by Karen Rubin
Travel Features Syndicate, goingplacesfarandnear.com
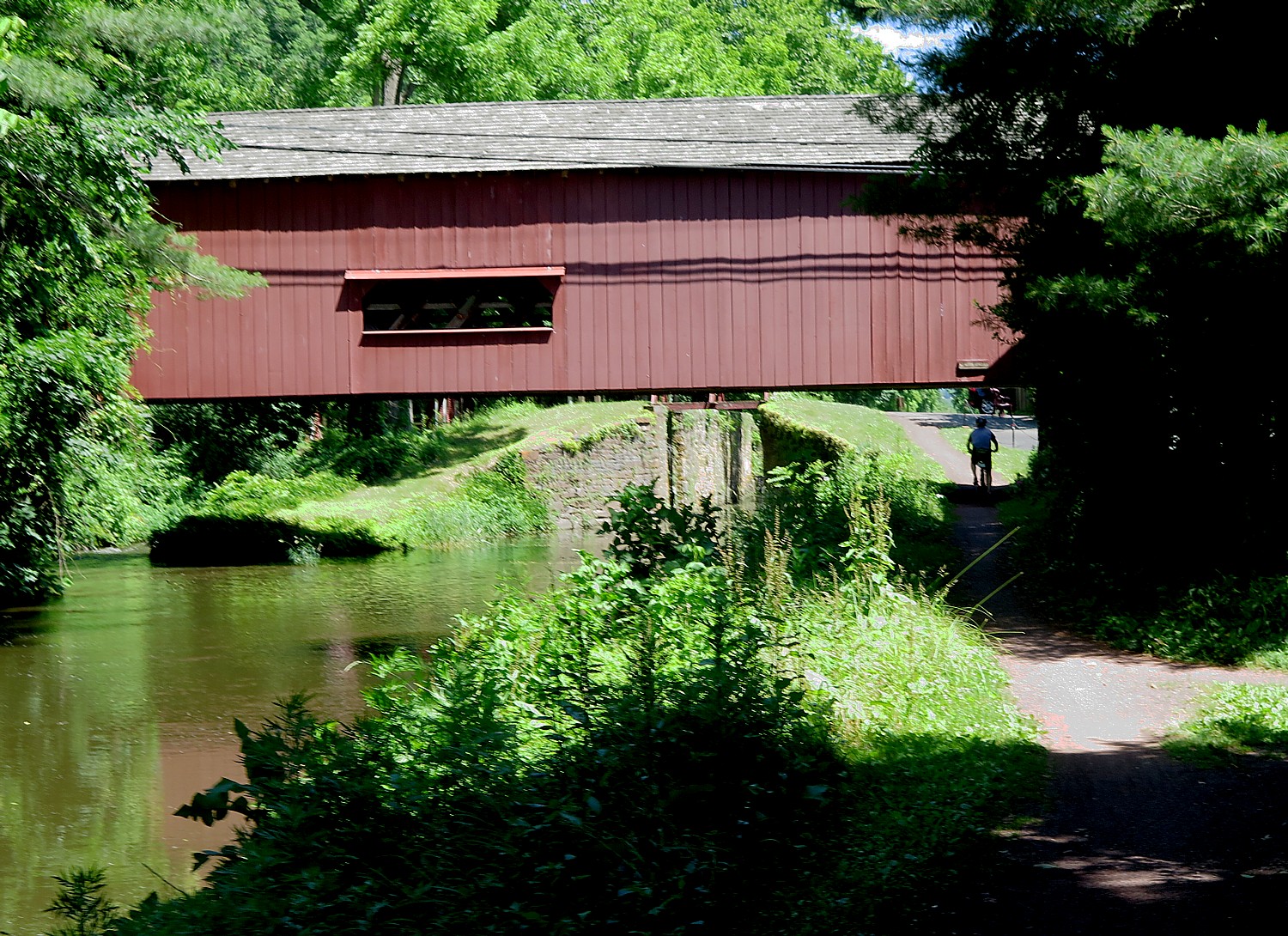
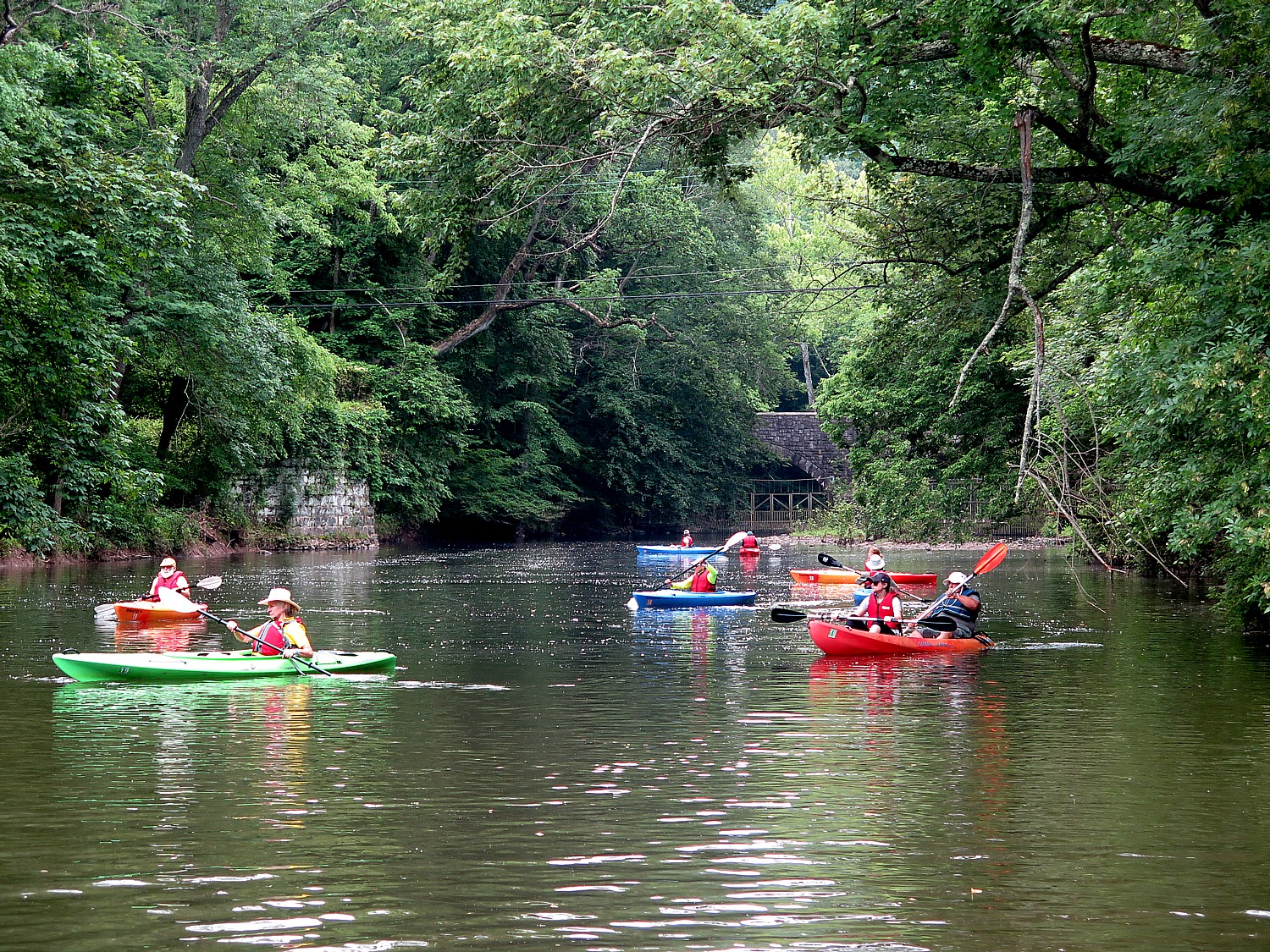
On the fifth and last day of our 160-mile Rails-to-Trails Conservancy Sojourn on the Delaware-Lehigh Trail, the 37-mile bike ride back to the Hugh Moore Park in Easton along the Pennsylvania side of the river, is absolutely beautiful.
