by Karen Rubin
Travel Features Syndicate, goingplacesfarandnear.com
On the Centennial of passage of the 19th Amendment, also known as the Susan B. Anthony Amendment, giving women the right to vote, Donald Trump made a grand gesture with much fanfare in issuing a pardon for Susan B. Anthony, who died in 1906.
Noting she was arrested in 1872 for voting before it was legal for women to vote, he exclaimed at the White House signing ceremony, “She was never pardoned! Did you know that she was never pardoned? What took so long?”
Actually, according to those who are the caretakers of her legacy, she wouldn’t have wanted to be pardoned.
In a statement headlined, “Objection! Mr. President, Susan B. Anthony must decline your offer of a pardon today,” Deborah L. Hughes, President & CEO of the National Susan B. Anthony Museum & House in Rochester, NY, stated, “Anthony wrote in her diary in 1873 that her trial for voting was ‘The greatest outrage History ever witnessed.’ She was not allowed to speak as a witness in her own defense, because she was a woman. At the conclusion of arguments, Judge Hunt dismissed the jury and pronounced her guilty. She was outraged to be denied a trial by jury. She proclaimed, ‘I shall never pay a dollar of your unjust penalty.’ To pay would have been to validate the proceedings. To pardon Susan B. Anthony does the same.
“If one wants to honor Susan B. Anthony today, a clear stance against any form of voter suppression would be welcome. Enforcement and expansion of the Voting Rights Act of 1965 would be celebrated, we must assure that states respect the 14th, 15th, and 19th Amendments to the United States Constitution. Support