By Karen Rubin, Travel Features Syndicate, goingplacesfarandnear.com
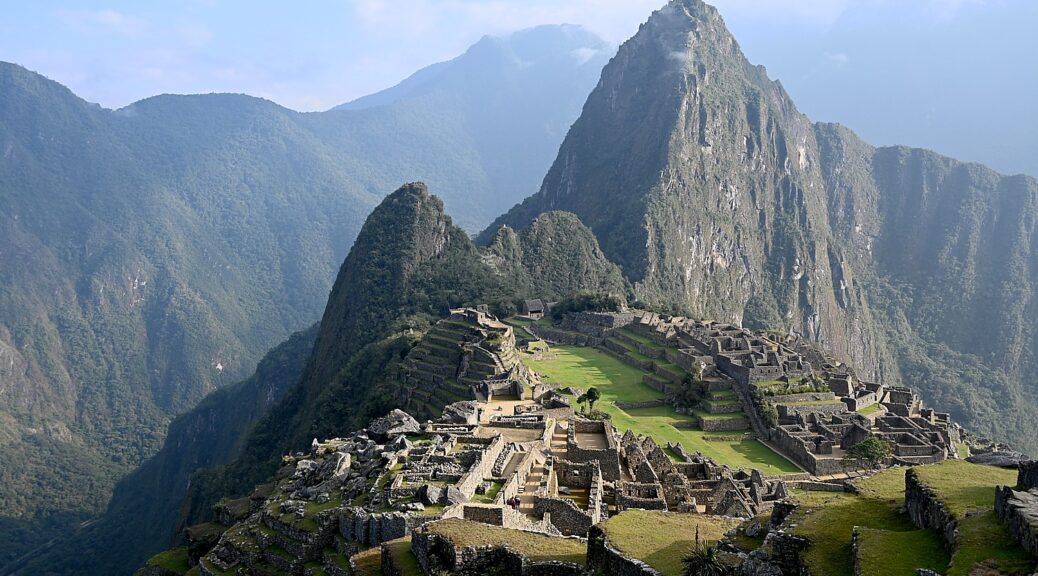
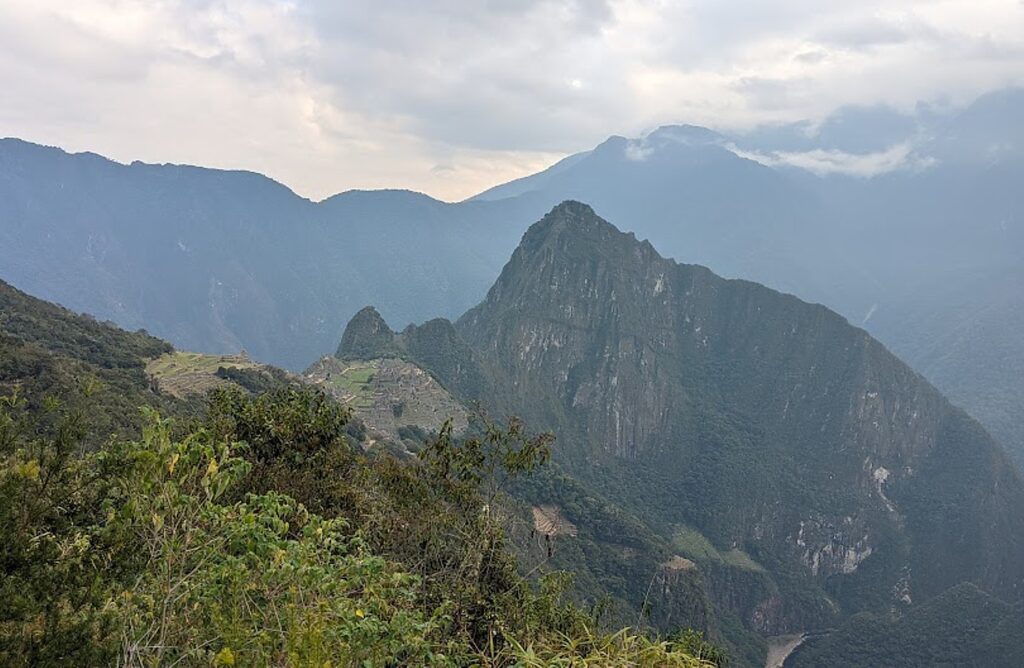
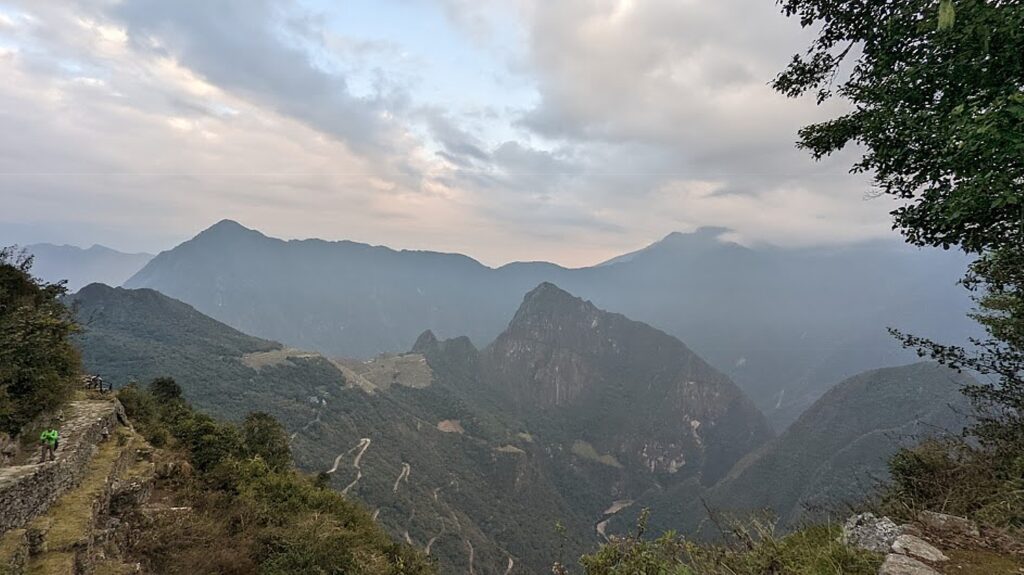
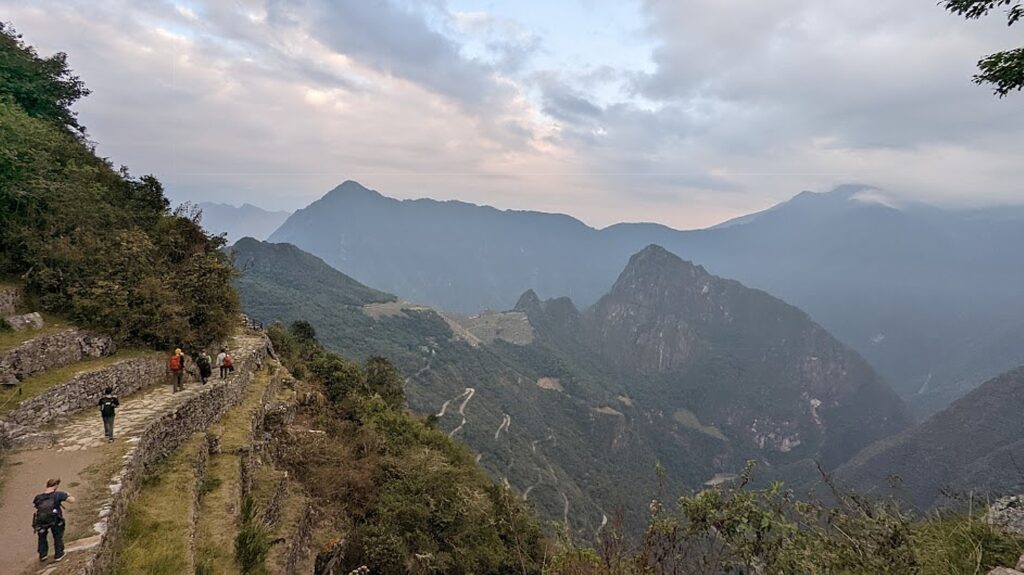
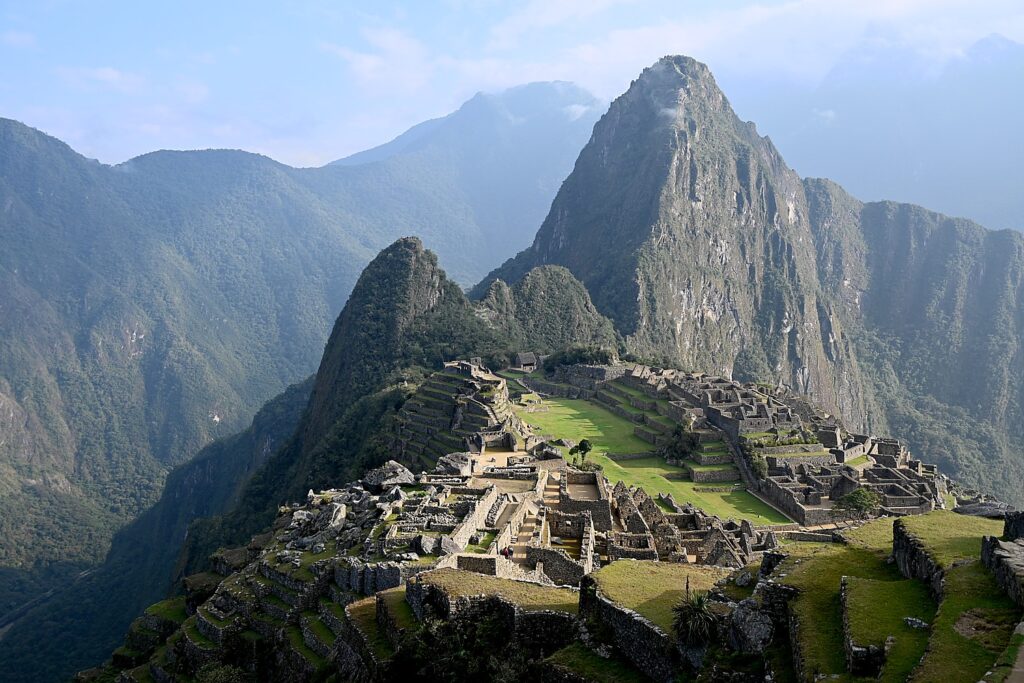
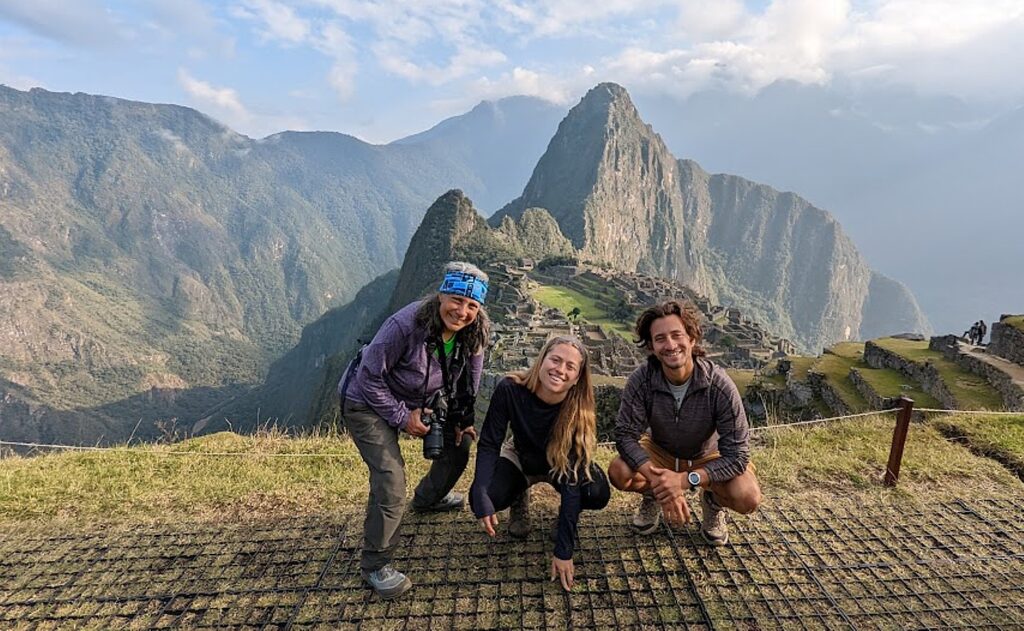
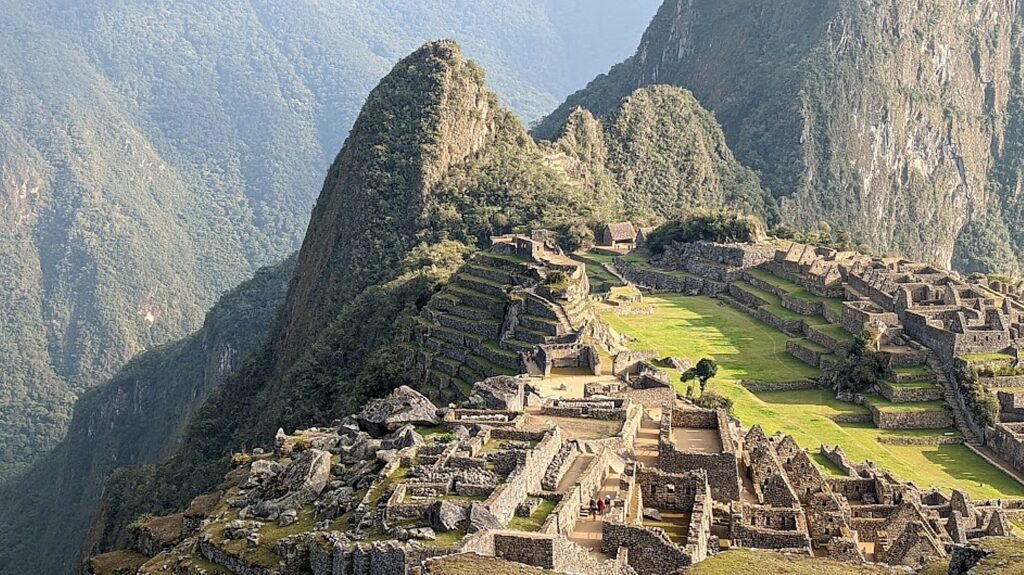
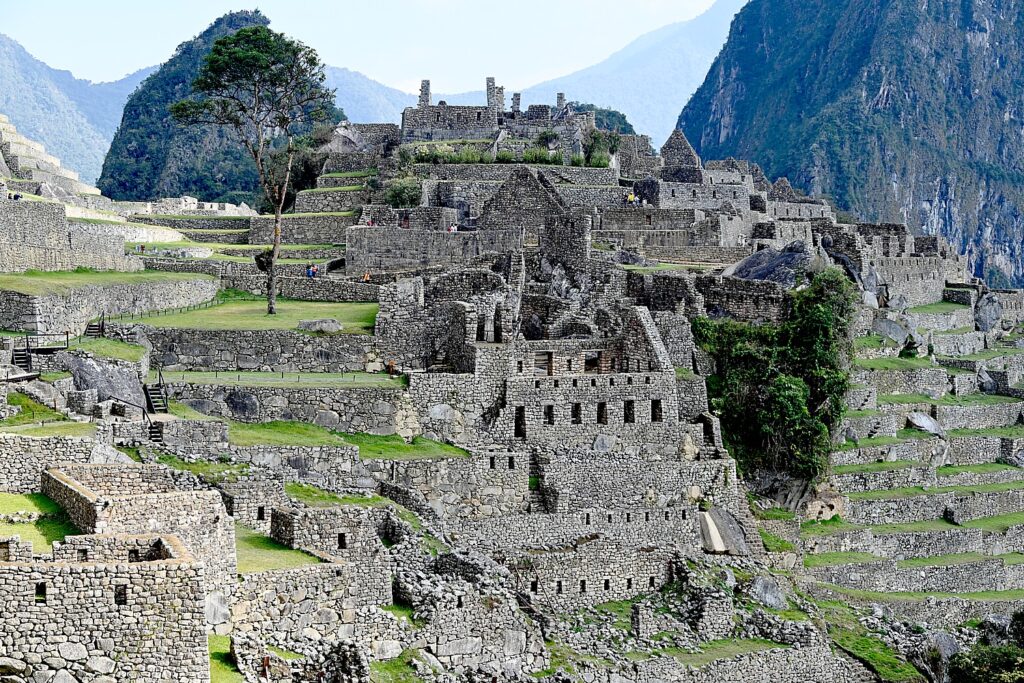
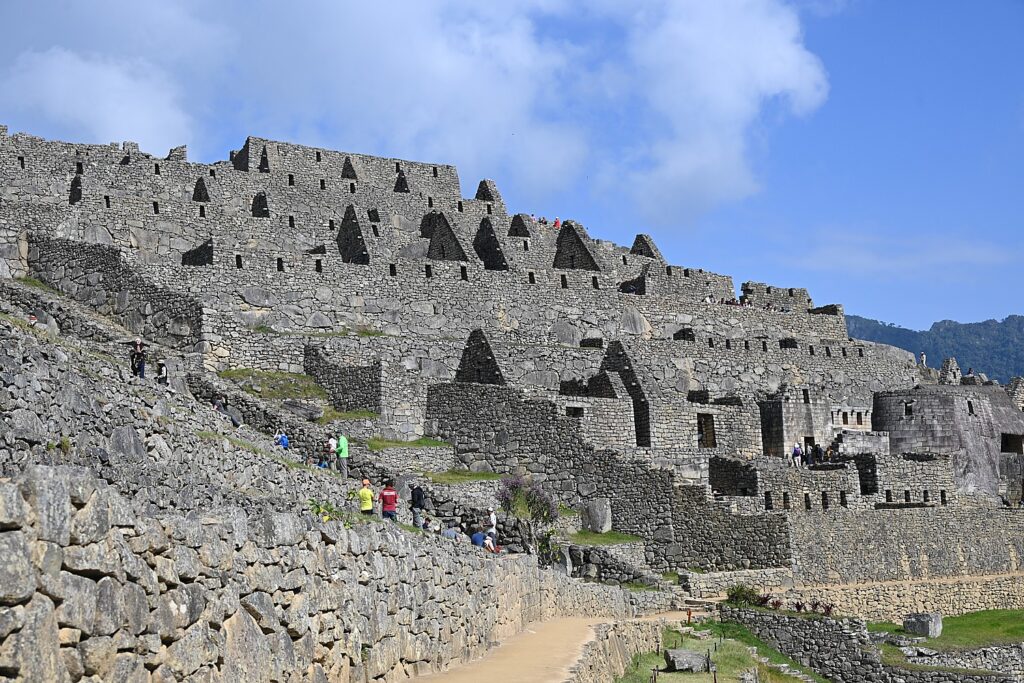
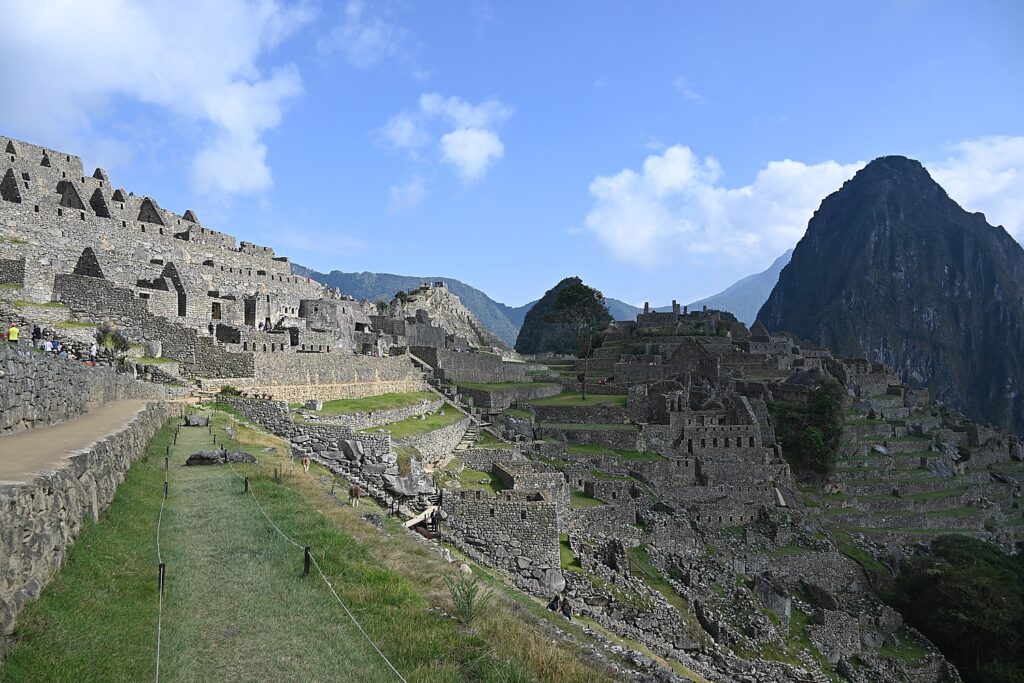
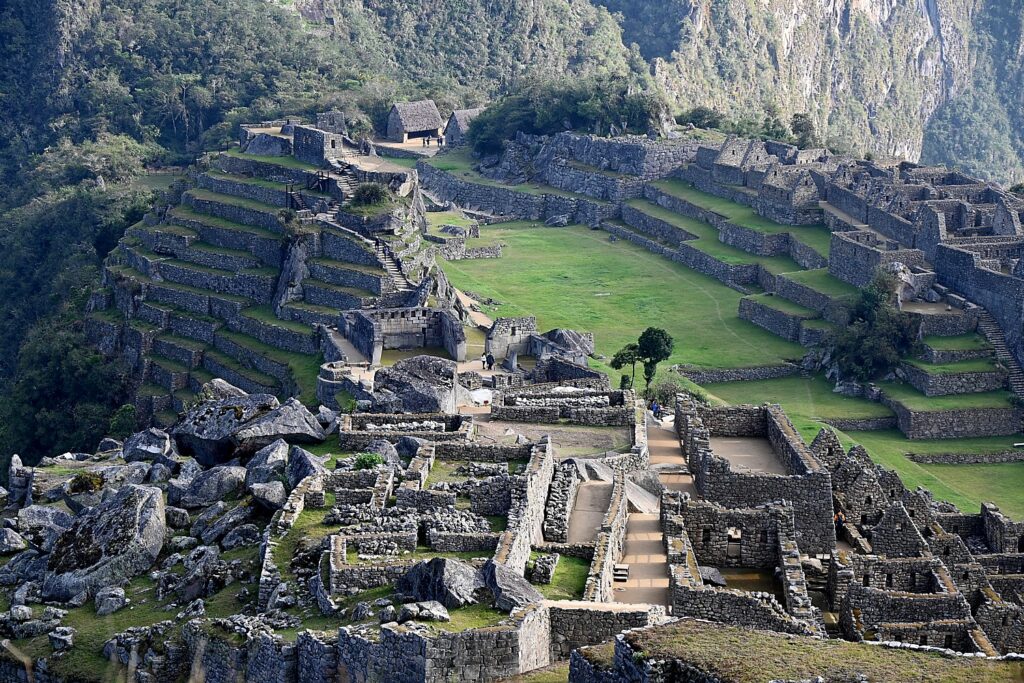
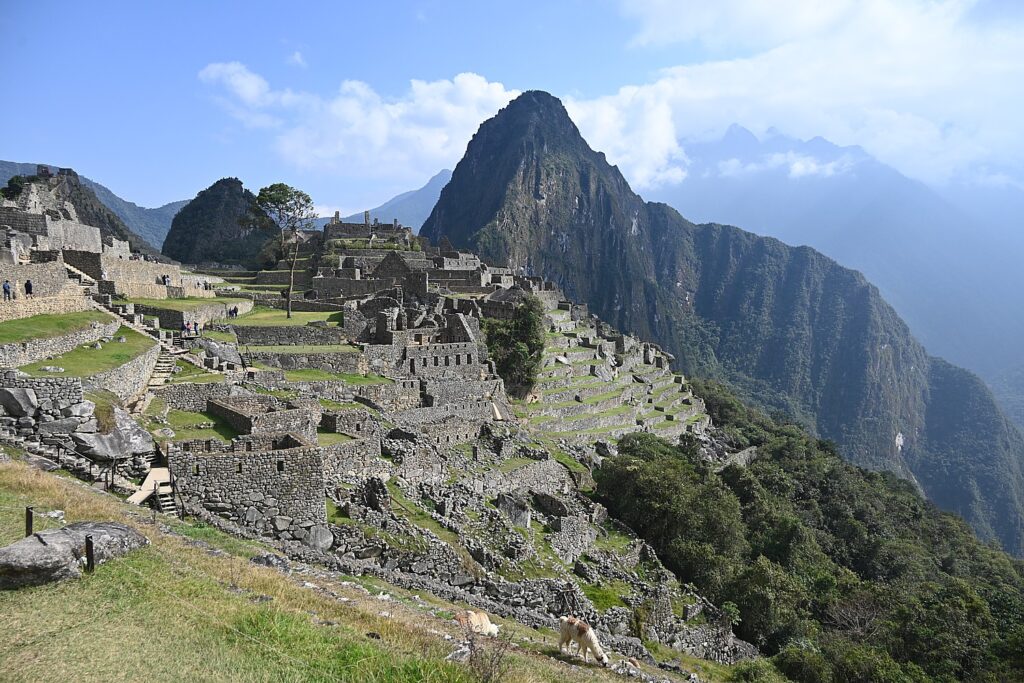
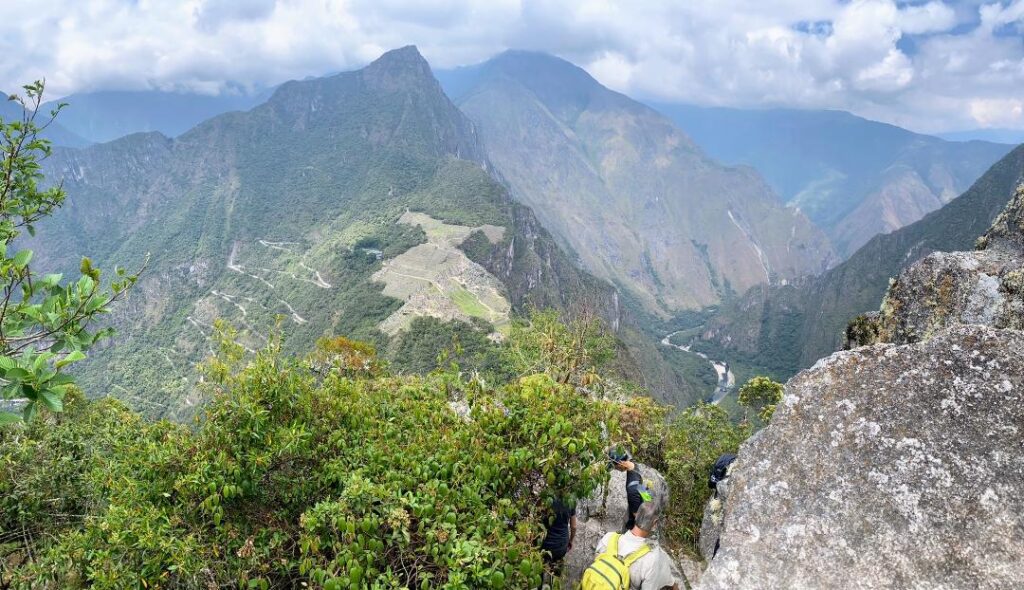
Machu Picchu, Peru’s jewel, along with the Galapagos, Ecuador’s treasure, are both national parks and UNESCO World Heritage sites. And both are models for the risks of overtourism and the rewards of responsible tourism.
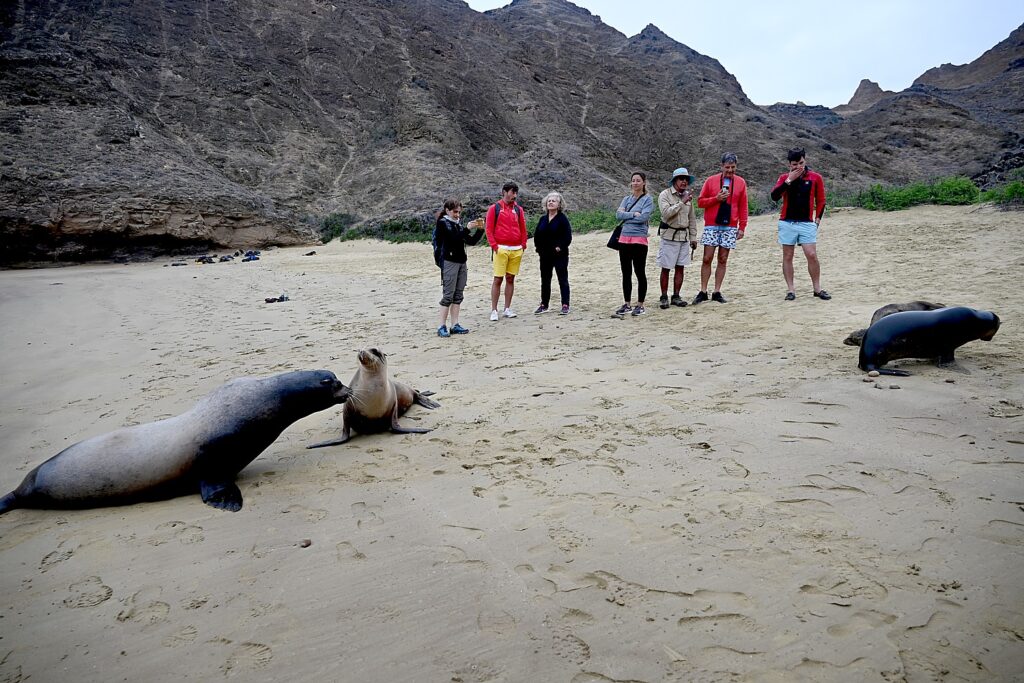
Without tourism, Ecuador would not have the funds to protect the animals or the habitat of the Galapagos.

