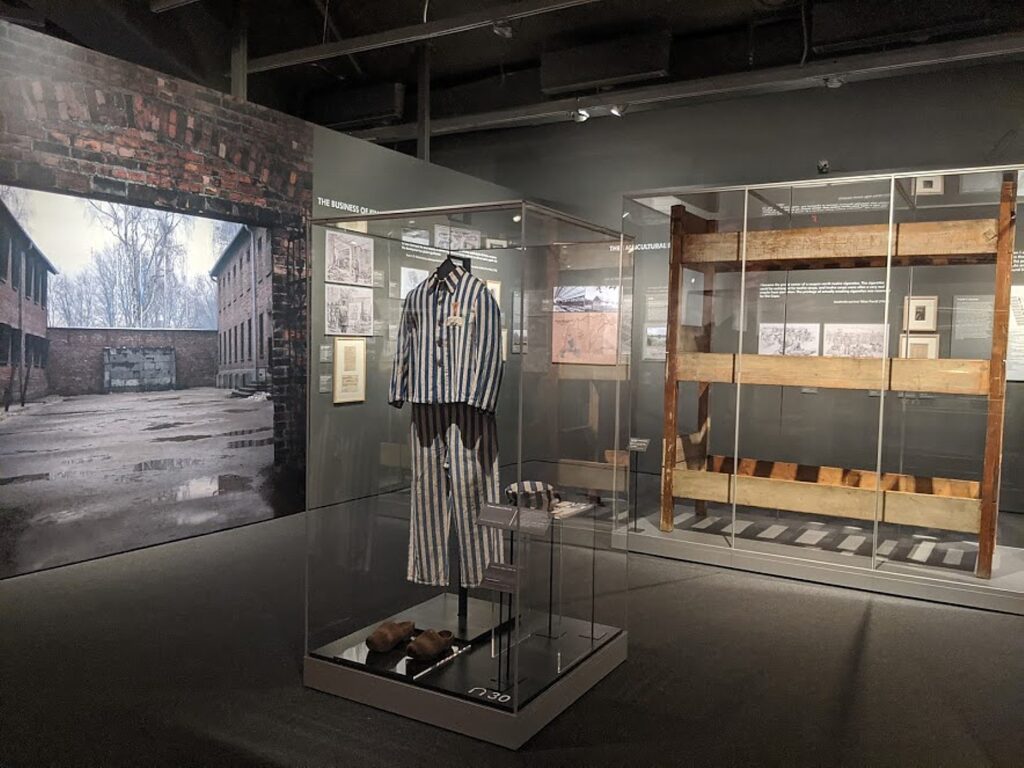
How did they keep such a monstrous secret? How they managed to move people by the thousands – trapping them into the freight cars when the people thought they were being resettled to a pleasant village where they would be allowed to work. They kept it a secret when immediately upon arriving at Auschwitz, they were separated into two groups. One line was pushed to showers, told to strip and were turned into slave labor – their hair shaved, arms tattooed, all their property stripped away along with their identity, their personhood, stuffed into a prison uniform with an appropriate identifying symbol as to their status.