for the Equal Rights Amendment would be well received. Advocacy for human rights for all would be splendid. Anthony was also a strong proponent of sex education, fair labor practices, excellent public education, equal pay for equal work, and elimination of all forms of discrimination.
“As the National Historic Landmark and Museum that has been interpreting her life and work for seventy-five years, we would be delighted to share more.”
We just celebrated the centennial of the passage of the 19th Amendment. But the journey to Women’s Right to Vote, goes back a century before, back to when Abigail Adams wrote her husband, John Adams, in 1776, “Remember the ladies.” He didn’t. The struggle began.
The journey toward Women’s Suffrage is long, and offers a long trail that can be followed, in order to experience first-hand something of what the struggle was like and pay proper respect to the Suffragists’ extraordinary courage, perseverance, and innovativeness. Here are some of the places to follow their footsteps and sense their spirit:
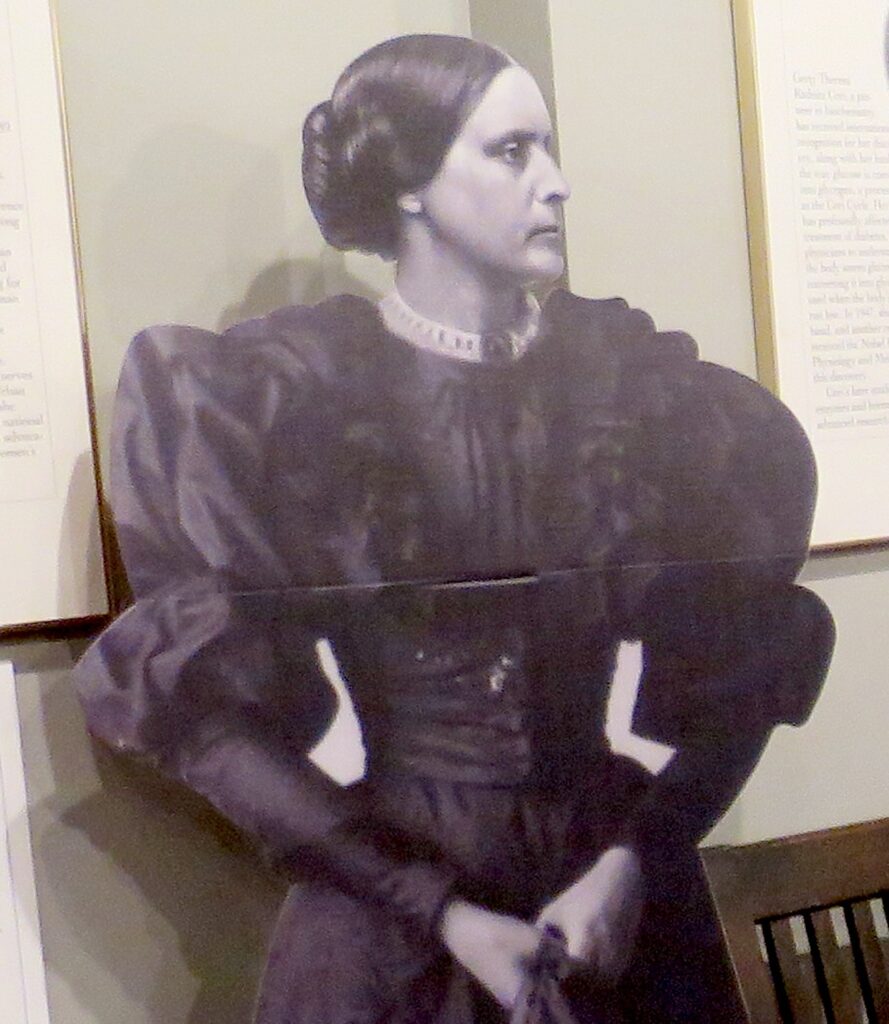

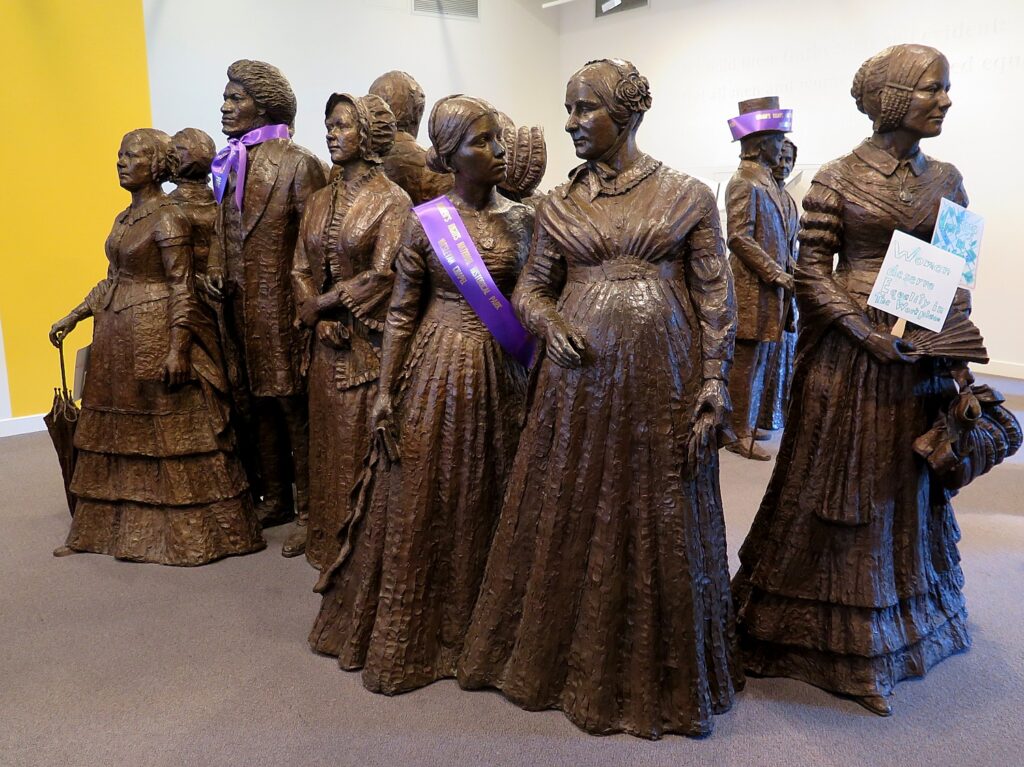
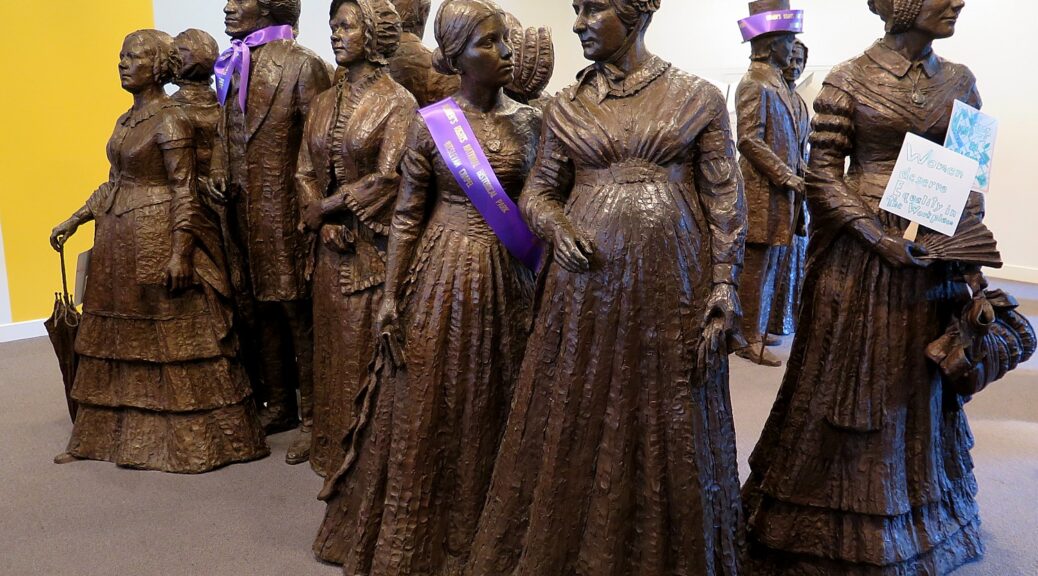
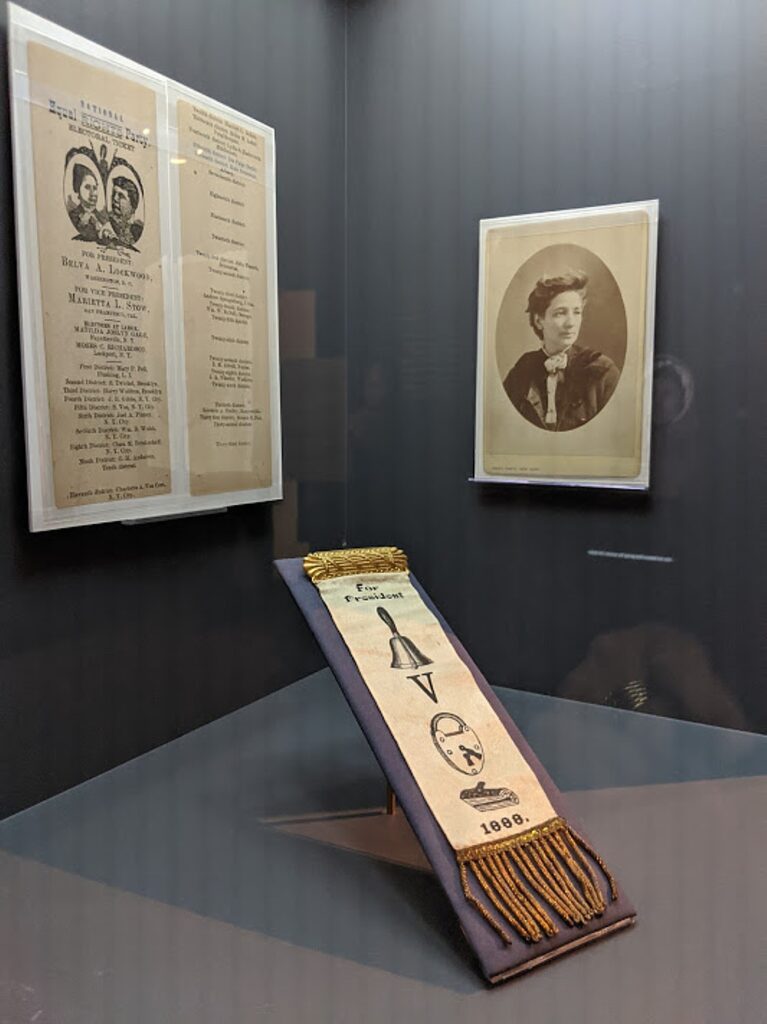
“The National Susan B. Anthony Museum & House, Rochester’s first National Historic Landmark, was home to the legendary suffragist, abolitionist and civil rights leader during her 40 most politically active years, as Visit Rochester proudly notes. “She served as president of the National American Woman Suffrage Association from her home on Madison Street. It was a hub for planning strategies, organizing campaigns, writing speeches, and preparing petitions. This was Anthony’s home base as she made countless trips throughout the United States, to Great Britain, and to Europe to support local suffrage campaigns and organize the International Council of Women.