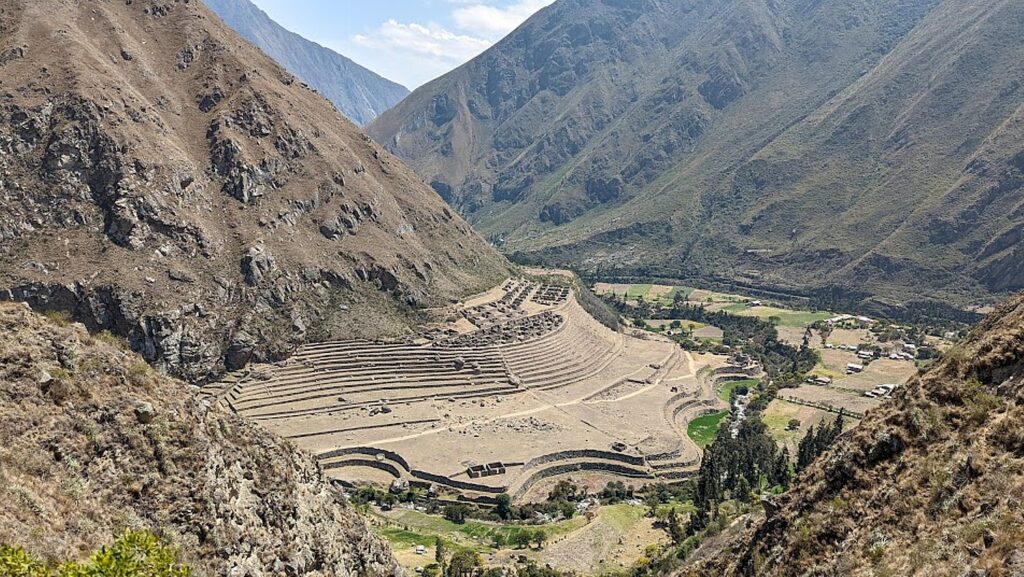
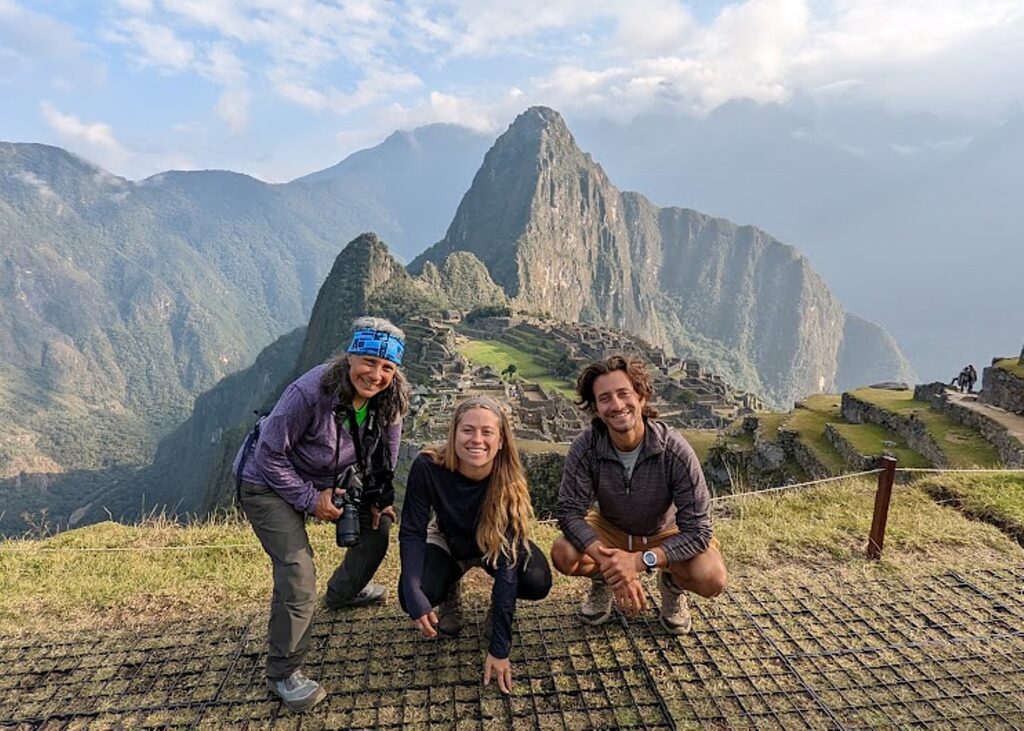
Without tourism to Machu Picchu, there would not be a Machu Picchu to visit, nor any of the other Incan sites along the Inca Trail, resurrected from 400 years of overgrowth. Without tourism, these porters who come from mountain villages would not have the income to supplement subsistence farming to provide a better life for their family. That was clear during the COVID pandemic lockdown.
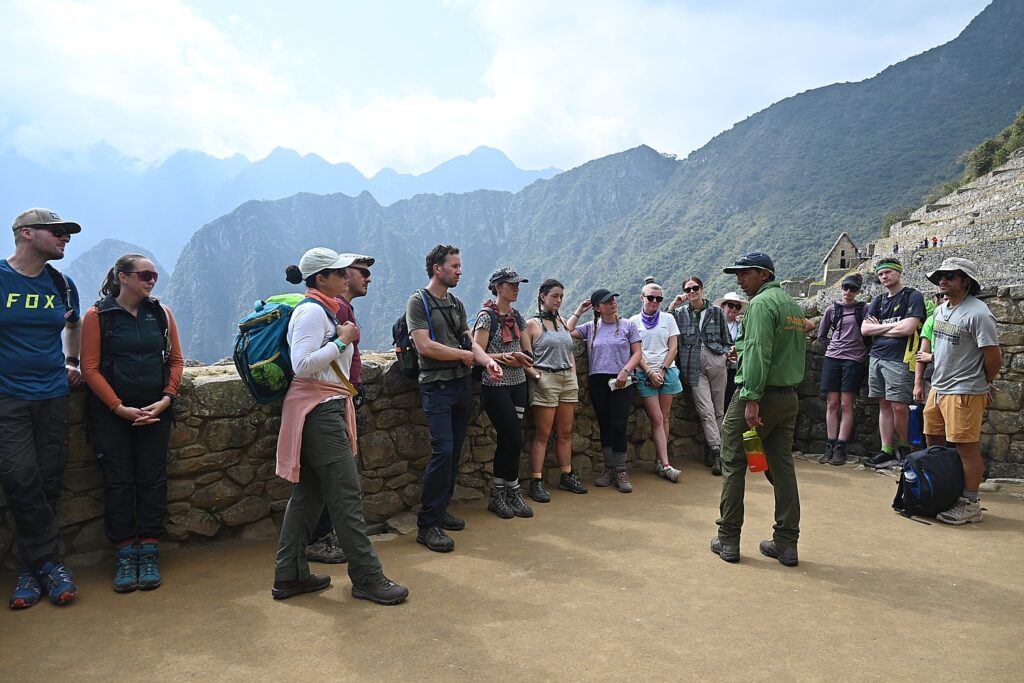
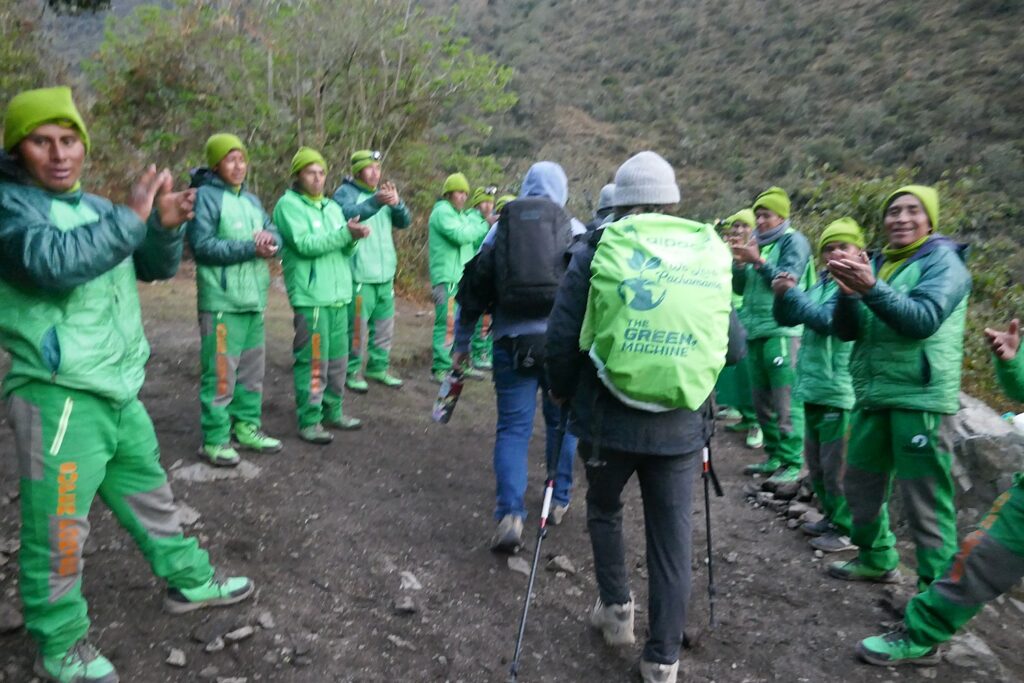
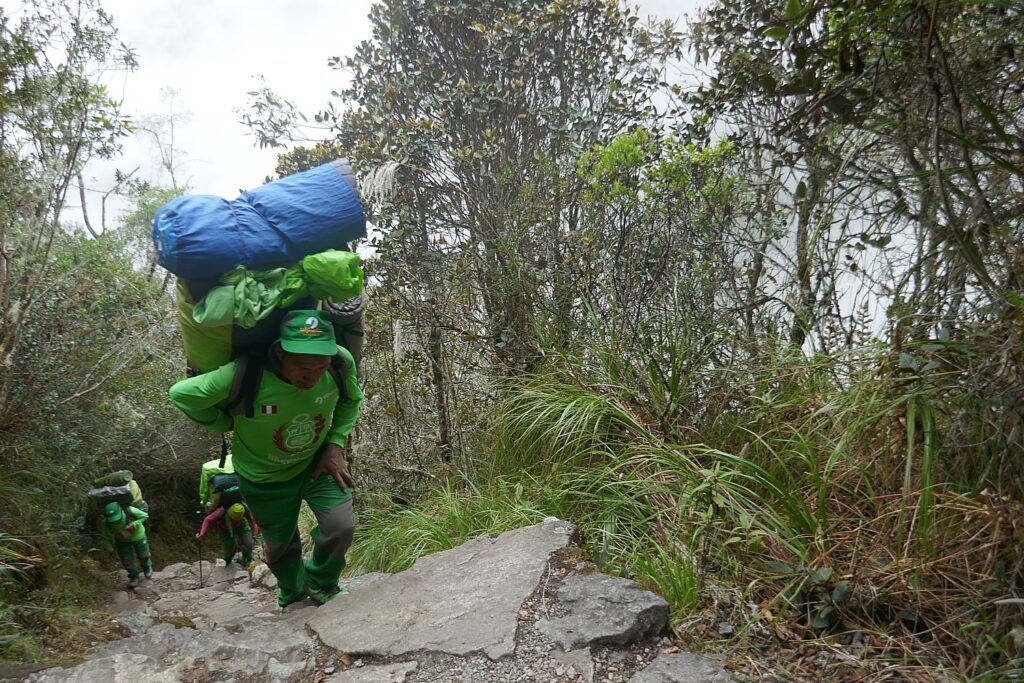
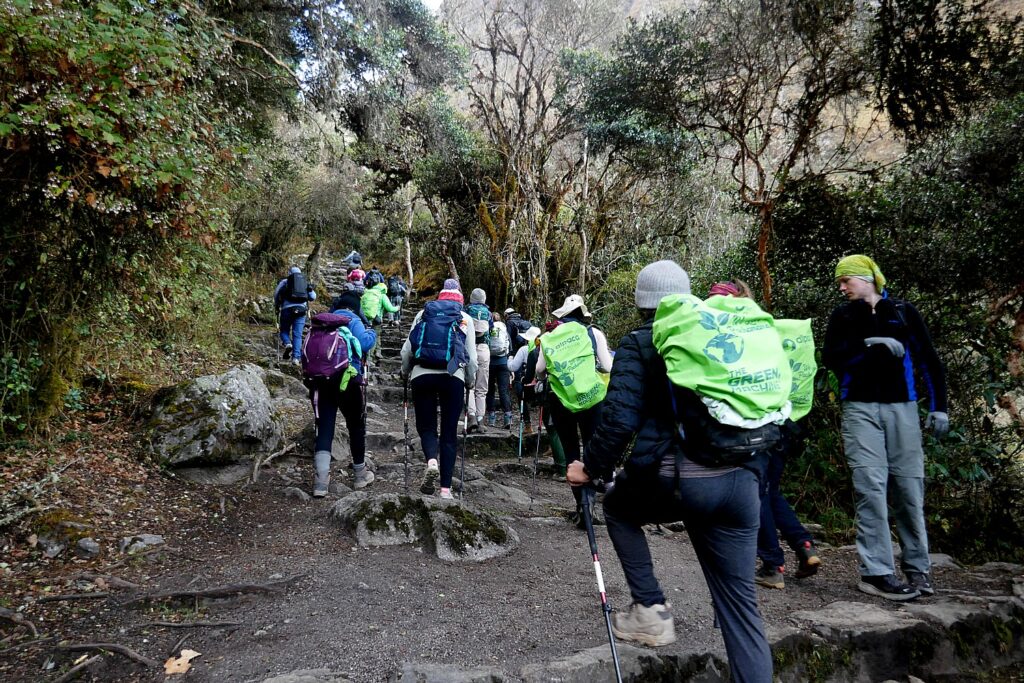
Both Galapagos and Machu Picchu limit the numbers of visitors, require visitors to visit with a licensed tour company and be guided (otherwise they muck up the place) and, similarly, put constraints on the tour companies, as well as development. In the Galapagos, ships are limited to 100 passengers; in Machu Picchu, trekking companies are limited to groups with a maximum of 16 trekkers, two guides and 22 porters, with each porter carrying a maximum of 25 kilos.