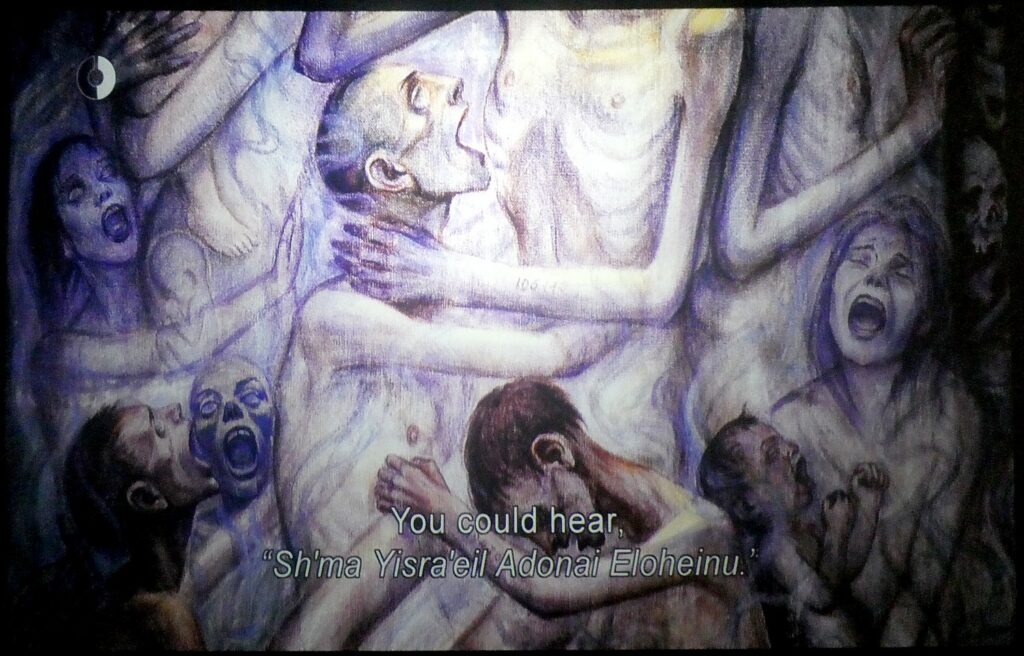

You continue on to learn what life was like in Auschwitz for the 200,000 who were not immediately murdered. You listen to harrowing testimonials by survivors, see part of an actual barracks.
Indeed, Auschwitz death toll of 1.1 million was the largest among all the German death camps. But it also had the greatest number of survivors – some 200,000 people brought to Auschwitz were sent to other camps before the war ended, and some 7,000 prisoners were liberated at Auschwitz in January 1945.

You leave this section, which is dark, almost completely black, into a room called “Persistence and Resistance,” which is off-white, round, with natural light streaming from a domed ceiling.
Persistence took the form of ways that the prisoners preserved their humanity.
Resistance took the form of getting the story of what was going on in Auschwitz out to the world, in the hopes that the Allies would bomb the killing center or disrupt the deportations, and preserving evidence that would ultimately hold perpetrators of such colossal evil accountable.
This is the most moving section of all – when I can finally start breathing again.
The Auschwitz SS aimed to destroy any possible solidarity between prisoners…‘Resistance’ in Auschwitz therefore consisted of acts in which prisoners, against all odds, showed solidarity with others. It included heroic actions made with a view to the larger world outside of the camp, grand gestures of generosity and small acts of kindness and charity, along with spiritual resistance. And it was expressed in the determination that-despite the best efforts of the SS – death in Auschwitz would not remain anonymous, and the victims would not remain without names.
I learn the amazing story of Witold Pilecki, a Second Lieutenant in the Polish Army who had himself arrested under the name Tomasz Serafinski and sent to Auschwitz in 1940 (prisoner no. 4859) in order to spy for the Polish government.
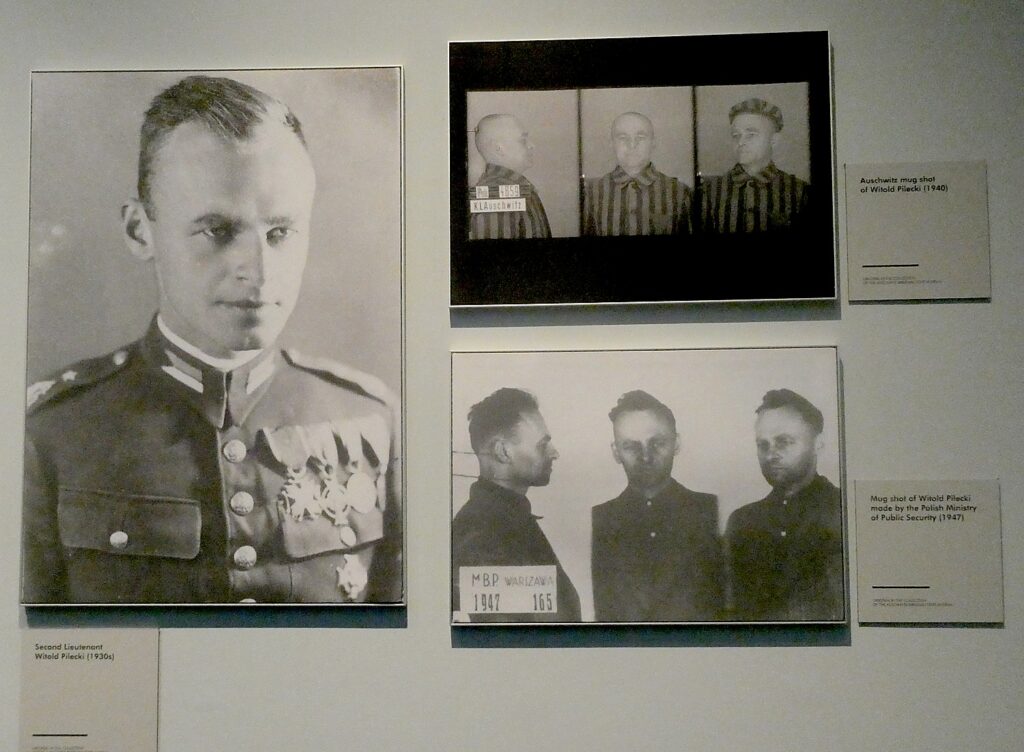

He managed to smuggle out messages about life and death in the camp while organizing fellow prisoners. In April 1943, Pilecki escaped, and returned to Warsaw to convince the Polish Resistance to attack Auschwitz in a coordinated effort with prisoners. But the commander who had sent him on his mission had been arrested, and the new leader judged an attack on the large and well-armed Auschwitz garrison to be suicidal. They also realized they wouldn’t be able to shelter the tens of thousands of inmates who might be freed. Pilecki wrote the first full report on conditions of Auschwitz and the mass murder of Jews in the gas chambers. The allies received the report but ignored it. Pilecki continued to fight the Germans, participating in the 1944 Warsaw Uprising.