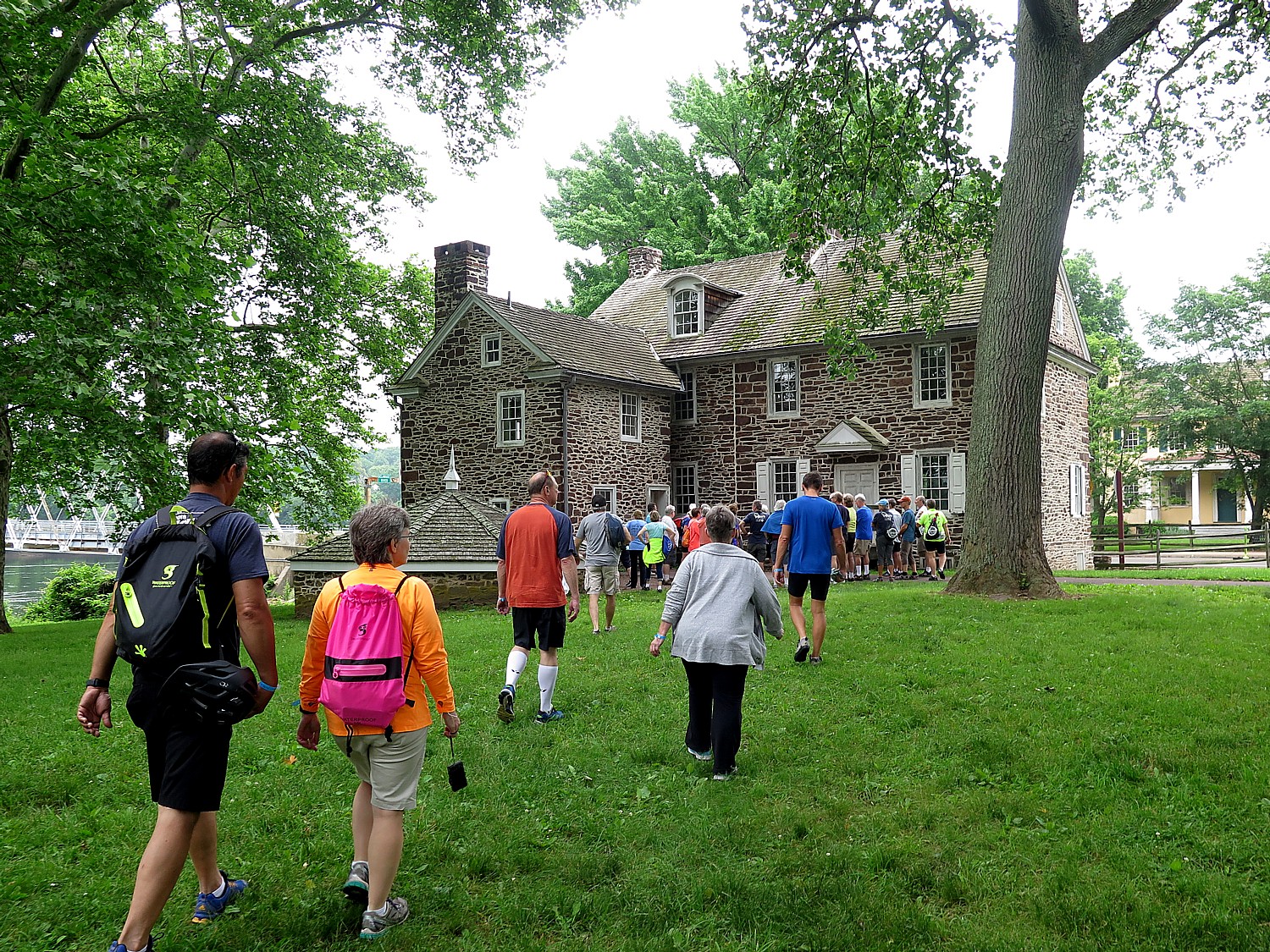
After spending our layover day exploring Washington Crossing State Park, our last night together was a true banquet (grilled steaks! beer!) served under a gorgeous pavilion at Bowman Hill, followed by a talent show by some of the more intrepid Sojourners which is surprisingly great in addition to being pure fun.