“Walk through rooms where Anthony met often with Elizabeth Cady Stanton and other leaders of the civil rights movement. Stand in the parlor where Anthony was arrested in 1872 for the ‘crime’ of voting.
“It’s not hard to imagine Anthony enjoying her talks with the famous orator and abolitionist Frederick Douglass over cups of tea in her parlor. Upstairs in the small bedroom where Anthony died in 1906, visitors can’t help feeling some sadness knowing she never had an opportunity to cast a legal ballot. Fourteen years after her death, the 19th “Susan B. Anthony” Amendment was finally ratified and women throughout America were welcome at polling places.” (www.visitrochester.com/susanb2020)
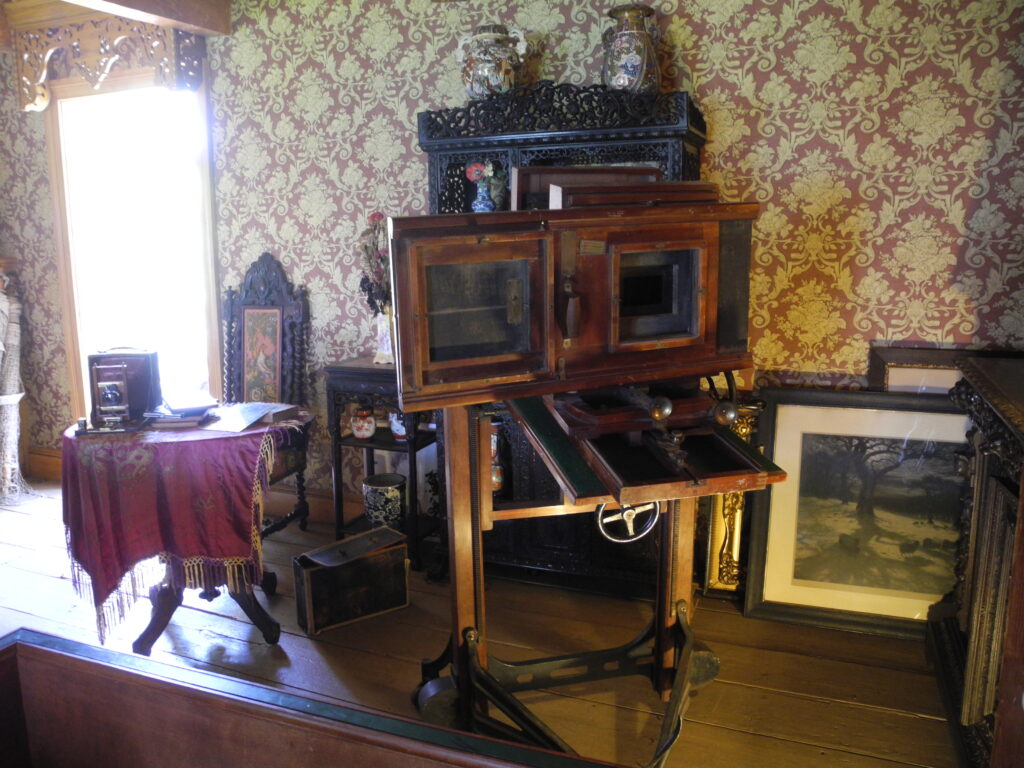
The 19th Amendment to the U.S. Constitution, also known as the Susan B. Anthony Amendment, was ratified in 1920, 14 years after Anthony died, in 1906. The house was her home from 1866 until her death here in 1906; it was the site of her famous arrest for voting in the presidential election of 1872. Her bedroom contains her original furniture, including the feather-star-pattern quilt on the bed that she made with her sister Hannah. The house is filled with photographs, memorabilia, and much of the Anthony family’s furniture. A museum room on the second floor illustrates major events of the woman suffrage movement, including extensive photographs of the people who worked so long and so hard to win voting rights for women.