Outrageously, in 1947, he was arrested by the Polish Communist government, tortured, and executed in 1948.
It was so critical to get information out that several risked their lives to smuggle information out.
I learn the story of The Auschwitz Protocols: In March 1944, Slovakian Jewish inmates Walter Rosenberg (aka Rudolf Vrba) and Alfred Wetzler observed the Nazi’s preparations for the arrival of transports from Hungary. With a lot of planning and luck, they escaped from Auschwitz on April 7, 1944 and fled to Slovakia in the hopes of warning the Jews of Hungary.
The testimony of Vrba and Wetzler, along with information supplied by Czeslaw Mordowicz and Arnost Rosin, who escaped Auschwitz on May 27, 1944, yielded the first substantial report of the use of Auschwitz as a death factory. It became known as the “Auschwitz Protocols” and detailed the continuing massacres in the gas chambers. But the information didn’t reach the Hungarians in time: beginning in May, over 400,000 Jews were deported and murdered. A summary of the report arrived in the US in July. That same month, the Red Army’s liberation of the Majdanek camp led to the publication in the US of sensational reports written by well-known journalists in America media. Though it didn’t succeed in its primary objective, the Auschwitz Protocols led to diplomatic pressure that forced the Hungarian government [the leader now fearing he would be tried for war crimes] to stop further deportations, saving the lives of over 150,000 Jews. It also triggered a debate among the Allies: what parts of Auschwitz could or should be bombed.
On August 20, Allied bombers attacked the IG Farben factory, but not Auschwitz camps.
“I firmly believed that [the daily killing in the crematoria] was possible because the victims who came to Auschwitz didn’t know what was happening there,” Auschwitz survivor Rudolf Vrba wrote in 1985. “I thought that if this would be made known by any means within Europe, this might stir up the Resistance outside and bring help directly to Auschwitz. And thus the escape plans are finally formulated and the escape took place on April 7, 1944.
The Sonderkommandos organized an ill-fated revolt in October 1944.
Roza Robota recruited women prisoners working in the munitions factory operating next to the camp to smuggle gunpowder off-site. Robota passed it to Timofei Borodin, a Russian technician, who carried it to the Sonderkommandos. Their aim was to destroy the crematoria and spark a rebellion.
But the uprising went awry. The Sonderkommandos of Crematorium 5, hearing they were to b e gassed, revolted ahead of schedule. On October 7, they killed 3 SS, wounded 12 and burned down Crematorium 4. At the same time, the Sonderkommandos of Crematorium 2 attempted a breakout.