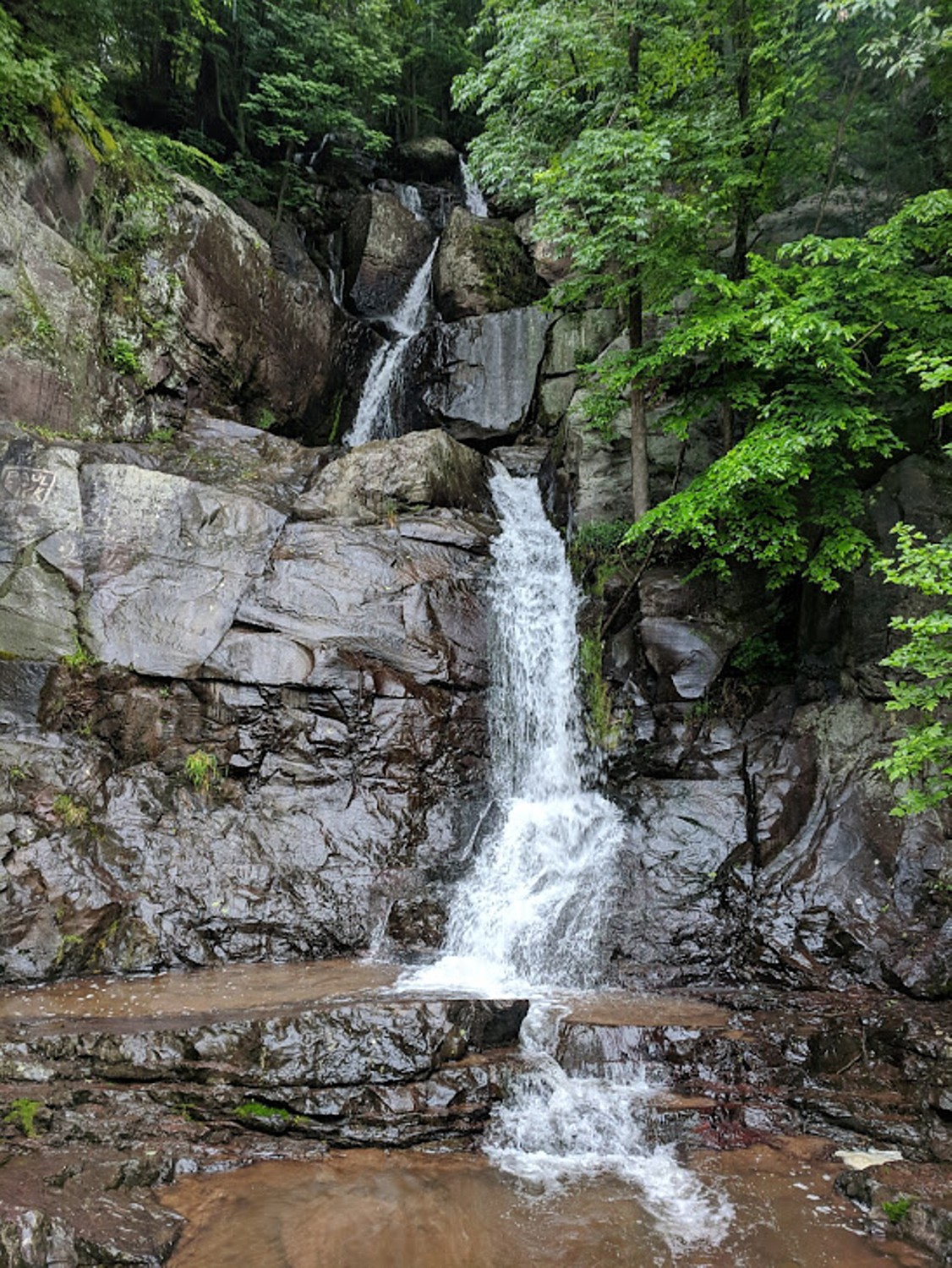
Biking back along the Delaware Canal State Park section of the D&L Trail, with its historic locks and bridges, I savor these views of bucolic villages and landscape.
On Day 3 of our Sojourn, we also got to experience part of another of my favorite greenways, the Delaware-Raritan Canal trail on the New Jersey side. Rails-to-Trails Conservancy’s TrailNation website offers an itinerary, but you can do a fabulous daytrip, starting on the trail just across from Princeton University, and biking north. You can ride 20 miles to the end, at Edison, NJ (or turn back when you feel you want to). I find this portion of the trail, which follows the canal, to be the most picturesque, particularly in fall. There are also places to rent a kayak or a canoe and you may even see the university crew team.
This Sojourn on the Delaware-Lehigh is a sentimental favorite for Rails-to-Trails Conservancy – returning to the trail that was the focus of the very first Sojourn, in 2002.
For the past 12 years, the annual Sojourn has been RTC’s way of celebrating accomplishments in repurposing disused rail lines and canal towpaths for biking, walking and recreation, as well as to showcase gaps in trails that its advocacy works to fill. This year’s Sojourn was a major celebration of the opening of a new bridge across the river at the village of Jim Thorpe in Pennsylvania, helping to complete the 160-mile long along the Delaware-Lehigh Trail.
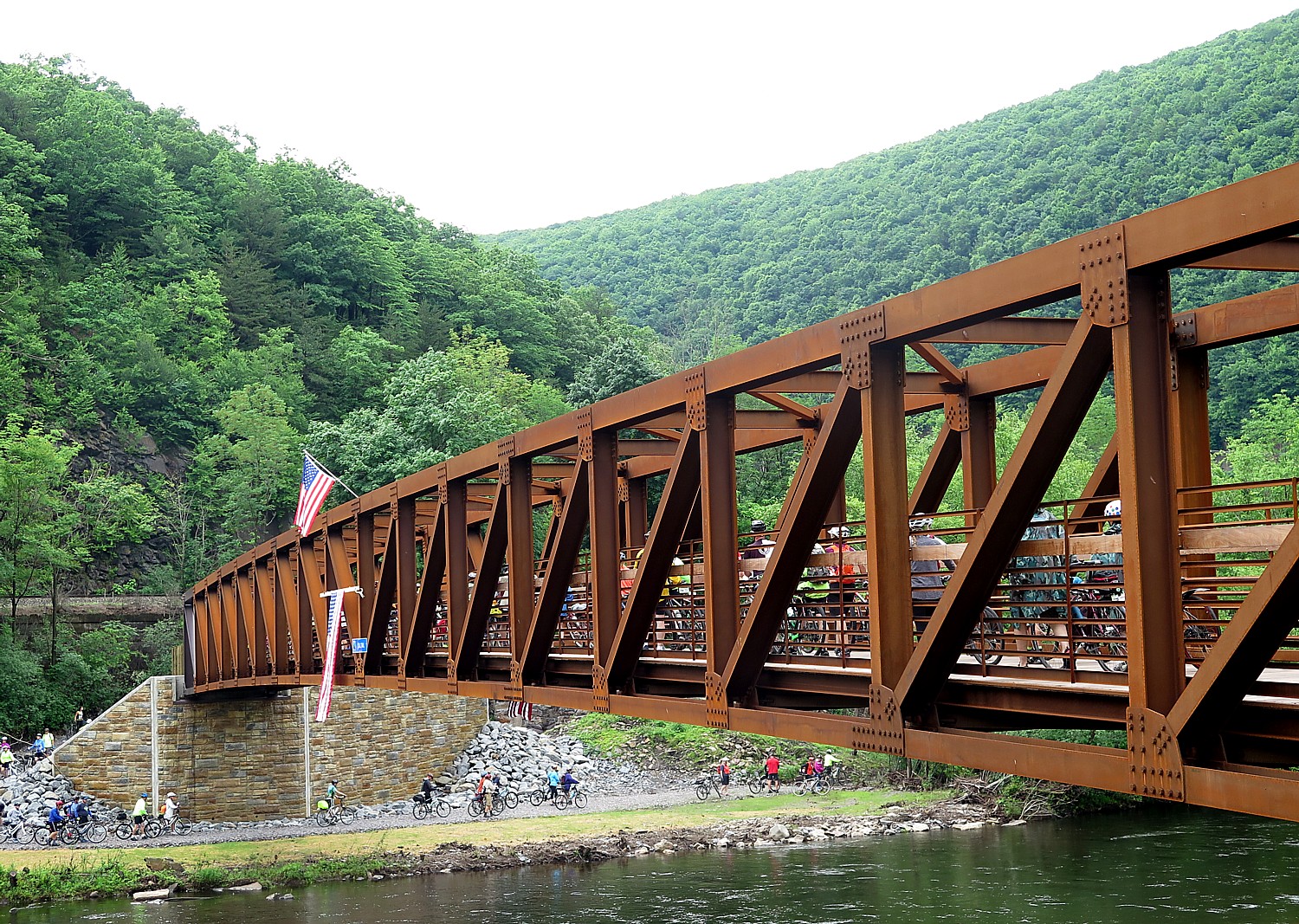

“Way back in 2002, the Rails-to-Trails Conservancy helped draw attention to our burgeoning efforts to build the D&L Trail from Wilkes Barre to Bristol, Pennsylvania. Today, as we welcome Sojourners back, the D&L Trail is about 92 percent complete and we hope to be fully connected by 2022,” Elissa Garofalo, the executive director of the Delaware & Lehigh National Heritage Corridor, wrote the Sojourners.