National Susan B. Anthony Museum & House 17 Madison Street Rochester, NY 14608 585/235-6124, www.susanbanthonyhouse.org
You can visit the Ontario County Courthouse, the site of Susan B. Anthony’s famous trial in 1873, just a short drive from Rochester in Canandaigua,
The final resting place for Susan B. Anthony, Jean Brooks Greenleaf (former president of the New York State Woman Suffrage Association), Frederick Douglass and many other important leaders of the abolitionist and women’s rights movements is Mt. Hope Cemetery in Rochester. There are guided tours and self-guiding maps.
This year is also the 200th anniversary of Susan B. Anthony’s birth, in 1820. The daughter of a Quaker family that promoted abolition and temperance, from the age of 6 and 25, from 1826 to 1845, she lived in Battenville, Washington County, and later in Center Falls, before her family moved to Rochester. So, on the 100th Anniversary of the 19th Amendment, Governor Andrew M. Cuomo announced an effort to stabilize and preserve Susan B. Anthony’s childhood home on Route 29 in Battenville. The work at the 1832 two-story brick home where Anthony lived from ages 13 to 19, is expected to be completed by September.
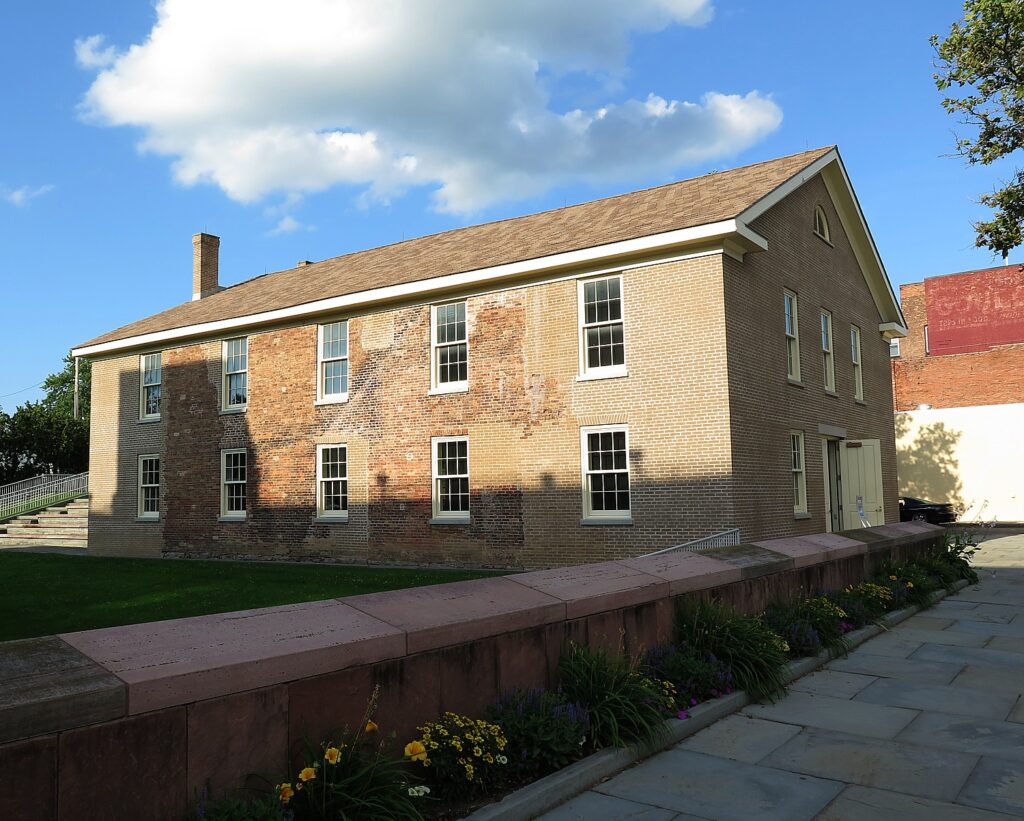

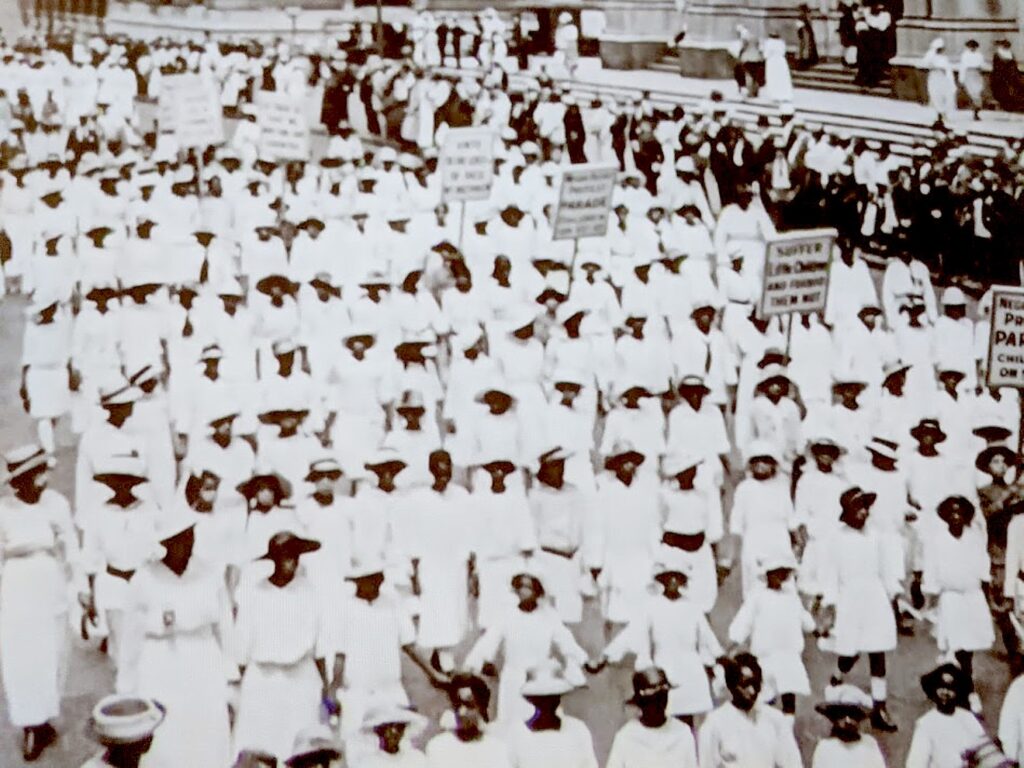
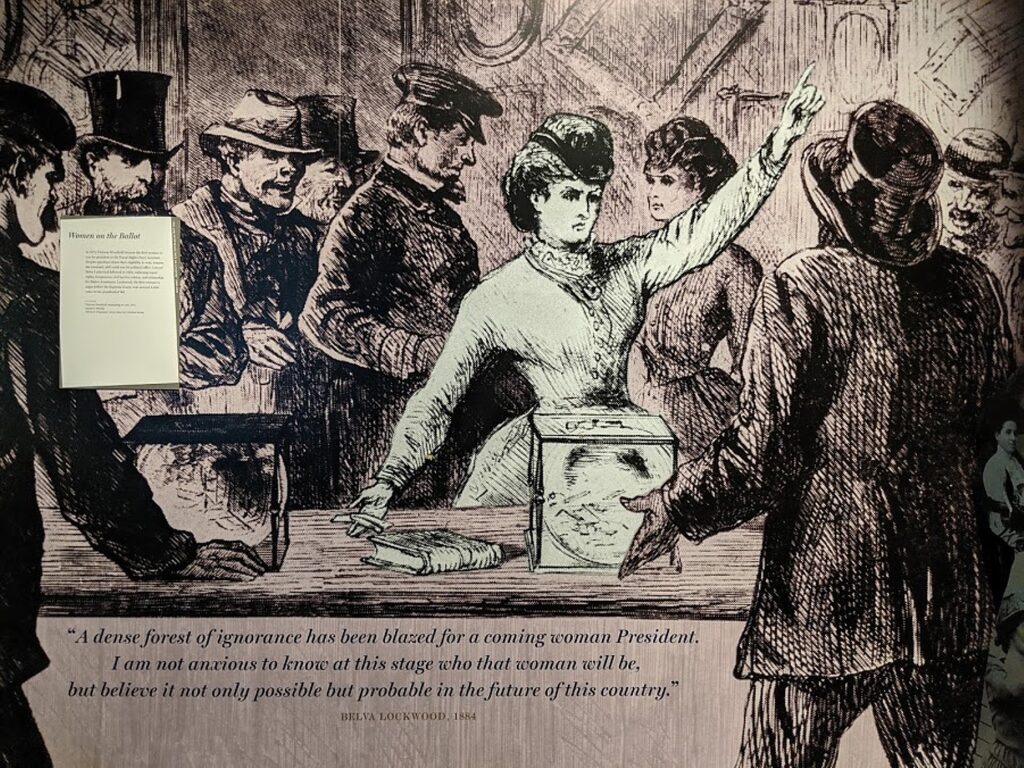
For many, the journey to women’s rights begins at The Women’s Rights National Park in Seneca Falls, New York, ostensibly the “birthplace” of the women’s suffrage movement, where the 1848 Convention offers the most identifiable launch-pad for the (ongoing) struggle. The actual exhibit, created during Ronald Reagan’s term, is disappointing, but you can visit Wesleyan Chapel where the convention took place.