In retaliation the SS killed 451 Sonderkommandos. The camp Gestapo identified Robota and three other Jewish women – Regina Sapirstein, Ala Gertner and Ester Wajeblum – as plotters. After weeks of torture they were hanged publicly. As the noose was placed around her neck, Robota cried out ‘Nekama;’ (Revenge!)

Auschwitz Sonderkommando Zalman Groiadowski (Sept 6, 1944), leaves a note. “Dear finder, search everywhere, in every inch of soil. Tons of documents are buried under it, mine and those of other persons, which will throw light on everything that was happening here. Great quantities of teeth are also buried here. We, the Sonderkommando workers, have expressly strewn them all over the terrain so that the world should find material traces of the millions of murdered people…”

This groundbreaking 18,000-square-foot exhibition takes up three floors, 20 thematic galleries. Through the artifacts and Holocaust survivor testimony, it brings you inside and re-creates the experience as best as possible, raising the alarm how the unimaginable, the inconceivable happened and can happen again. The commentary notes that one demagogue like Hitler could not have produced the Holocaust.
“Genocide is a social act,” the audio guide says toward the end of the exhibit. “It requires a society who conspires…But the same society can resist.”
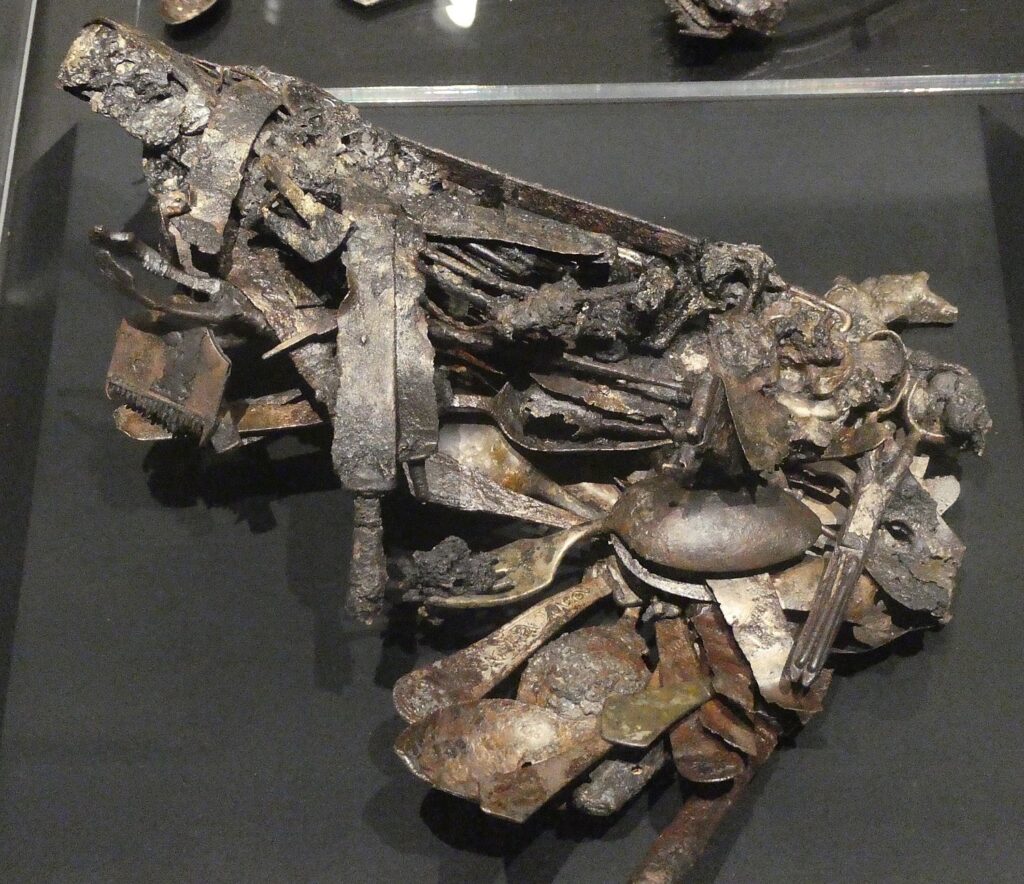

But there is one question that is not answered: who, what and how those who administered torture, who beat and murdered and presided over such intense suffering. That is a critical question to knowing whether such a thing could happen again. Just what percentage of a given population are sociopaths?