“While we are still a work in progress, the route of the D&L is one that celebrates the legacy of innovation, risk, resilience and beauty of America’s 19th century Industrial Revolution. As you travel our mine-to-market path, I hope you will revel in the wonders that my co-workers and I are fortunate to help celebrate, preserve and inspire connections every day.” (http://delawareandlehigh.org/).
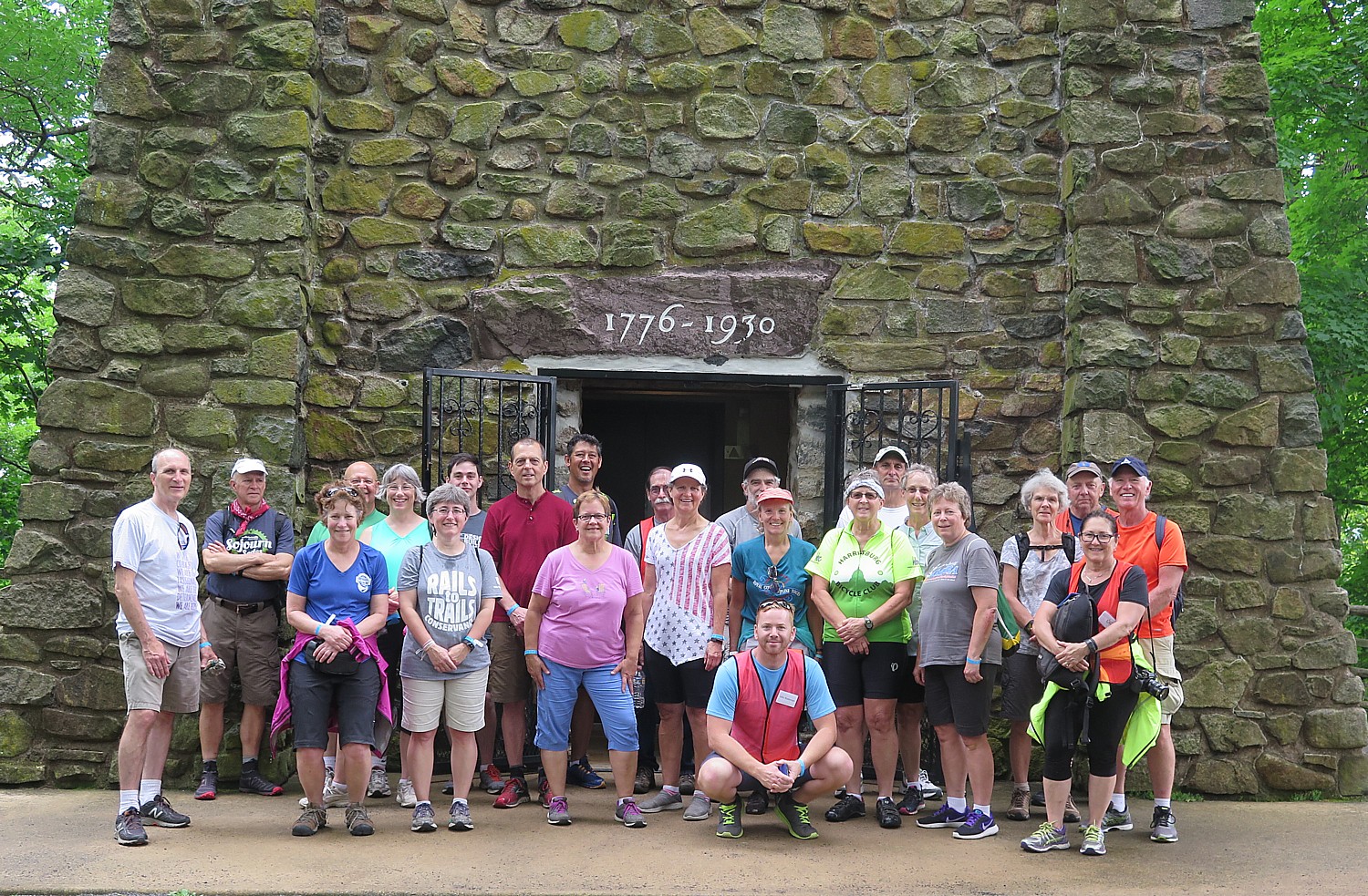
But the 300 Sojourners – so many who have done multiple trips (I’ve done three, including two on the Great Allegheny Gap) – were disheartened to learn this year’s fully supported five-day bike/camping tour was Rail-to-Trails Conservancy’s last, at least for now. (It is hoped local trail groups or biketour companies would host similar annual supported tours). The reason? So the nonprofit organization can concentrate/focus on advocacy of preserving and repurposing trails – TrailNation –some 10,000 miles of multi-use trails, already. (You can find these trails on Rails-to-Trails Conservancy’s site, traillink.com.)
The urgency has come because the Trump Administration has pulled funding that had been available for more than a decade to help communities take back these resources for their own benefit – including local economic revitalization as well as improving the quality of life and healthful outdoor recreation – and changed regulations to make it harder for communities to take back these trails.
For example, an important tool for advocates seeking to acquire and repurpose abandoned rail corridors has been Railbanking, a federal statute which provided the mechanism for communities across the country to convert former railways into thriving rail-trails that boost local economies and create healthier, more vibrant communities while protecting rail corridors for generations to come. The process requires complicated agreements between the railroad owners of the corridor and local trail managers and necessitates multiple extensions beyond the six-month period provided in the law. Now the Trump Administration’s Surface Transportation Board (STB) is proposing to significantly restrict the timeframe for these negotiations.