The women organized the convention and prepared a document laying out their grievances, the “Declaration of Sentiments,” which was modeled after the Declaration of Independence and mimicked its language in describing the tyranny under which women were forced to live. The document outlined 11 resolutions to “declare our right to be free as man is free…” At the close of the convention, all the resolutions passed with the exception of the ninth resolution, guaranteeing a woman’s right to vote.
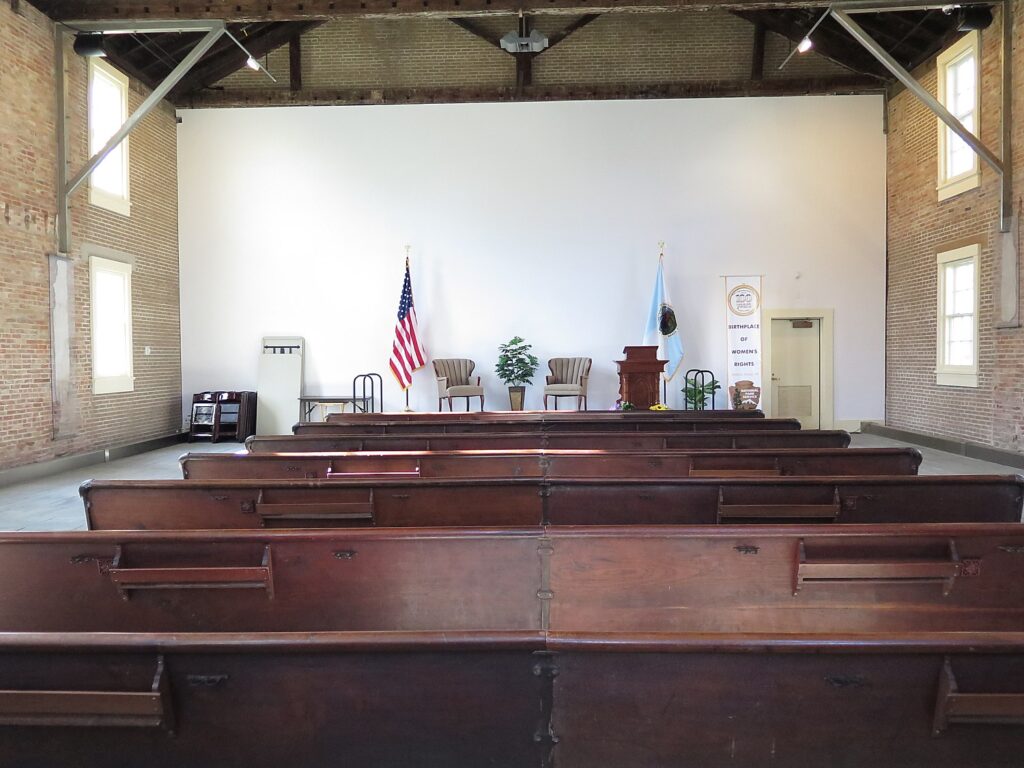

Out of the 300 people who attended (the chapel had a balcony then; men were allowed to attend the second day), only 100 signed the Declaration of Sentiments, and of these, 68 were women and 32 were men). (Forty percent of those who attended were Quakers, who already accommodated more equal roles for women.)
The history of the Wesleyan Chapel can be a metaphor for the ambivalence of American society to women’s rights: From 1843-1871 it was chapel, then an opera house/performing arts hall; then a roller skating rink, a movie theater (in 1910s), then a Ford dealership, and ironically enough, finished its days as a laundromat before facing a wrecking ball. “Women fought to save the building,” the Ranger says. It was only in 1982, during the Reagan Administration, that it was turned into a national park.
At this writing, with the COVID-19 restrictions, the Visitor Center is only open Tuesday and Thursday (10-4), historic homes are closed, but Ranger Programs have resumed outdoors and the grounds are open daily. Check the site for updates.