The reality of the benefits of tourism is harshly apparent when it is taken away – as during the COVID pandemic lockdowns, or conflict, or natural disaster – when so many lose their livelihoods and agencies and organizations lose the capital to maintain and preserve the historic, heritage and natural sites.
Tourism goes even further than that. I believe tourism the greatest force for peace, understanding , cooperation and progress that humanity has ever devised. Tourism has provided the funding – and the demand – to unearth these Incan sites, and in the process, sparked a renewed desire for Peruvians to appreciate their heritage.
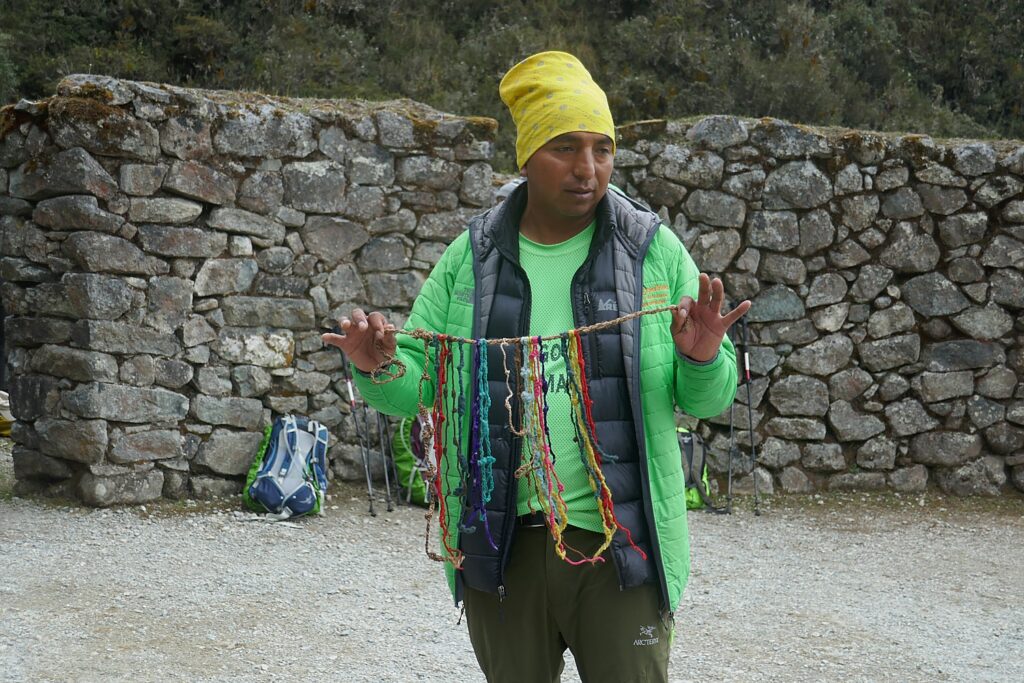