Rails to Trails Conservancy has its work cut out for it – no wonder the non-profit organization, advocates for its 160,000 members and supporters, 31,000 miles of rail-trails and multi-use trails, and more than 8,000 miles of potential trails waiting to be built, is focusing on advocacy and activism. The Trump Administration has done everything possible to reverse course on repurposing obsolete railways and canalways to multi-purposed trails that provide alternatives to climate-choking cars and already strapped public transportation (largely in response to donors with a stake in fossil fuels like the Kochs who are spending their lobbying dollars to kill transit projects, see New York Times).
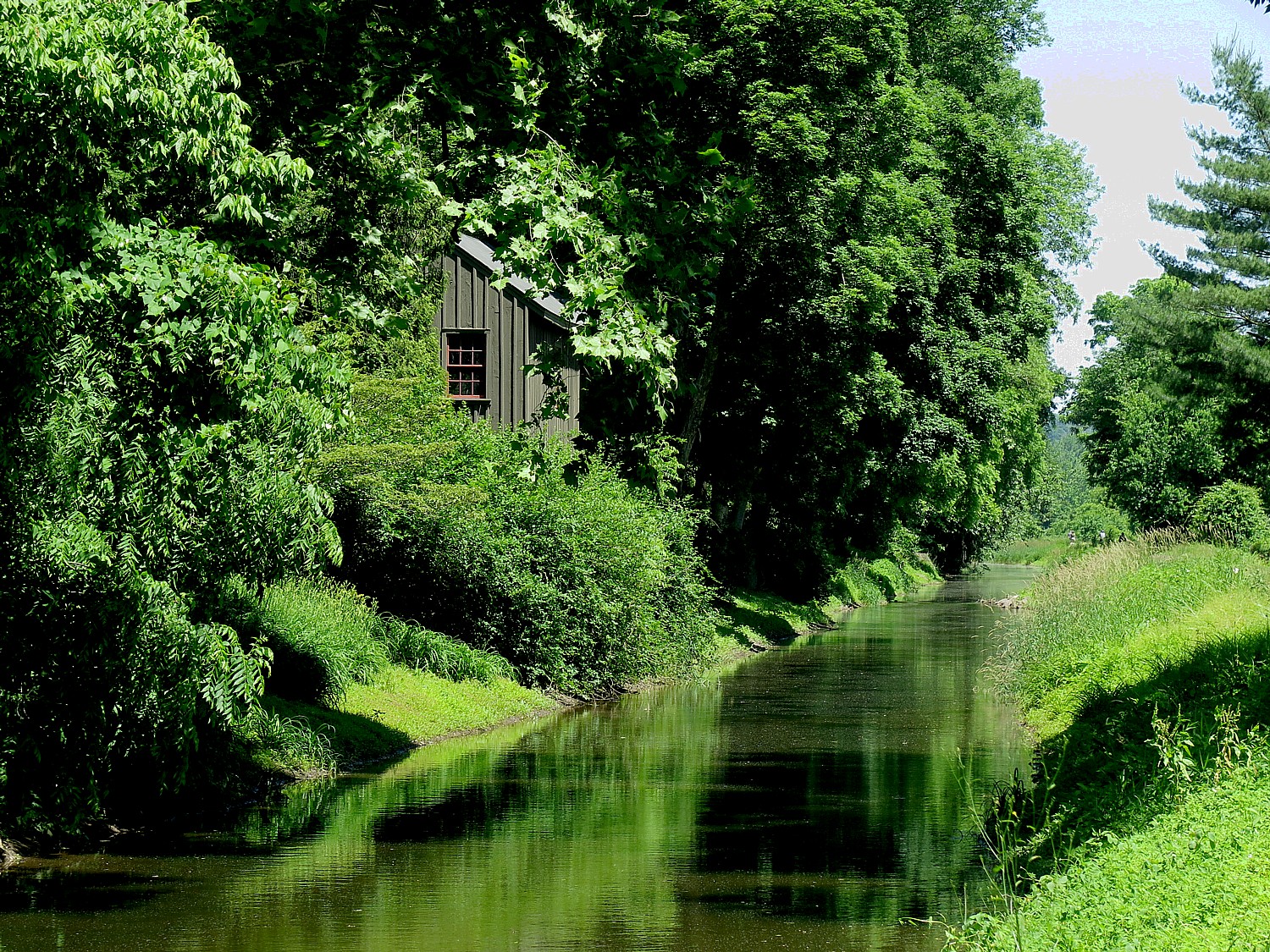

It is ironic because, as we see as we bike, these communities were originally built in the service of a fossil-fueled economy and have collapsed largely because of changing technology. The Trump Administration is desperately trying to rekindle that economy and quite literally, force society back a century instead of propel us forward into the 21st century.
But as Rails-to-Trails Conservancy points out, promoting biking and walking infrastructure can be an answer to so many of the ills facing communities today. According to the Rails-to-Trails’ website:
Traffic Congestion: Biking and walking infrastructure can be a solution to local traffic congestion. Pilot studies have proven that people will choose biking and walking over driving for daily trips if the infrastructure is in place. In Minneapolis, Minn., for example, 28% of all trips don’t rely on a car (Nonmotorized Transportation Pilot Program: 2014 Report).
Building more highways and roads has failed to stem the rise in congestion. Between 1982 and 2011, the number of hours of vehicle delay in urban areas rose 360%, even as the number of highway and road miles increased by 61% (Texas A & M’s Annual Urban Mobility Report).
Economic Development: Trails boost the desirability and value of the homes and neighborhoods they connect to. Prospective homebuyers in Ohio, for example, were willing to pay an additional $9,000 to be located 1,000 feet closer to a trail, according to 2012 study by University of Cincinnati School of Planning.
Trails and pathways have been proven to increase activity in downtown business areas by making it easier for people to get to stores without having to worry about parking and traffic. A study found the business occupancy rate in downtown Dunedin, Fla. increased from 30% to 95% with the opening of the nearby Fred Marquis Pinellas Trail. (Investing in Trails).
Transportation Patterns: Americans are already beginning to shift away from cars for daily transportation in favor of biking, walking and transit systems. This generation of young Americans is the first since the invention of the automobile to be less likely to get a driver’s license than their parents. (See: Transportation and the New Generation, 2012).
More than one-quarter of all trips we make are less than a mile—an easy walking distance—and nearly one-half are within three miles—an easy biking distance. Trail networks create the infrastructure that encourage and enable people to walk and bike as part of their daily lives.
Biking and walking is not just “an urban trend.” RTC’s 2012 report, Beyond Urban Centers showed that the share of work trips made by bicycle in small towns is nearly double that of urban centers.
Social Equity: Comprehensive trail systems can bridge gaps within and between communities, creating new access to jobs, physical activity and outdoor recreation-offering connected active transportation options to the more than 90 million Americans without a car.

Health: Obesity is the most pressing public health crisis of our age, particularly among children. Obesity costs America more than $190 billion in reactive healthcare spending each year. Making walking and biking a regular part of daily activities by providing convenient pathways is one of the most cost-effective ways to combat physical inactivity – something we cyclists on the Sojourns saw constantly.