There are some clues provided in the statements that are presented:
Once Hitler had decided that the “Final Solution” would be enacted, one important question remained: Who was to be in charge of the genocide? Heinrich Himmler sought this responsibility as he believed it would help him consolidate his power.
Auschwitz commandant Rudolf Hoss (1946) testified, “I visited Treblinka to find out how they carried out their exterminations. I did not think his methods were very efficient. I used Zykon B, a crystallized prussic acid dropped into the death chamber from a small opening. It took from three to 15 minutes to kill the people. Another improvement we made over Treblinka was that at Treblinka the victims almost always knew that they were to be exterminated and at Auschwitz we endeavored to fool the victims into thinking that they were to go through a delousing process.”
“The children, they’re not the enemy at the moment. The enemy is the blood inside them. The enemy is the growing up to be a Jew that could become dangerous. And because of that the children were included as well.” (Former Auschwitz SS man Oskar Groning explaining in a 2004 interview why he condoned killing Jewish children).
The exhibition explores the dual identity of the camp as a physical location—the largest documented mass murder site in human history—and as a symbol of the borderless manifestation of hatred and human barbarity.
Consider this: Jews had lived in Germany for 1000 years before the Holocaust; they had lived in the Polish town of Oswiecim.that the Germans renamed Auschwitz and repurposed for a killing factory for hundreds of years. It was only 10 quick years between when Hitler was democratically elected Chancellor in 1933, to the Final Solution in 1942. By the time Germany surrendered, two years later, 6 million Jews – two-thirds of Europe’s Jewish population – had been exterminated.
That’s how fast things can descend into unimaginable evil.
Groundbreaking Exhibition
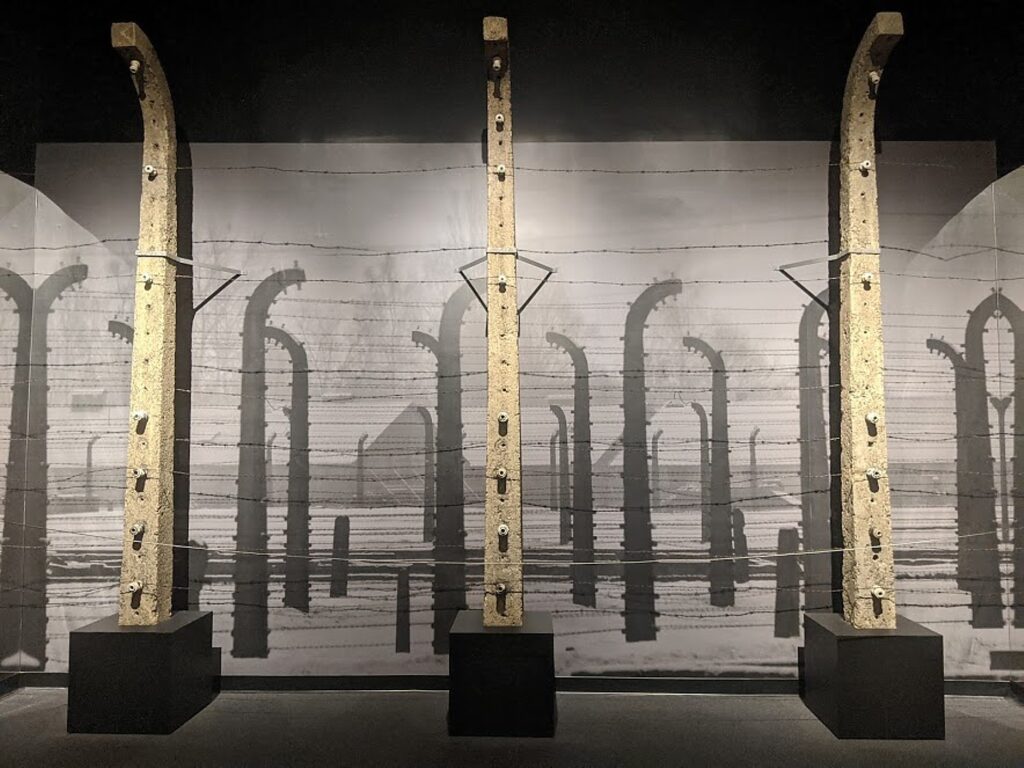
Produced by the international exhibition firm Musealia and the Auschwitz-Birkenau State Museum in Poland, the groundbreaking exhibition is the largest ever on Auschwitz with more than 700 original objects and 400 photographs. The New York presentation of the exhibition allows visitors to experience artifacts from more than 20 international museums and institutions on view for the first time in North America, including hundreds of personal items—suitcases, eyeglasses and shoes—that belonged to survivors and victims of Auschwitz. Other artifacts include: concrete posts that were part of the fence of the Auschwitz camp; part of an original barrack for prisoners from the Auschwitz III-Monowitz camp; a desk and other possessions of the first and the longest-serving Auschwitz commandant Rudolf Höss; a gas mask used by the SS; Picasso’s Lithograph of Prisoner; and an original German-made Model 2 freight train car of the type used for the deportation of Jews to the ghettos and extermination camps in occupied Poland.