But yes, tourism has to be kept in balance, to avoid exploitation and the negative impacts overtourism can have. That is what Sustainable, Responsible Tourism is about.
Many travelers these days have Responsible Travel in mind when they choose destinations, experiences and travel companies – down to the airlines, cruiselines, hotels and tour operators. Indeed, Alpaca Expeditions highlights its Sustainability bona fides at its website (alpacaexpeditions.com).
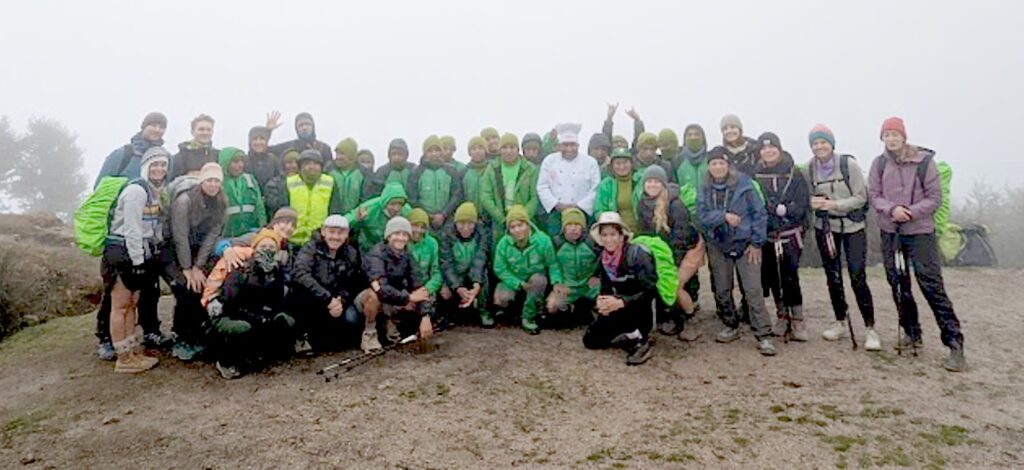
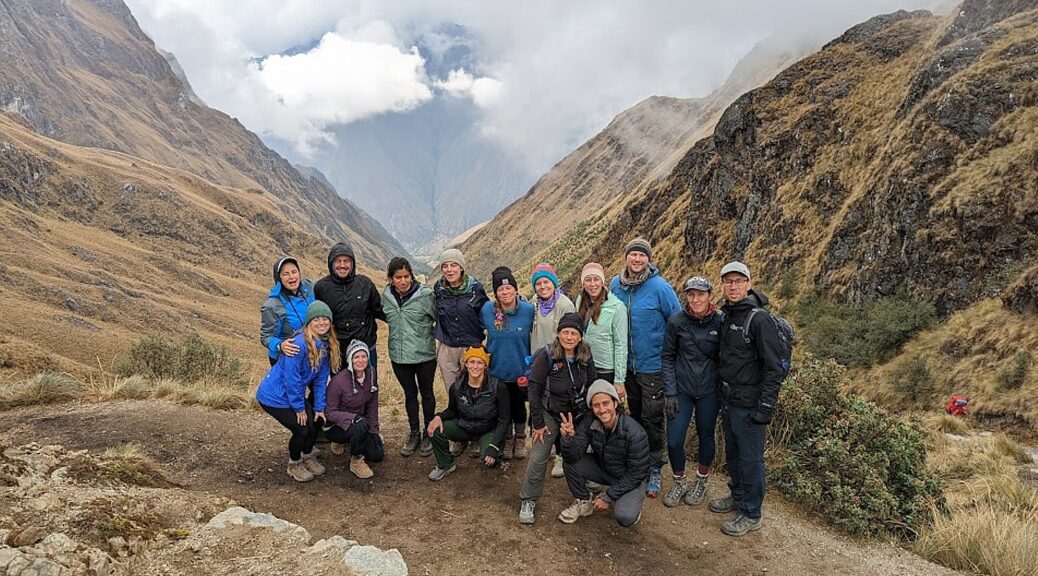
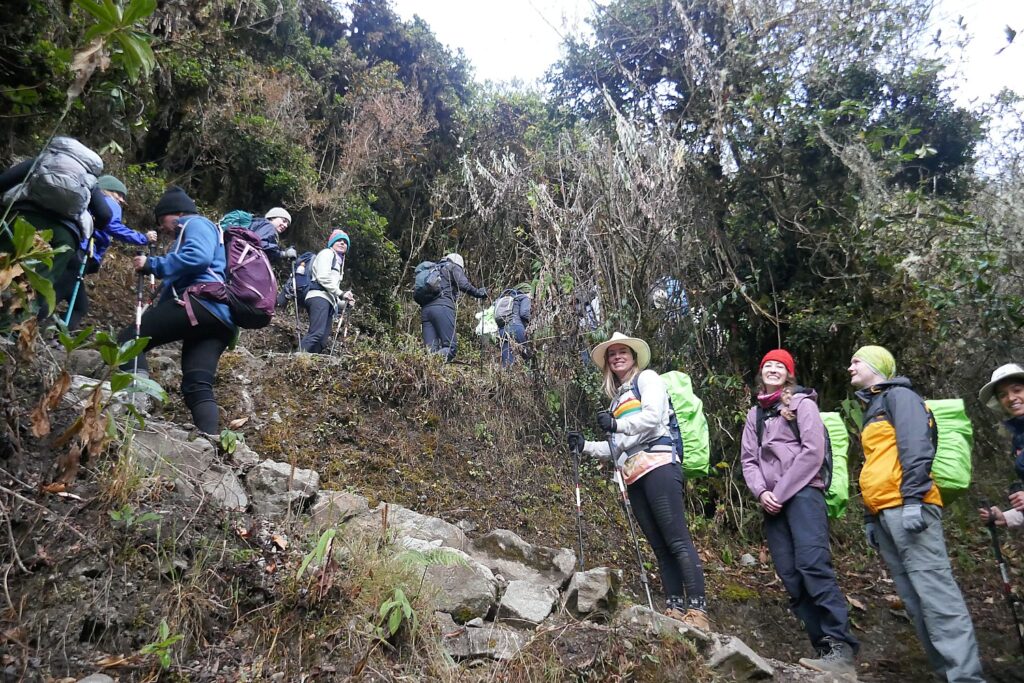
And on this four-day, three-day Inca Trail trek, I could really assess how well Alpaca Expeditions’ fulfilled its lofty promise of being a “sustainable and responsible” tour company, with a “unique service philosophy dedicated to our porter welfare equally to our client services, fair and kind travel, equal employer with a focus on women’s rights in tourism.”
In fact, all of these promises were confirmed during our visit. Alpaca Expeditions can stand as a model of the importance of responsible, sustainable tourism – both in preserving Machu Picchu and the historic sites along the Inca Trail and as a model for other travel enterprises. You can see it in the comparative prosperity of Cuzco, once the capital of the Incan Empire and the epicenter of the Incan world.
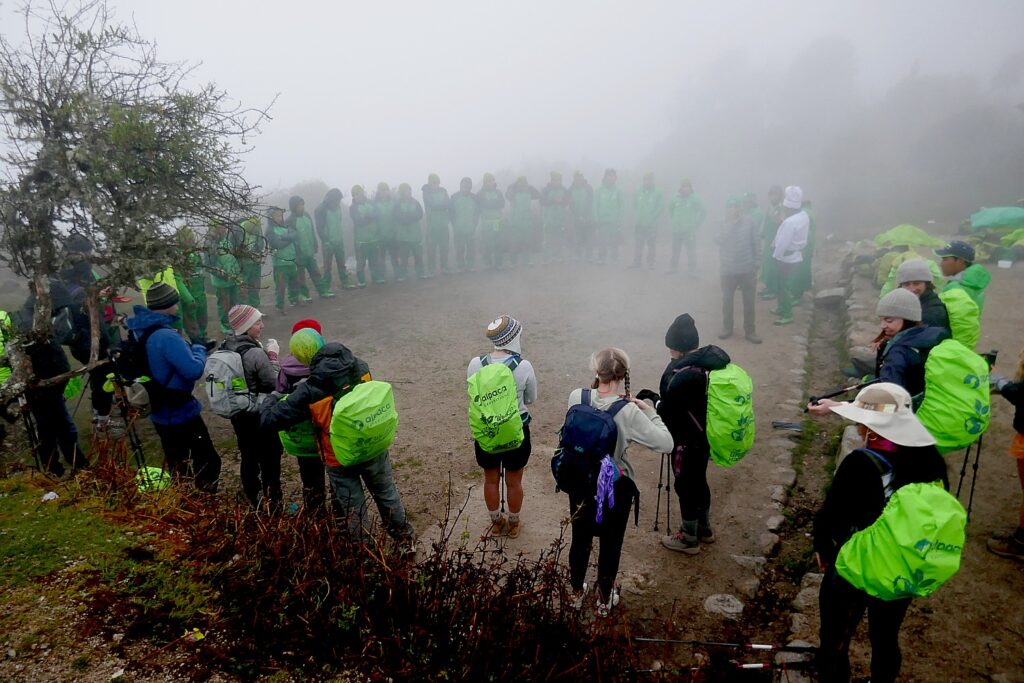