When people have safe places to walk within 10 minutes of their home, they are one and a half times more likely to meet recommended activity levels than those who don’t. Comprehensive trail systems can give people new access to outdoor recreation opportunities.
Protecting the Environment: The environmental benefits of green infrastructure are strongest when open spaces are connected. Trail networks contribute to a healthy environment by protecting precious open space while encouraging active modes of transportation that reduce air pollution, traffic congestion and climate change.
The Beauty of Bike Tours
Bike tours are my favorite way to travel these days.
Biking gives you a sense of place – you travel at a speed to see a lot, but also slow enough, with no barriers to really focus on small and big details. You can stop and literally smell roses (or photograph wild flowers), or chat with the fellows in period dress at the historic lockmasters house in Freemansburg, take time to review a poster showing migration patterns of birds. Camping makes a big difference in the experience.
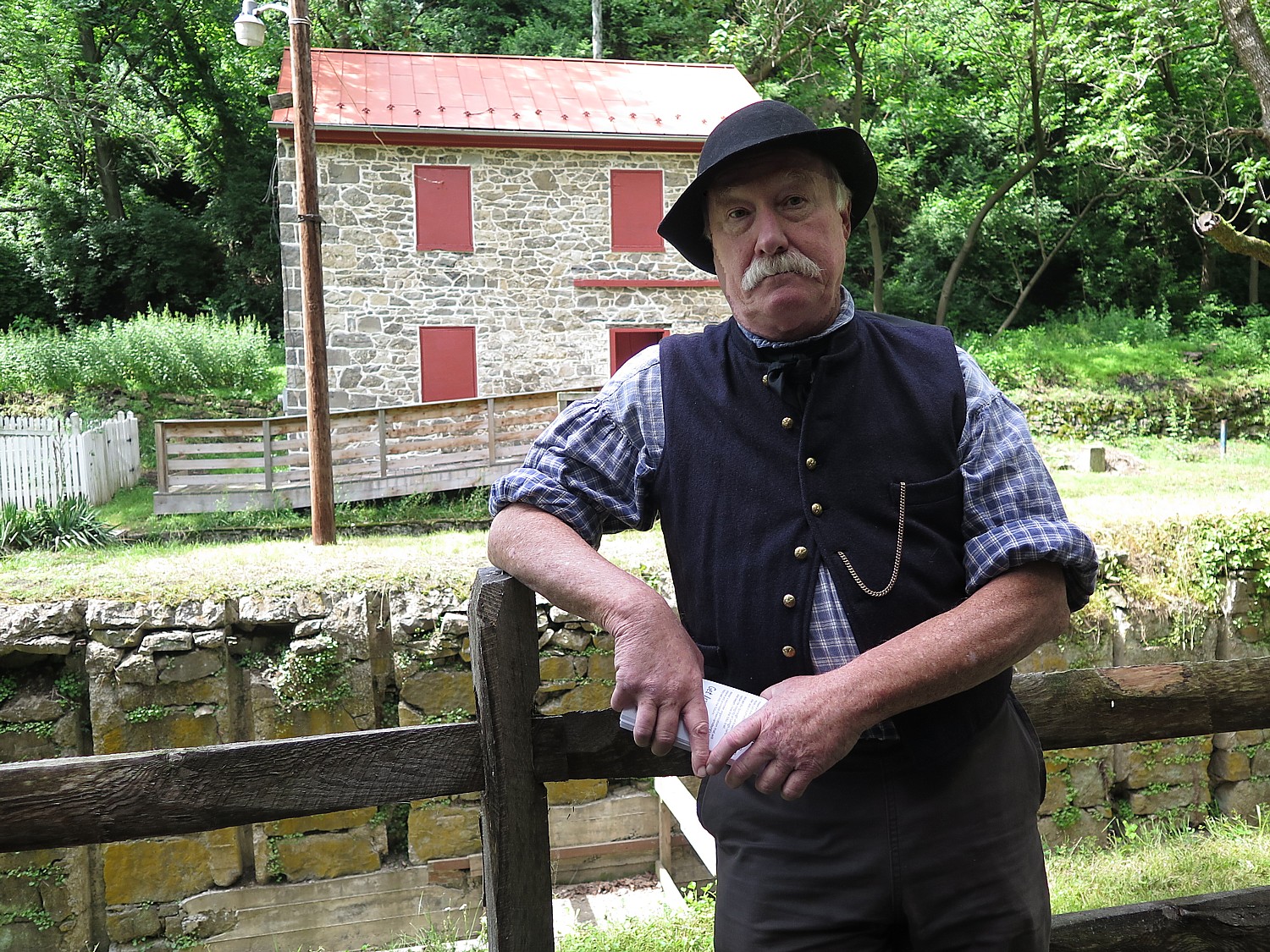

There are private bike tour companies that service many of these trails apart from these organized rides, notably Wilderness Voyageurs (which operated Rails to Trails Conservancy’s Sojourns in the past, and is offering five-day trips on the Erie Canal and offers trips on the Katy Trail in Missouri, www.wilderness-voyageurs.com) that offer these itineraries as supported rides, most typically with inn-to-inn accommodations. Road Scholar offers all-inclusive bike trips geared to seniors (www.roadscholar.org)
There are also outfitters, like Pocono Bike, that provide shuttle service to take you back to a starting point for hub-and-spoke kind of itineraries (which works well at Washington’s Crossing and the Jim Thorpe, where there are lovely inns in a most charming town). Pocono Bike offers full day, half-day, as well an overnight stay in historic downtown Jim Thorpe. Convenient access points allow for one way rides up to 36 miles, while two and four day overnight getaways feature up to 138 miles of trail through the D&L National Heritage Corridor (stunning in the fall foliage). (A four-day inn-to-inn bike trip goes from Jim Thorpe to Washington’s Crossing; the company also offers whitewater rafting trips and “pedal & paddle” trips. https://poconobiking.com/the-trail/ 800-whitewater.)
But these large-scale programs, organized around groups like Rails-to-Trails Conservancy and Parks & Trails NY, which bring together hundreds of people from all over the country, even the world, add a new and marvelous dimension to the experience – a sense of community, especially because of the opportunity to do supported camping. And these group programs are also organized with so many other features – special activities like entertainment and tours, museums and attractions stay open for us, put on special guides, and whole communities who come out onto the trail to welcome us. Not to mention putting the trip in reach of many more people because they tend to have a modest per diem cost (about $125 per day including most meals).