The exhibition also features 10 artifacts on loan from the Anne Frank House in Amsterdam, which include the spilled, dried beans Anne wrote about in her diary and that were later discovered lodged between the cracks of stairs in the home where she hid from the German Nazis. The beans have never been displayed anywhere before. Most recently, the Museum announced the exhibition’s incorporation of a shofar (a ram’s horn that is made into a special wind instrument used during Jewish High Holiday services) that was hidden and clandestinely blown in the Auschwitz. The shofar was newly added to the exhibition on the cusp of the High Holy days and temporarily transported to two New York City synagogues to be blown on Rosh Hashanah and Yom Kippur.
The Museum of Jewish Heritage has incorporated into the exhibition nearly 100 rare artifacts from its collection that relay the experience of survivors and liberators who found refuge in the greater New York area. Alfred Kantor’s sketchbook and portfolio that contain over 150 original paintings and drawings from Theresienstadt, Auschwitz, and Schwarzheide; the trumpet that musician Louis Bannet (acclaimed as “the Dutch Louis Armstrong”) credits for saving his life while he was imprisoned in Auschwitz; visas issued by Chiune Sugihara, a Japanese diplomat in Lithuania often referred to as “Japan’s Oskar Schindler”; prisoner registration forms and identification cards; personal correspondence; tickets for passage on the St. Louis; and a rescued Torah scroll from the Bornplatz Synagogue in Hamburg, postcards sent home in order to deceive family members as to what was really going on at the camp.
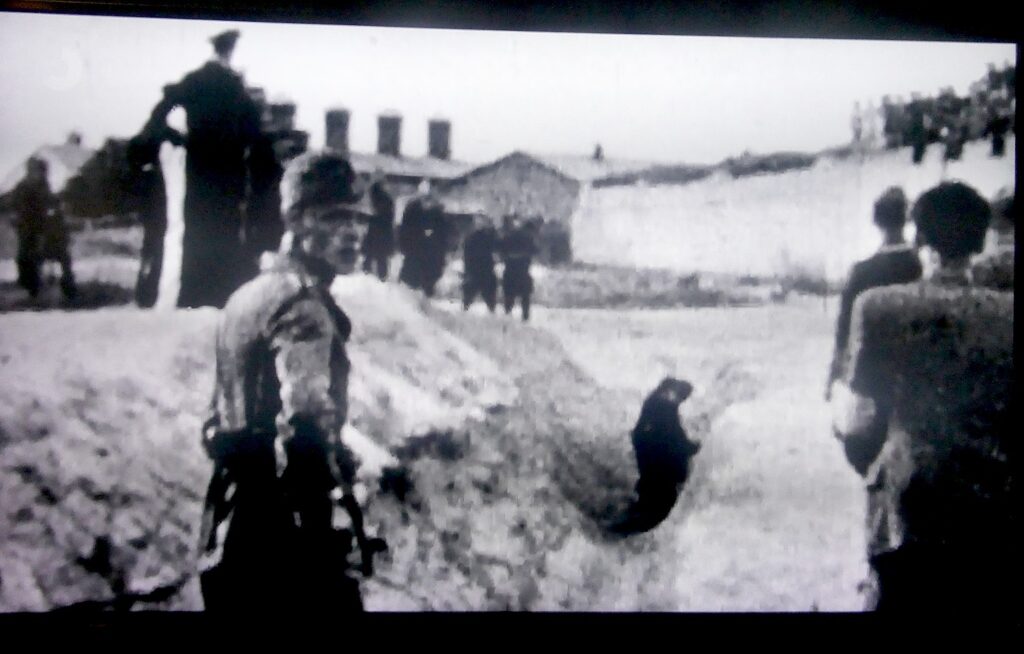

Most profound is a film that has survived showing a killing field in which the killers are so casual, even bored by the routine as villagers look on, and the four photos of Crematorium 5 smuggled out by Alberto Errera, a Jewish-Greek army officer who joined the resistance during the German occupation, assuming the name Aleksos (Alex) Michaelides. Captured, Errera was sent to Auschwitz in April 1944 and selected for the Sonderkommando. On August 9, Errera attempted an escape but was captured, tortured and killed.