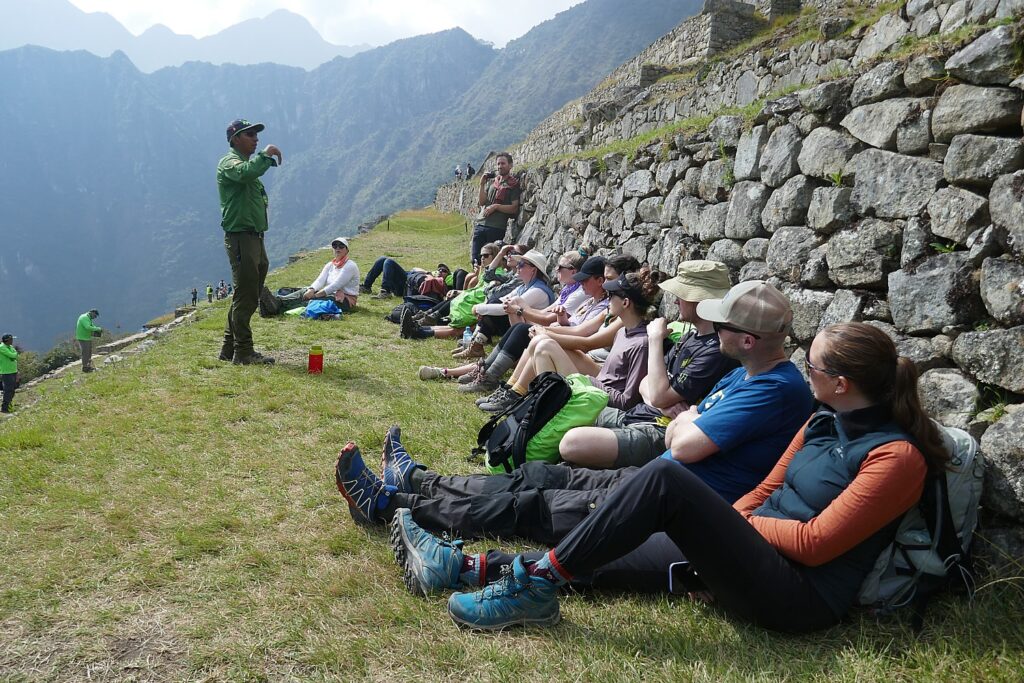
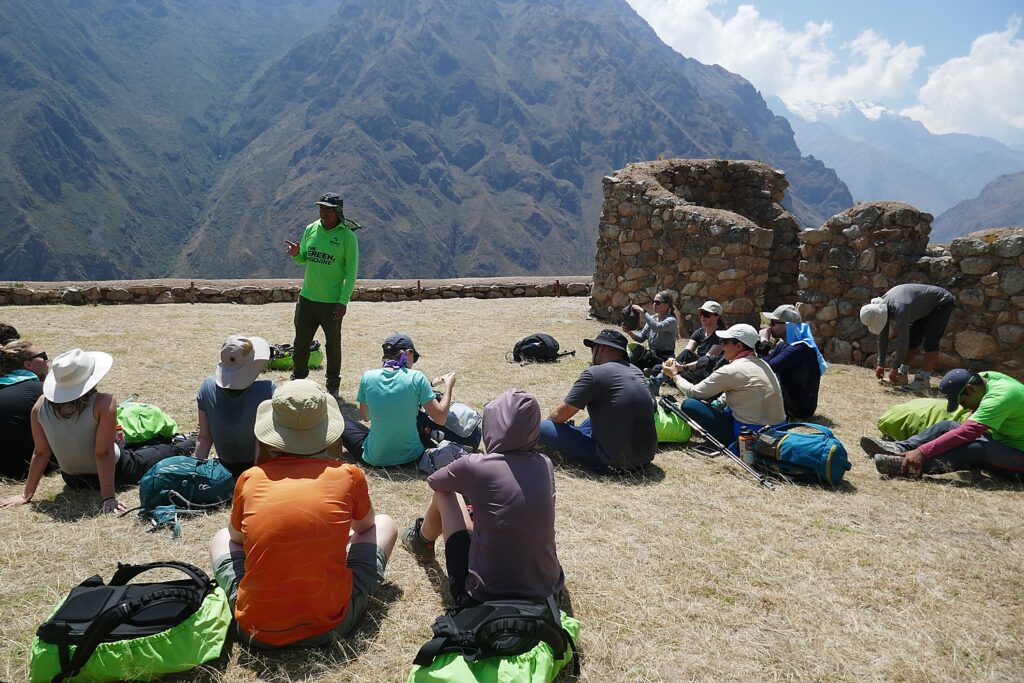
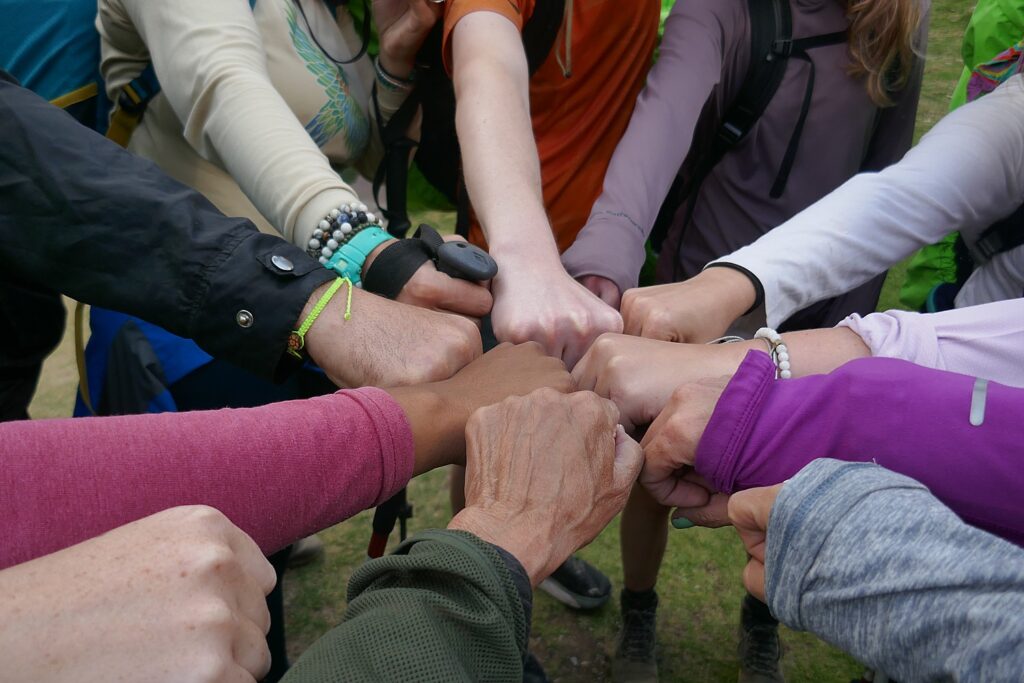
So, on the third day of the four-day Inca Trail trek – in the morning before we head out and again this evening – our Alpaca Expeditions guide, Lizandro Aranzabal Huaman, creates opportunities for us to get to know who our porters, chefs and staff are who are making this experience possible, and they to know us. This is what Responsible Tourism is all about – a connection, appreciation and an opportunity to improve the lives of the local community, and, similarly, an appreciation for the guests whose tourism dollars provide them a better quality of life as well as the funds to preserve and protect their heritage.
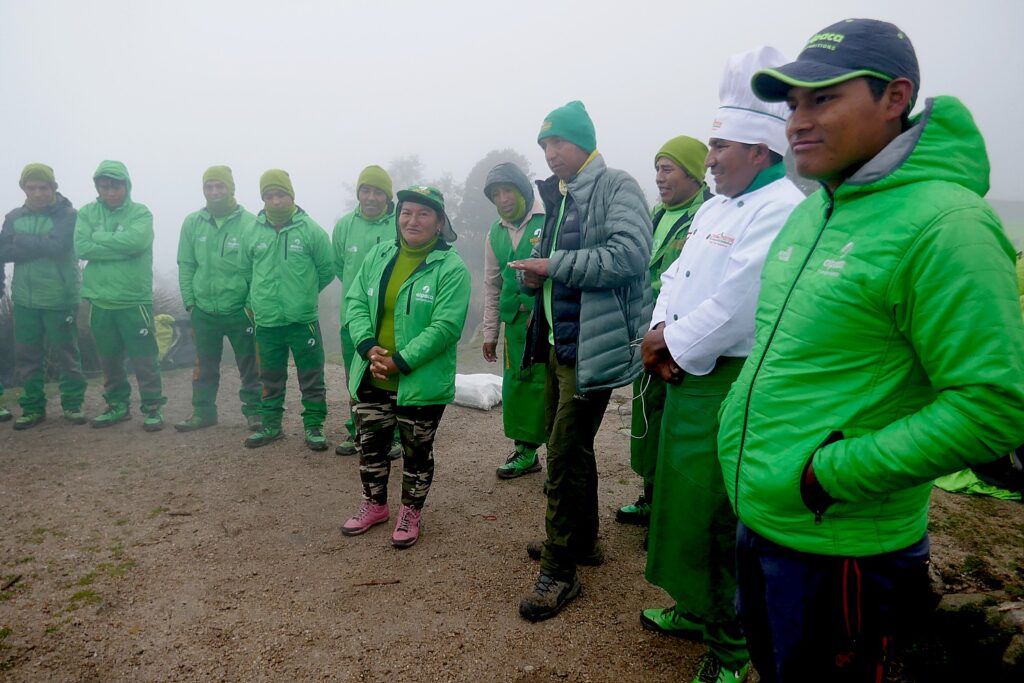