Women’s Rights National Historical Park, a National Park Service site, 136 Fall Street, Seneca Falls, NY 13148, 315-568-0024, www.nps.gov/wori/index.htm
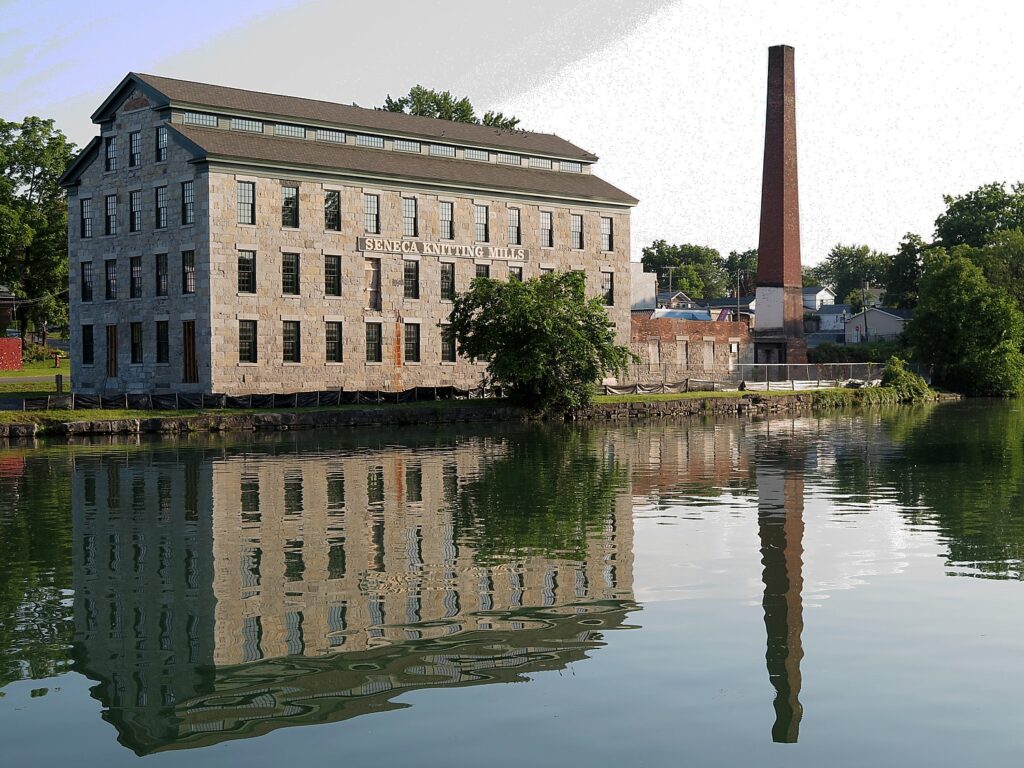

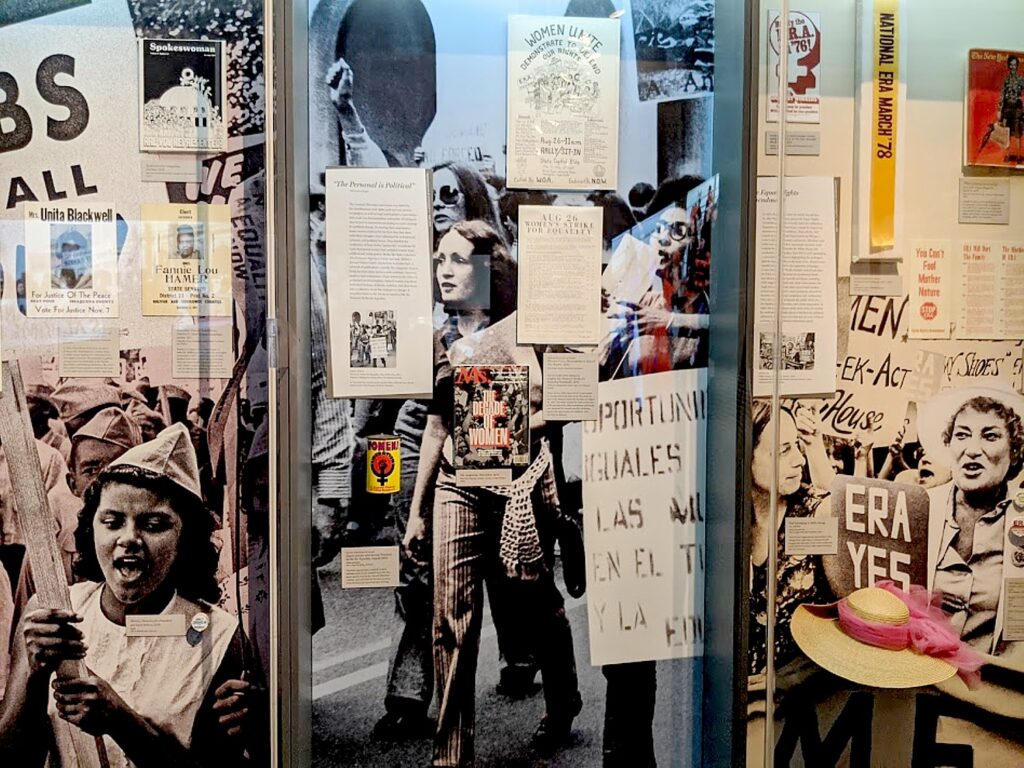
In contrast, The National Women’s Hall of Fame, now in its new location in the rehabilitated 1844 Seneca Knitting Mill building, remains the more meaningful and inspiring exhibit, putting faces on the long, long diverse parade of women, in the place “where it happened.” Indeed, women factory workers, fired for demanding equal pay, provided the seed for the convention (which initially did not seek women’s vote, but rather equal rights to pay, property and custody of children).
The Hall, housed up until last fall in a former bank building, only opened in the new location this spring, but immediately forced to shut down due to the coronavirus.
It has reopened, with timed reservations. Among the new features: a new Hall of Fame display listing Inductees and their areas of accomplishment; a section called “Why Here?” highlighting why all of this history happened in Seneca Falls and the story of the Seneca Knitting Mill and the women who worked there.