Most poignant are the video testimonials of survivors describing their personal experiences.
Also on display from the Museum of Jewish Heritage collection is Heinrich Himmler’s SS helmet and his annotated copy of Hitler’s Mein Kampf, as well as an anti-Jewish proclamation issued in 1551 by Ferdinand I that was given to Hermann Göring by German security chief Reinhard Heydrich on the occasion of Göring’s birthday. The proclamation required Jews to identify themselves with a “yellow ring” on their clothes. Heydrich noted that, 400 years later, the Nazis were completing Ferdinand’s work. “These artifacts stand as evidence of a chapter of history that must never be forgotten.”
The information is presented as clearly, simply, directly, forth-rightly and in excruciatingly personal terms, but it is all still so hard to comprehend, to process, the magnitude, the scale of cruelty.
The artifacts and materials in the exhibition are on loan from more than 20 institutions and private collections around the world. In addition to the Auschwitz-Birkenau State Museum and the Museum of Jewish Heritage – A Living Memorial to the Holocaust, participating institutions include Yad Vashem in Jerusalem, Anne Frank House in Amsterdam, United States Holocaust Memorial Museum in Washington, Auschwitz Jewish Center in Oświęcim, the Memorial and Museum Sachsenhausen in Oranienburg, and the Wiener Library for the Study of the Holocaust and Genocide in London.

Auschwitz. Not long ago. Not far away. was conceived of by Musealia and the Auschwitz-Birkenau State Museum and curated by an international panel of experts, including world-renowned scholars Dr. Robert Jan van Pelt, Dr. Michael Berenbaum, and Paul Salmons, in an unprecedented collaboration with historians and curators at the Research Center at the Auschwitz-Birkenau State Museum, led by Dr. Piotr Setkiewicz.
“When we, the Musealia curatorial team set out to design the Auschwitz exhibition, we realized that we faced a difficult problem. In Auschwitz over a million people, mostly Jews, were murdered shortly after their arrival or suffered and died in unimaginable circumstances. How does one create an exhibition about such a dark chapter in human history that, in our understanding, is not long ago and happened in a place not far away? How does one make the public, that has so many opportunities to explore a great city like New York, decide that it would want to see such an exhibition? Our tools were straightforward: a narrative told through more than 700 original artifacts, 400 original images, 100 stories, made present by means of filmed testimonies and quotes – all revealing individual experiences of a history we must learn from,” said Dr. Robert Jan van Pelt, Chief Curator.
Following the New York presentation, the exhibition will tour to other cities around the world.
Visiting
You need 2 ½ to four hours to see just this exhibit (I was there five hours before I realized it). hours).
Entry is by timed ticket available at Auschwitz.nyc. Audio guide (available in 8 languages) is included with admission. Tickets are $25 Flexible Entry (entry any time on a specific day); $16 Adults; $12 Seniors and People with Disabilities; $10 Students and Veterans; $8 Museum Members.
FREE for Holocaust survivors, active members of the military and first responders, and students and teachers through grade 12 in schools located in New York, New Jersey, and Connecticut (with valid school-issued ID).