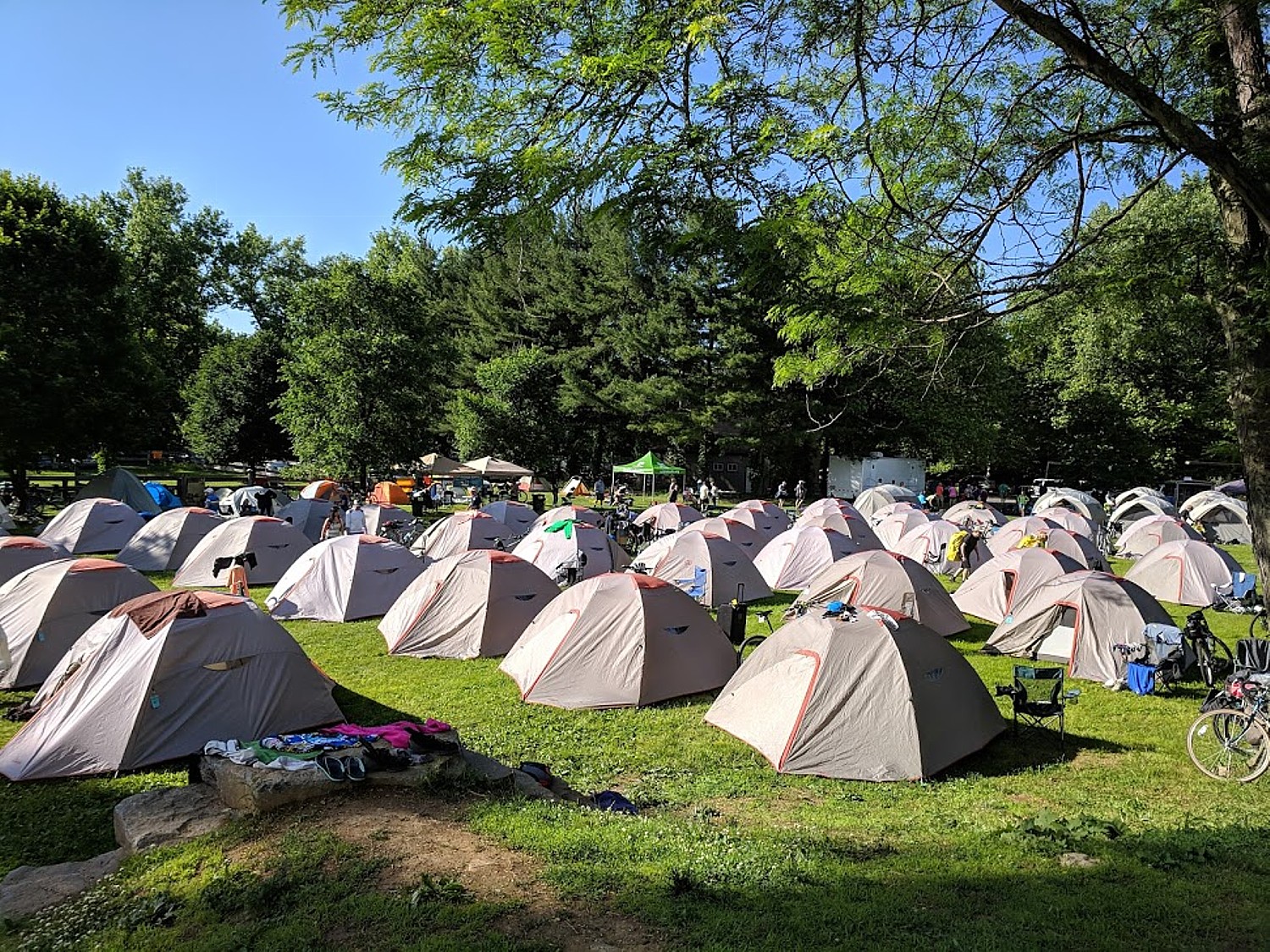

Rails to Trails Conservancy is holding out the possibility that the local trail alliances will host their own trips, either as day trips, hub-and-spoke or multi-day. Indeed, there are organizations that do annual cross-state itineraries (not necessarily on trails but on roads): in Maine (Bike Maine is taking reservations for its Sept . 7-14, 2019 ride, 207-623-4511, ride@bikemaine.org, ride.bikemaine.org), or agencies such as Missouri State Parks which offers an annual supported ride along the Katy Trail. New York State’s Parks & Trails NY (518-434-1583, www.ptny.org) does the sensational eight-day, 400-mile Cycle the Erie biketour from Buffalo to Albany, which to my mind, offers the best panorama to tell the story of how America came to be (“400 miles and 400 years of history”).
TrailNation
Giving up operating the annual Sojourn, however, will allow Rails-to-Trails to concentrate on its TrailNation work so that many more communities have access to trails. These TrailNation projects take an innovative approach to how trails and active transportation systems are built—from concept to implementation— by demonstrating the power of trails to create healthy, thriving communities. Rails-to-Trails works with local advocacy groups, offering political, financial and technical expertise. For example (from RTC’s website):
Baltimore Greenway Trails Coalition: A game-changing urban trail network that will link three existing Baltimore City trails to form a 35-mile loop connecting the city’s diverse neighborhoods and natural features with the downtown core. When complete, this project—a partnership between RTC and Bikemore—will transform the public realm by opening up bike and pedestrian access to major civic institutions and destinations around the city, and provide equitable, low-stress access to open space, transportation and recreation. Only 10 additional miles are needed to close critical gaps (https://www.railstotrails.org/our-work/trailnation/baltimore-greenway-trails-coalition/).
Bay Area Trails Collaborative, consisting of some 36 organizations, agencies and businesses, is working to develop an ambitious 2,700-mile regional trail network that will connect the San Francisco Bay Area—its trails, people and places—in innovative new ways. The regional trail network the Collaborative is working to create will provide safe biking and walking routes for millions of people across nine counties to get to jobs, parks, shopping areas, educational institutions and cultural and civic sites (https://www.railstotrails.org/our-work/trailnation/bay-area-trails-collaborative/).
Capital Trails Coalition is working to create a 676-mile network of multiuse trails throughout the Washington, D.C. metropolitan region. RTC is a founding partner in this coalition which was initiated by the Washington Area Bicyclist Association (https://www.railstotrails.org/our-work/trailnation/capital-trails-coalition/)
The Circuit Trails: An innovative, regional urban trail network that is connecting people of all ages to jobs, communities and parks in the nine-county Greater Philadelphia-Camden, NJ, region will encompass 800 miles of trails on both sides of the Delaware River by the time of the project’s completion in 2040, and more than 50 percent of the region’s population—over 3.1 million people—will live within a mile of the trail network.