The porters, chefs and guides – 22 of them to 15 of us (there is actually one fellow who is the “sanitation engineer” charged with maintaining the private portable potty; two of the porters are brothers, aged 62 and 68, and one is a woman, which is still unusual) – come mostly from the same mountain village and leave their families for weeks on end in order to do these treks, but at least they have the camaraderie of their friends.
Lizandro’s own story is illustrative. On our first day of the four-day Inca Trail trek, as we walk through one of the mountain villages, he tells us that village was where he grew up – his family is among 96 who still live there. He used to lead a pack horse on the trail since he was 4.

“In my community there was no school. My parents sent me for education –I stayed with an uncle for three years until my parents couldn’t pay for school. I met a chef and became a porter at 18 years old, 15 years ago.“ He learned English from the trekkers . His first word, he tells us, was “baby spoon” when he was 18.

“Fifteen years ago, porters were exploited by companies – they hired fewer to make more profit,” Lizandro tells us. “Then, they carried 40-45 kilos; companies didn’t provide uniforms, equipment, back support, not even food. They had to carry their own blanket and did not have a tent. Salaries were 50 Soles for a four-day hike – not even $15.
“My first hike was so difficult, a porter made me take coca leaves. I got 50 Soles for a tip. 15 years ago in Peru, 50 Soles was a lot – 1 sole could buy 20 breads, now it only buys 2 breads.”
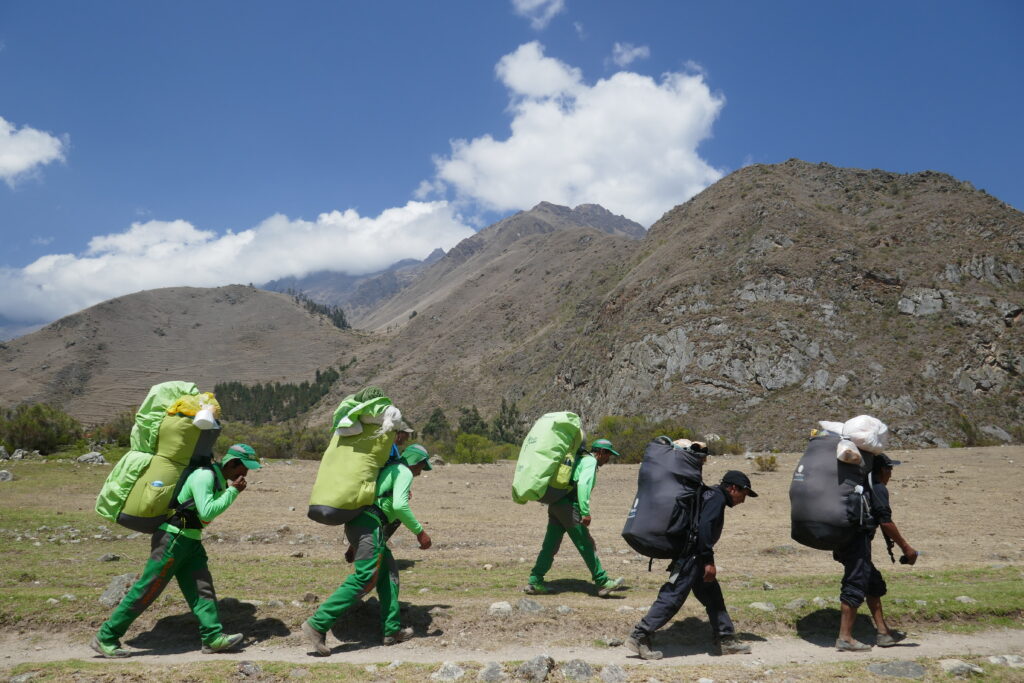

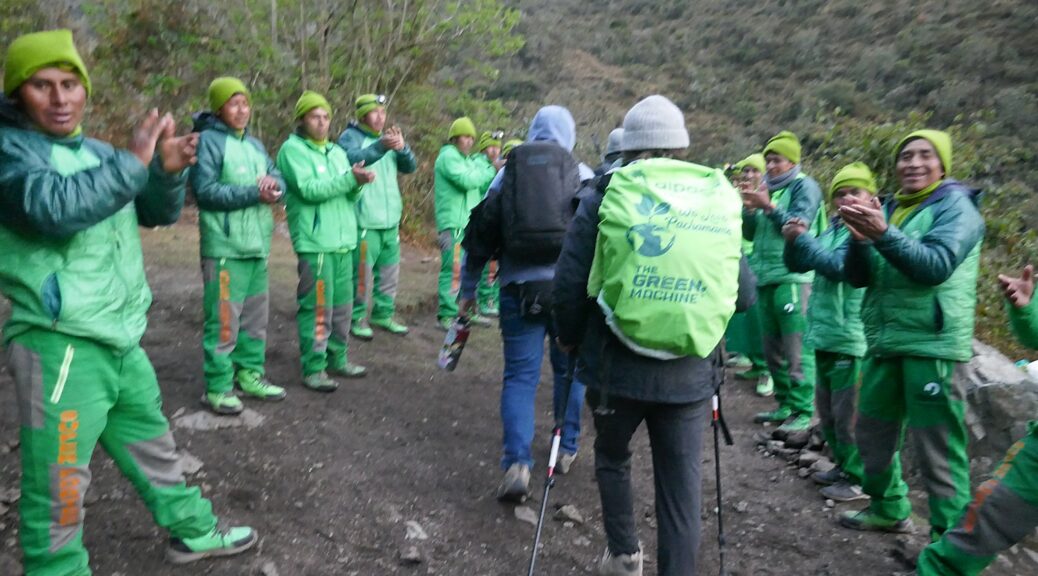
Then, 15 years ago, the porters organized with the help of the Cuzco government, and got regulations to provide better conditions. Now the porters carry a maximum of 28 Kilos (the first 2 days are still heavier because they are carrying food supplies, and the packs are heavier when it rains, but lighten as we consume food) and guests are restricted to bringing 7 kilos including a sleeping bag in the duffel which is supplied.
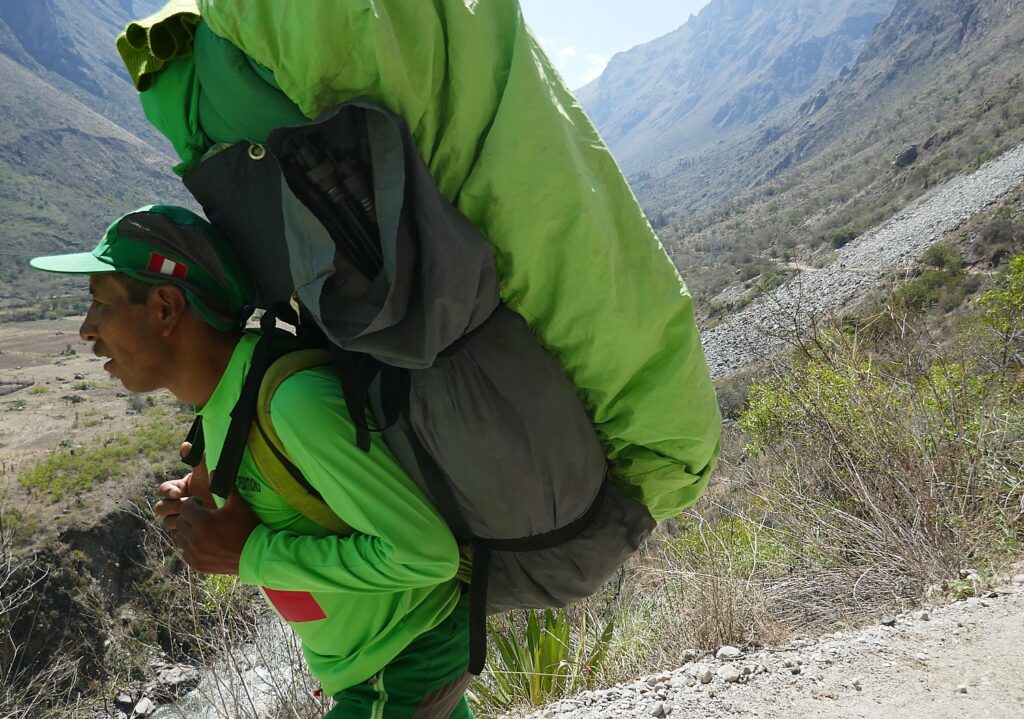