“We invite visitors to delve into the history of what happens when women innovate or lead with an interactive exhibit that challenges widely-held assumptions. Visitors can ‘weave’ themselves into the story in a participatory exhibit, and we ask visitors for their own stories of women who have inspired them. The exhibits encourage visitors to engage in creating our future and to understand the possibility of a world where women are equal partners in leadership.” (See the Women of the Hall, the inductees into the Hall of Fame: https://www.womenofthehall.org/women-of-the-hall/)
National Women’s Hall of Fame, 1 Canal St., Seneca Falls, NY 13148, 315-568-8060, Womenofthehall.org; make reservations, https://national-womens-hall-of-fame.myshopify.com/products/national-womens-hall-of-fame-admission
Visit the home of Matilda Joslyn Gage, who was important to developing the arguments for women’s rights, but has too often been overlooked because she did not attend the Seneca Falls convention in 1848. Gage was a noted speaker and writer on woman’s suffrage and an abolitionist. She and her husband used their home as a station for the Underground Railroad to help escaped slaves. She worked closely with prominent women’s rights leaders Susan B. Anthony and Elizabeth Cady Stanton, often holding meetings in her home. Her lifelong motto and gravestone inscription reads “There is a word sweeter than Mother, Home or Heaven; that word is Liberty.”
Less well known about Matilda Gage is that many of her ideas for women’s rights came from the Iroquois Indians, who had a maternal society where women could be chiefs, own property and have custody of their children. Also, she was the mother-in-law of L. Frank Baum, author of “The Wizard of Oz.” The Gage Center is also an educational resource for discussion and dialogue about the human rights issues to which she dedicated her life. (210 E. Genesee Street, Fayetteville, matildajoslyngage.org
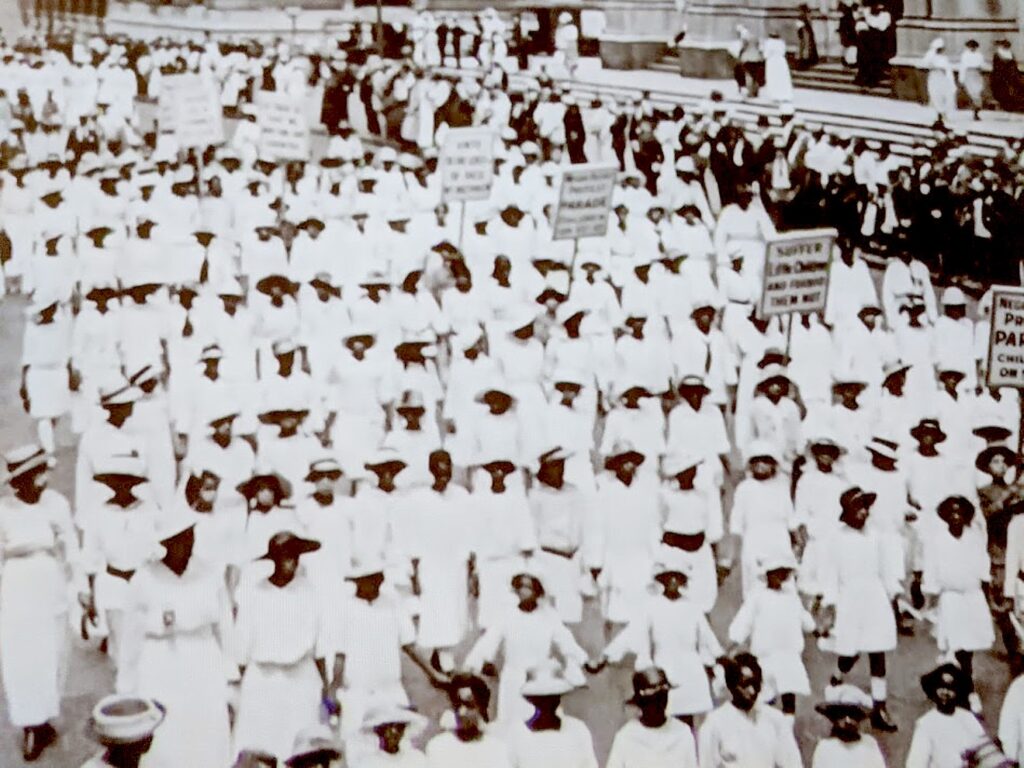

Closer to home, you can join the long women’s march to voting rights at The New-York Historical Society when it reopens its indoor exhibits on Friday, September 11, to see the temporary exhibition Women March. (See www.nyhistory.org/exhibitions/women-march). Check the site for opening hours; timed Tickets are required. More details: www.nyhistory.org/safety. (New-York Historical Society, 170 Central Park West, New York, NY 10024, 212-873-3400, www.nyhistory.org).
______________________
© 2020 Travel Features Syndicate, a division of Workstyles, Inc. All rights reserved. Visit goingplacesfarandnear.com, www.huffingtonpost.com/author/karen-rubin, and travelwritersmagazine.com/TravelFeaturesSyndicate/. Blogging at goingplacesnearandfar.wordpress.com and moralcompasstravel.info. Send comments or questions to [email protected]. Tweet @TravelFeatures. ‘Like’ us at facebook.com/NewsPhotoFeatures