Industrial Heartland Trails Coalition, comprising more than 100 organizations, and led by the Pennsylvania Environmental Council, the National Park Service and RTC, is working to establish the Industrial Heartland as a premier destination with a 1,500-miles-plus multiuse trail network stretching across 48 counties in four states—Pennsylvania, West Virginia, Ohio and New York. A key undertaking is the 238-mile Parkersburg to Pittsburgh (P2P) trail corridor, a game-changing project that will stimulate economic development and small-business investment for the dozens of small Appalachian towns it connects, creating benefits that will help transform the entire project footprint (https://www.railstotrails.org/our-work/trailnation/industrial-heartland-trails-coalition/)
The Lower Rio Grande Valley Active Plan is a blueprint for a 428-mile trail network that will link the rich natural, cultural and historical resources the area is known for. Sponsored by the Valley Baptist Legacy Foundation, University of Texas School of Public Health, RTC and 10 communities in Cameron County, the Active Plan will support job creation, tourism spending and economic development and serve as a “catalyst” for healthier lifestyles in one of the most underserved areas of the country (https://www.railstotrails.org/our-work/trailnation/lower-rio-grande-valley-active-plan/)
The Miami Loop is a 225-mile trail vision to expand transportation options, make biking and walking safer and more equitable, strengthen the regional economy, reduce the area’s carbon footprint, and improve health and wellness across Miami-Dade County. (https://www.railstotrails.org/our-work/trailnation/miami-loop/)
Route of the Badger, a partnership of RTC and the Wisconsin Bike Fed, is envisioned to be a world-class, 500-plus-mile regional trail system that connects people towns and counties, providing opportunities for physical activity, tourism, connections to nature, recreation and stronger businesses along the route (https://www.railstotrails.org/our-work/trailnation/route-of-the-badger/)
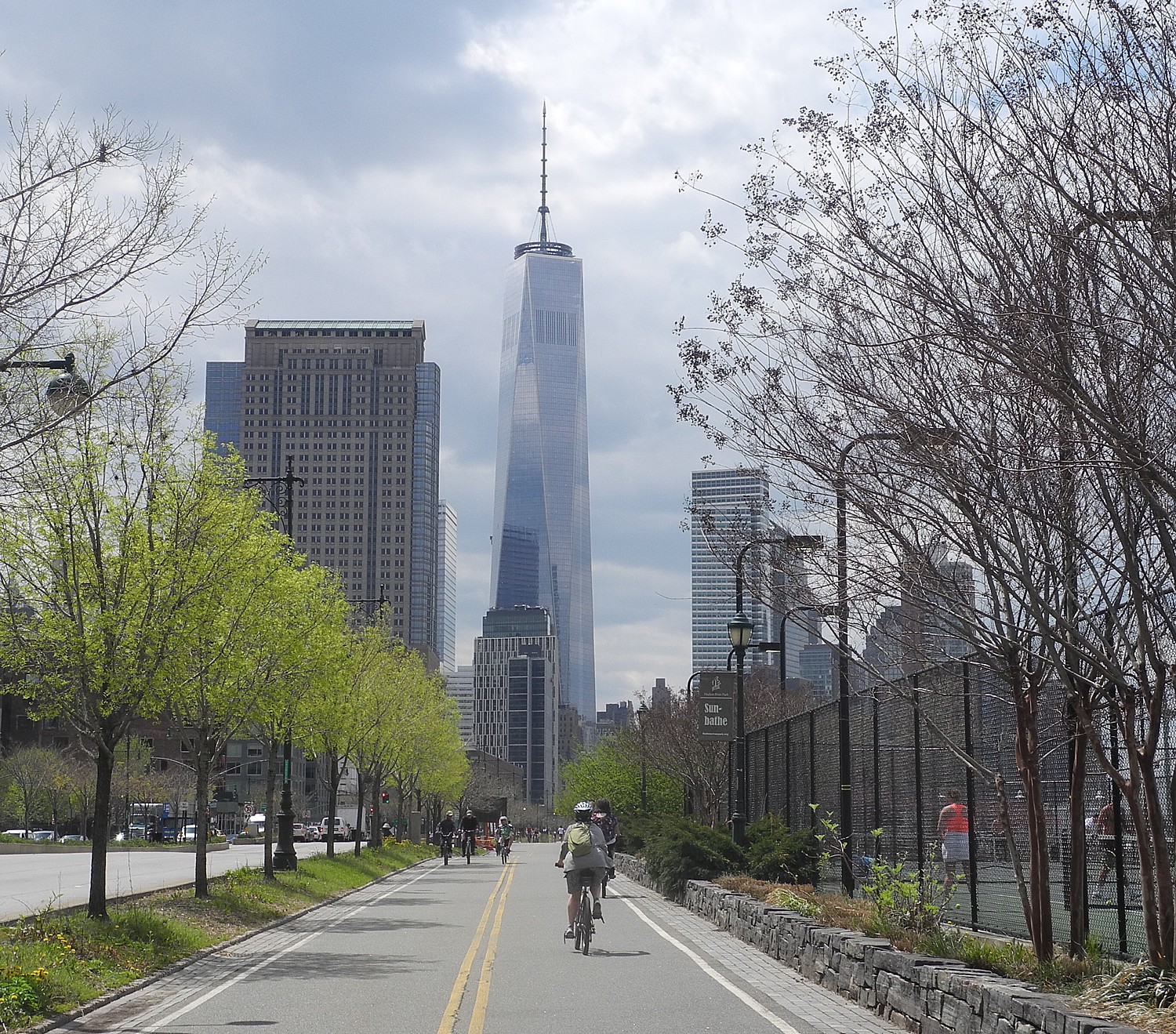

Empire State Trail: Notably, Parks & Trails NY, another organization which is committed to developing multi-purpose trails, has been active over the years in completing the 353-mile Erie Canalway. Now New York State is taking that initiative even further, spending $200 million to develop and connect 750 miles of multi-purpose trails (including 350 miles of new trails) of the east-west Erie Canalway Trail and the north-south Hudson River Valley Greenway. The Empire State Trail will enable someone to bike from the tip of lower Manhattan up to the Canadian border, and across the state, from Buffalo to Albany; it is targeted for completion in 2020 (https://www.ny.gov/programs/empire-state-trail)
Rails-to-Trails Conservancy is a nonprofit organization dedicated to creating a nationwide network of trails from former rail lines and connecting corridors; with a goal of creating more walkable, bikeable communities in America. RTC offers TrailLink, a free service that lets you access RTC’s 30,000 miles of trail maps and itineraries and downloadable mobile app. Rails-to-Trails Conservancy, 2121 Ward Court, NW, Washington, DC 20037, 866-202-9788, railstotrails.org, TrailLink.com.
See also:
Biking the Delaware & Lehigh Trail, Showcased on Rails-to-Trails Conservancy’s Last Sojourn BikeTour
_____________________________
© 2018 Travel Features Syndicate, a division of Workstyles, Inc. All rights reserved. Visit goingplacesfarandnear.com, www.huffingtonpost.com/author/karen-rubin , and travelwritersmagazine.com/TravelFeaturesSyndicate/. Blogging at goingplacesnearandfar.wordpress.com and moralcompasstravel.info. Send comments or questions to FamTravLtr@aol.com. Tweet @TravelFeatures. ‘Like’ us at facebook.com/NewsPhotoFeatures