“It’s difficult for porters (from mountain village) to be away from family for these periods of time, but typically they come from the same community so have friends. Some commute six hours by bus/train and then 2-3 hours walk back to home, so many prefer to do 5-6 groups and then go home for 5-6 days, do some farming and then come back to hike. Normally, they do 6-7 trips a month.”
When the COVID pandemic forced a lockdown and there were no tourists coming (one Japanese tourist actually had to stay in Peru a full year before he could go back to Japan, which was closed to the outside, and was the first visitor back to Machu Picchu), Lizandro had to go back to his village and do farming.
The government has yet to restore the full numbers of visitors to Machu Picchu after reopening from the pandemic – before, 7,000 were allowed per day; the number had just been increased to 5,000 from 4,000 (only 200 trekkers per day on the Inca Trail). “We thought it would take a couple of years but recovery has been quick,” he said.
Now, even though the porters are protected, some companies still make them carry heavier packs and do not provide hiking boots; some porters still hike in sandals instead of boots, Lizandro says.
Raul Ccolque who founded Alpaca Expeditions, grew up in a small town in the Sacred Valley and while he was studying tourism, worked as a porter (from 2000-2003) and later as a tour guide. Ccolque witnessed firsthand how companies exploited their porters – not only were they poorly paid, but they would also be badly bruised or injured due to carrying heavier loads than necessary, without proper hiking boots or uniforms, sleeping bags. They even had to supply their own food.
Raul set out to create a company that would remedy this inhumane situation.
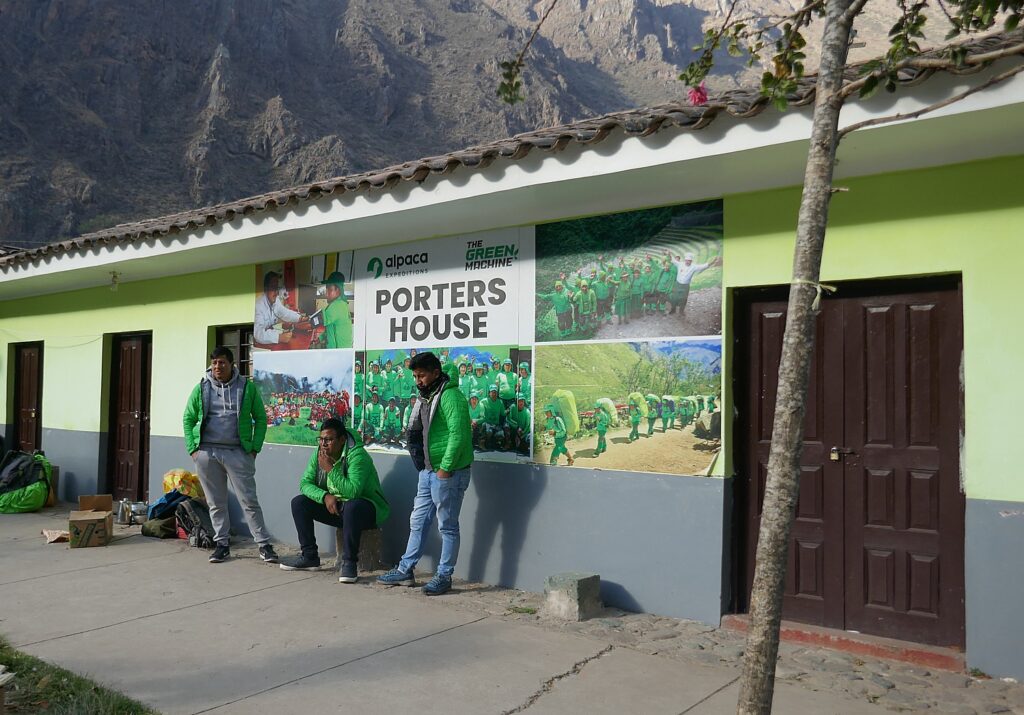

“Most of our porters live in a village outside of Cusco – typically 2 to 4 hours away. We cover all entrance fees (45 soles – $15 US per porter) and transportation to and from the trek for our porters, separate from their salary,” the website says. “They are paid directly after the trek, which prevents them from traveling back to Cusco before heading home. Unfortunately, this is an uncommon practice. They receive better wages, health insurance [not a given in Peru] and all of their equipment for free. This includes hiking boots, pants, jerseys, fleeces, jackets, hats, flashlights, sleeping bags, and amazing food to eat. We make sure they have a comfortable bed in a lovely room to sleep before (and after if needed) the trek instead of crashing on a floor like others.” Alpaca Expeditions built Porters House where they stay between trips.
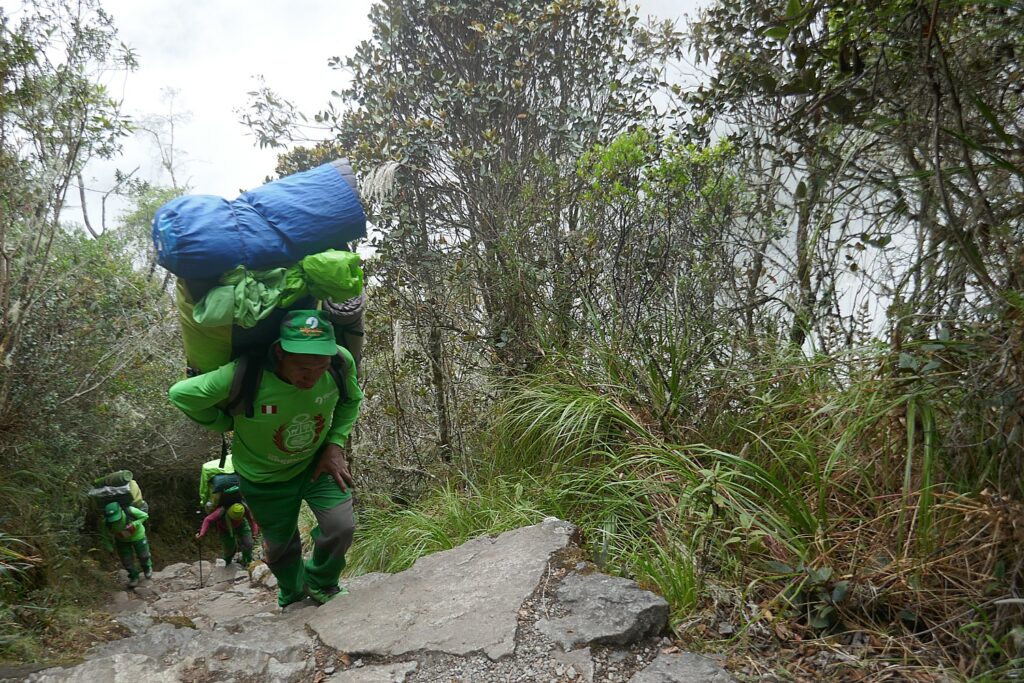

“While the government allows each porter to carry up to 25kg, we keep our limit at 20kg. Each porter will carry up to 15kg from the company and 5kg of their own personal stuff. This is why it’s so important to keep your personal duffel within weight restrictions and not exceed our allowed 7kg. You will see other companies carrying more than the allotted weight, but we will not allow our porters to carry this burden. Every year Alpaca Expeditions provides new sleeping bags and sleeping pads for each porter. We provide them all the gear they need along the hike, our jackets, for example, are all lined and warm, and our boots are all waterproof. Our porters eat the same food as the guests; the chef cooks enough for all the trekkers and porters [that’s why our platters are so enormous and there are so many dishes made]. Of course, the porters are carrying the food supplies, so with each day, at least that load gets lighter.”
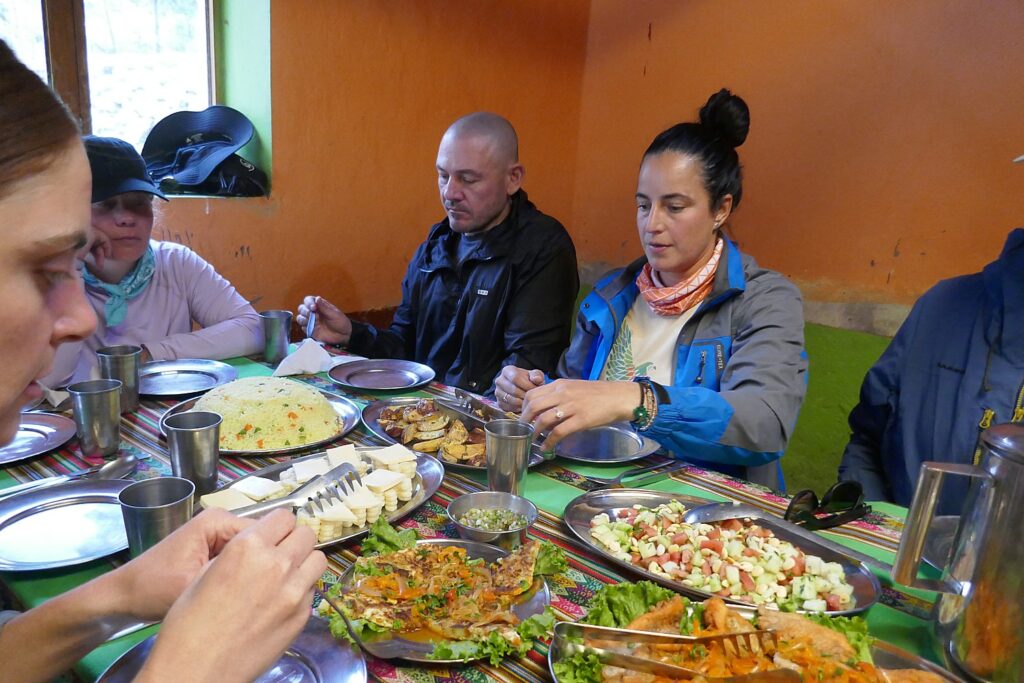

Also, “In keeping with the Andean concept of ‘ayni’, or giving back to the community, Alpaca Expeditions has numerous social projects,” the company states. “Our pride and joy has been ‘adopting’ the highland villages where our porters’ families have lived for centuries as subsistence farmers. Several times a year we go to these villages to help supply their schools with books, computers and basic hygiene supplies. We have even provided the funds necessary to employ a teacher. We have also started a tree planting project that reintroduced 3,000 of the indigenous, but rapidly disappearing Queuña tree. Alpaca Expeditions is dedicated to improving our community and sharing these social projects.” The company is also working with a local clinic in Cusco to provide dental care and skin examinations for the children of each of its porters’ villages.
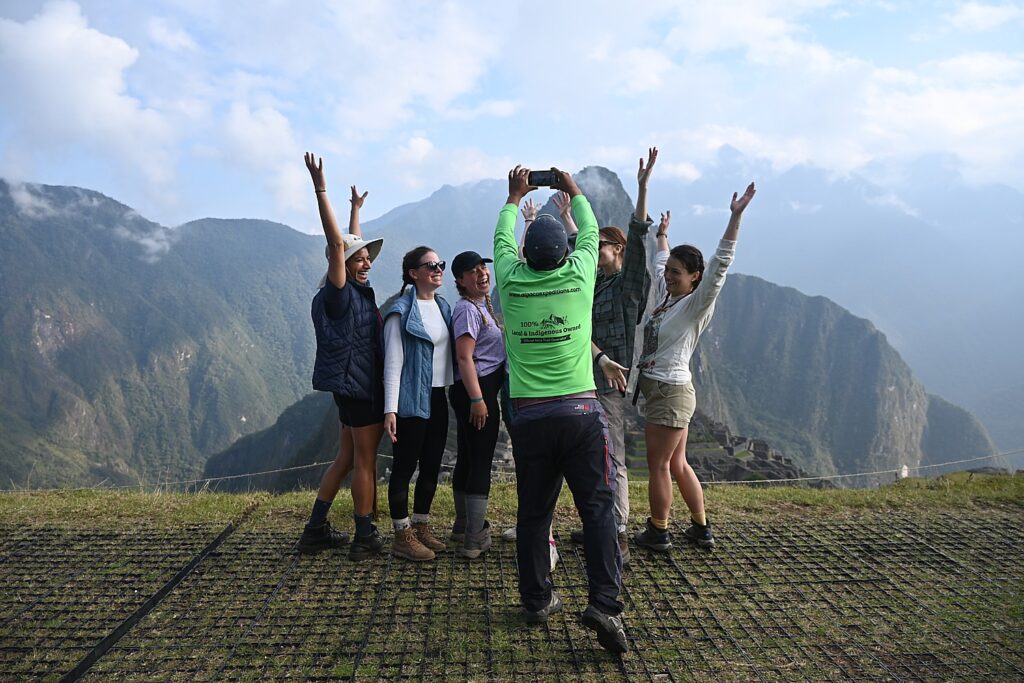

Lizandro tells us that most of the porters, even though they have done the trek umptium times, along with their families in the mountain villages, have never actually visited Machu Picchu themselves – the porters leave our group early on the last morning to make a 6 am train back to Ollantaytambo. But among the programs that Alpaca Expeditions offers is an opportunity for the porters to visit Machu Picchu with their families.
The company says it has bought land in Cusco to build dormitories, classrooms and teaching kitchens for its team. “We will have English classes, computer classes and cooking classes here for any member of our team and their family to use, free of charge. This is a huge project for us that we are really excited about.”
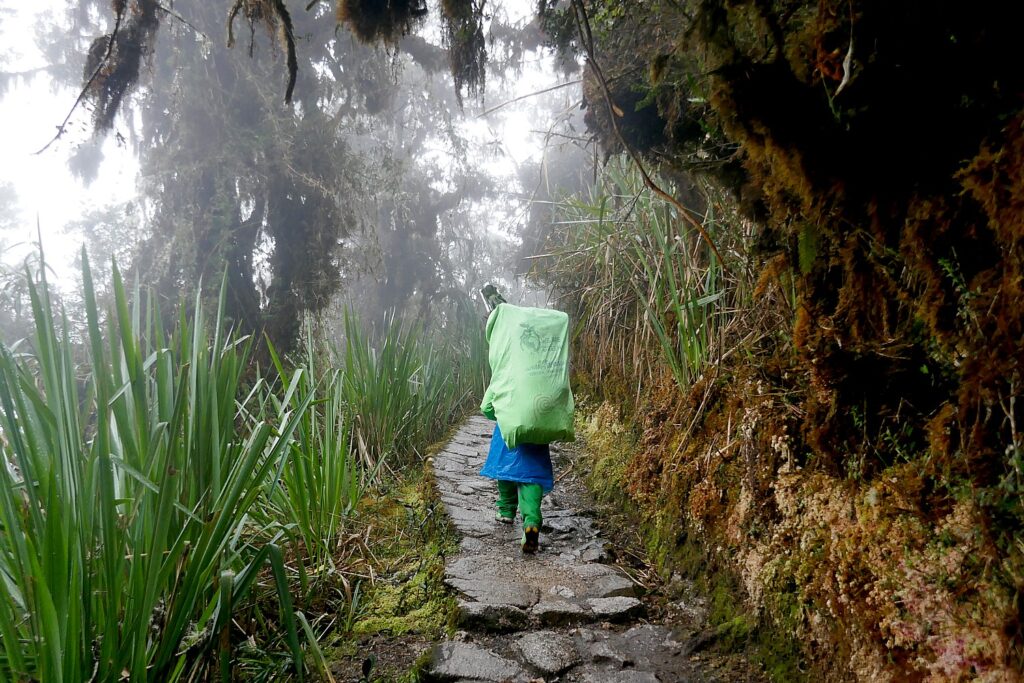