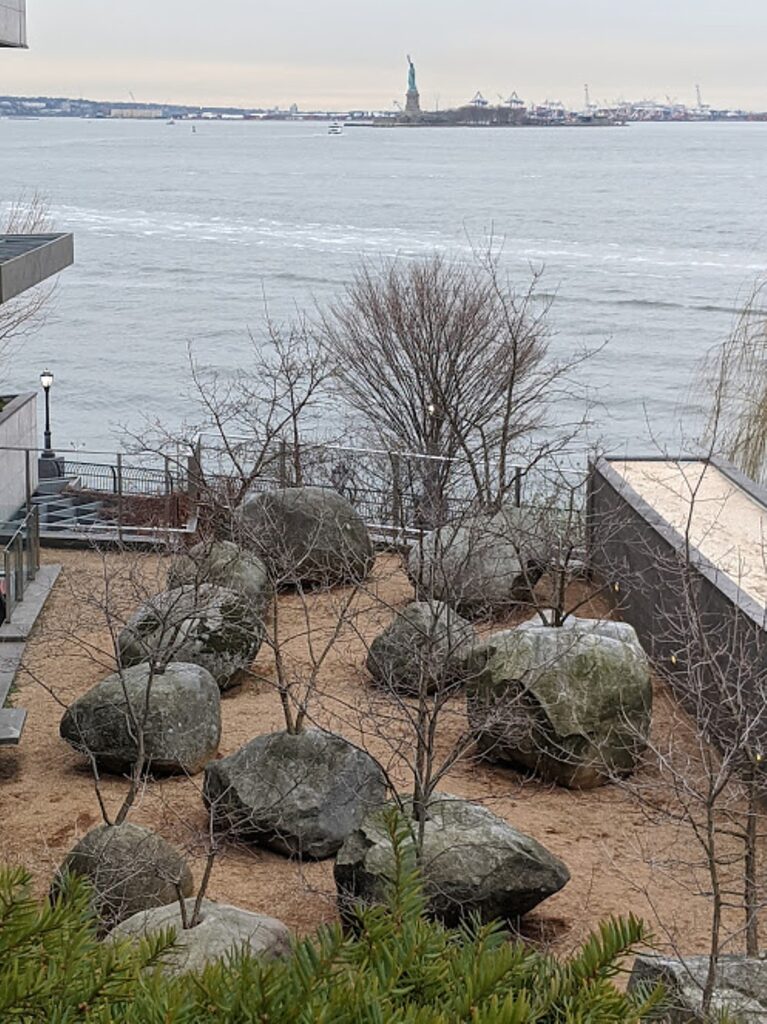

The Museum of Jewish Heritage – A Living Memorial to the Holocaust is New York’s contribution to the global responsibility to never forget. The third largest Holocaust museum in the world and the second largest in North America, since 1997, the Museum of Jewish Heritage has welcomed more than 2.5 million visitors; it maintains a collection of more than 40,000 artifacts, photographs, documentary films, and survivor testimonies and contains classrooms, a 375-seat theater (Edmond J. Safra Hall), special exhibition galleries, a resource center for educators, and a memorial art installation, Garden of Stones, designed by internationally acclaimed sculptor Andy Goldsworthy. Set in the southernmost tip of Manhattan overlooking the New York Harbor, the Museum completes the cultural and educational triad with the Statue of Liberty and Ellis Island, visible from its balcony.
The Museum also partners with Jewish Heritage Travel – offering heritage trips to Germany & France; Poland; The Baltics; Germany; Spain & France; Argentina; and India (jhtravel.org, 845-256-0197).
The Museum is closed on Saturdays, Jewish holidays, and Thanksgiving.
Museum of Jewish Heritage – A Living Memorial to the Holocaust, 36 Battery Place, New York City, 646-437-4202, mjhnyc.org.
_________________________
© 2020 Travel Features Syndicate, a division of Workstyles, Inc. All rights reserved. Visit goingplacesfarandnear.com, www.huffingtonpost.com/author/karen-rubin, and travelwritersmagazine.com/TravelFeaturesSyndicate/. Blogging at goingplacesnearandfar.wordpress.com and moralcompasstravel.info. Send comments or questions to FamTravLtr@aol.com. Tweet @TravelFeatures. ‘Like’ us at facebook.com/NewsPhotoFeatures