People used to be able to do the Inca Trail trek on their own, doing their own camping. But they left such a mess, the government now requires every person going to Machu Picchu to obtain a permit and go with a licensed tour company. Still, Alpaca Expeditions has found the need to extend its “eco-friendly” and “sustainable” values beyond its own staff and guests. “Not only do we clean up after ourselves, but we even have campaigns where our staff cleans up the messes others have left behind. There is a key concept in the Andean cosmovision known as ‘ayni’. It means ‘reciprocity’ – that as you take, you must give back. We are dedicated to treating our beautiful Mother Earth, known as Pachamama in Peru, with respect and honor in exchange for all the abundance she gives to us.”
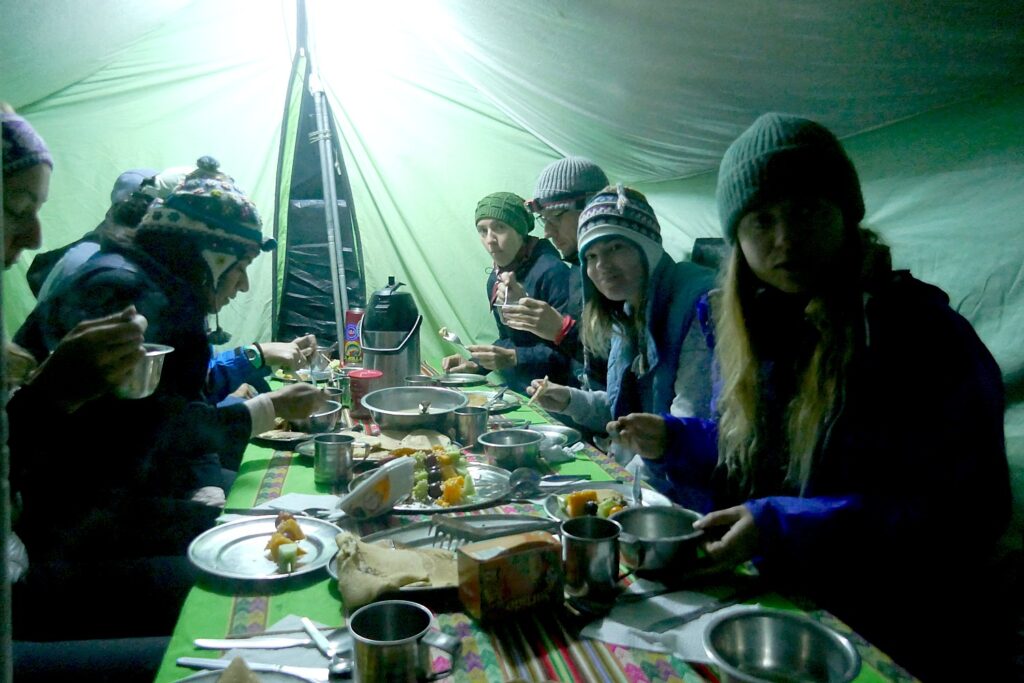
When it comes to my turn to introduce myself, I can’t help but reveal that I turned 71 this day, and this “trip of a lifetime” could only be possible because of them. (Later that evening, the chef presents me with the most magnificent, decorated birthday cake, which took three hours to prepare with the camping-style equipment he uses.)
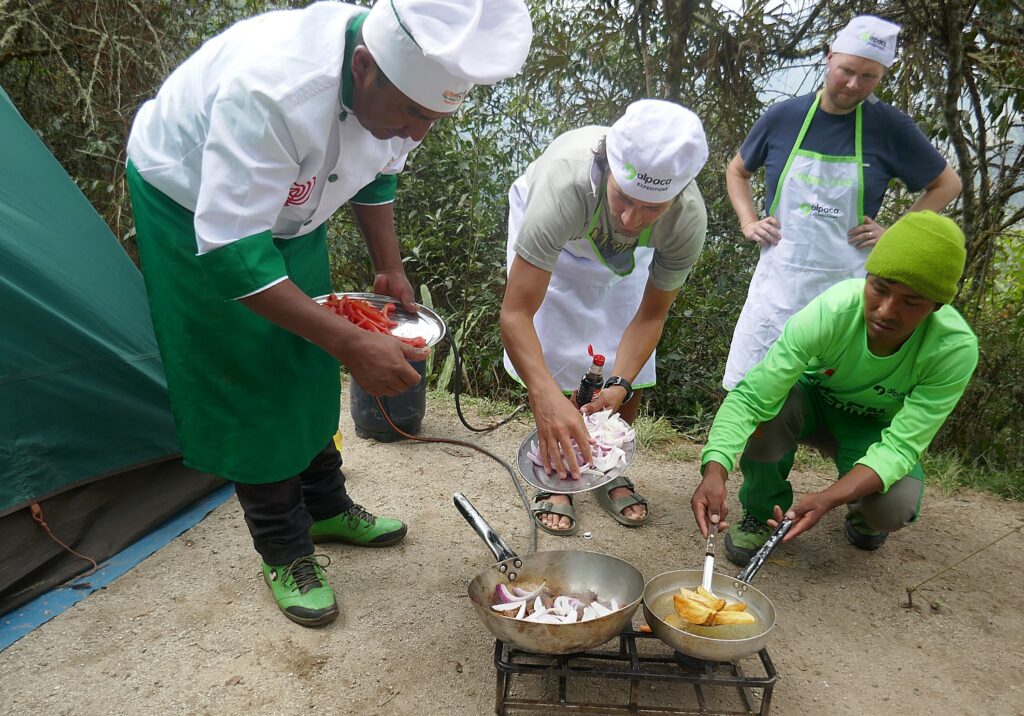

At the evening gathering, the night before we will reach Machu Picchu on the Inca Trail, Lizandro suggests that if there is anything that we would leave behind, that we donate it to the porters. Sarah and Eric compile a bunch of their stuff (the Inca Trail trek was the grand finale to six months of their travel odyssey) and bring it to the Alpaca Expeditions office the next day when we are back in Cuzco.
Alpaca Expeditions is clearly on the same page in appreciating the importance of responsible, sustainable tourism. But I would suggest there is still more to do, and perhaps Alpaca Expeditions, because it has become such a leader, could persuade the government to make some changes.
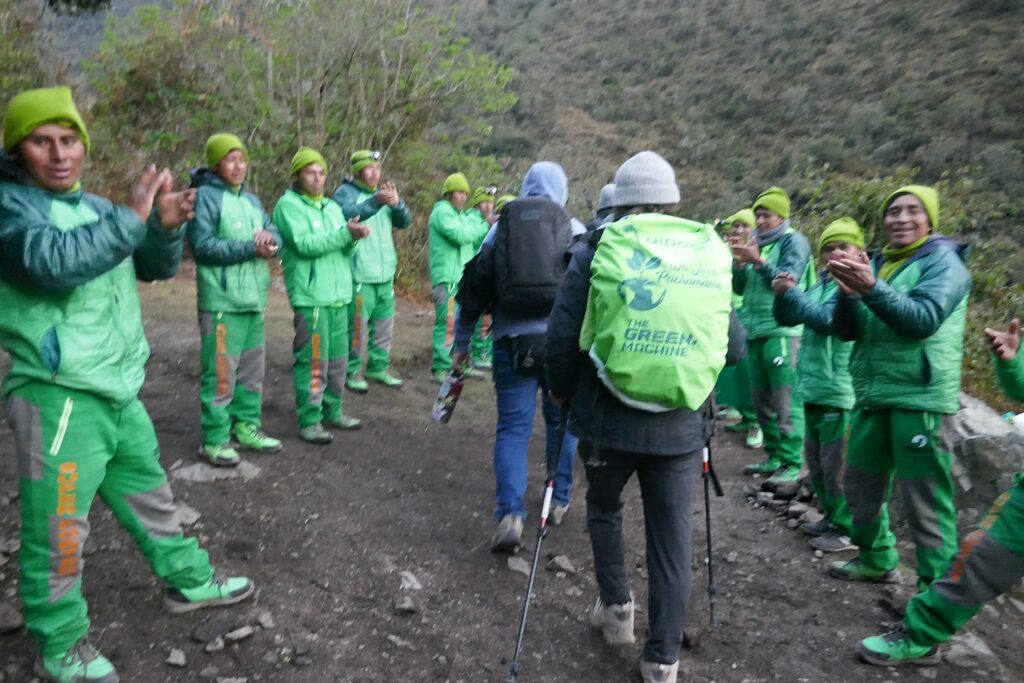

The trekking companies used to only hire uneducated men from the mountain villages – just as Lizandro was – whose opportunities were limited (considering how smart and articulate he is – basically learning English from the trekkers, one can only imagine all the opportunities he might have had if public education was available to him growing up). But not that long ago, the government made public education universal. And as a result, fewer are coming forward to be the porters because other opportunities are open to them. Now I wonder, whether a shortage of porters will inhibit the increase in tourism and trekking, which provides most of the dollars necessary to support the preservation and conservation, and the economic activity and jobs. In fact, all of us trekkers are not just appreciative of the porters, but feel somewhat guilty as we make way for them to pass us (!!) on the trail, thanking them as they go by.
So here’s an idea: the government, which already has campsites with public restrooms, and facilities for the Park Rangers, that they build storage sheds at the campsites so the operators can store the tents, tables and infrastructure for the season. In this way, they can reduce the loads that the porters have to carry. Then, more young people would probably sign up for the experience – if not a career – and in this way, the companies would have enough porters to support the number of trekkers, whose dollars fuel this virtuous cycle. That’s human ecology.
The permits to do the Inca Trail trek are limited to 500 a day for all the trekking companies (which includes 200 for trekkers and 300 for porters and staff) and get booked up months in advance.
More information: Alpaca Expeditions, USA Phone: (202)-550-8534, [email protected], [email protected], https://www.alpacaexpeditions.com/
See also:
VISIT TO PERU’S SACRED VALLEY IS BEST WAY TO PREPARE FOR INCA TRAIL TREK TO MACHU PICCHU
INCAN SITES OF PISAC, OLLANTAYTAMBO IN PERU’S SACRED VALLEY ARE PREVIEW TO MACHU PICCHU
ALPACA EXPEDITIONS’ INCA TRAIL TREK TO MACHU PICCHU IS PERSONAL TEST OF MIND OVER MATTER
DAY 1 ON THE INCA TRAIL TO MACHU PICCHU: A TEST
DAY 2 ON THE INCA TRAIL TO MACHU PICCHU: DUAL CHALLENGES OF DEAD WOMAN´S PASS, RUNCURACCAY
DAY 3 ON THE INCA TRAIL TO MACHU PICCHU: TOWN IN THE CLOUDS, TERRACES OF THE SUN & FOREVER YOUNG
DAY 4 ON THE INCA TRAIL: SUN GATE TO MACHU PICCHU, THE LOST CITY OF THE INCAS
__________________
© 2022 Travel Features Syndicate, a division of Workstyles, Inc. All rights reserved. Visit goingplacesfarandnear.com, www.huffingtonpost.com/author/karen-rubin, and travelwritersmagazine.com/TravelFeaturesSyndicate/. Blogging at goingplacesnearandfar.wordpress.com and moralcompasstravel.info. Visit instagram.com/going_places_far_and_near and instagram.com/bigbackpacktraveler/ Send comments or questions to [email protected]. Tweet @TravelFeatures. ‘Like’ us at facebook.com/NewsPhotoFeatures