By Karen Rubin, Travel Features Syndicate, goingplacesfarandnear.com
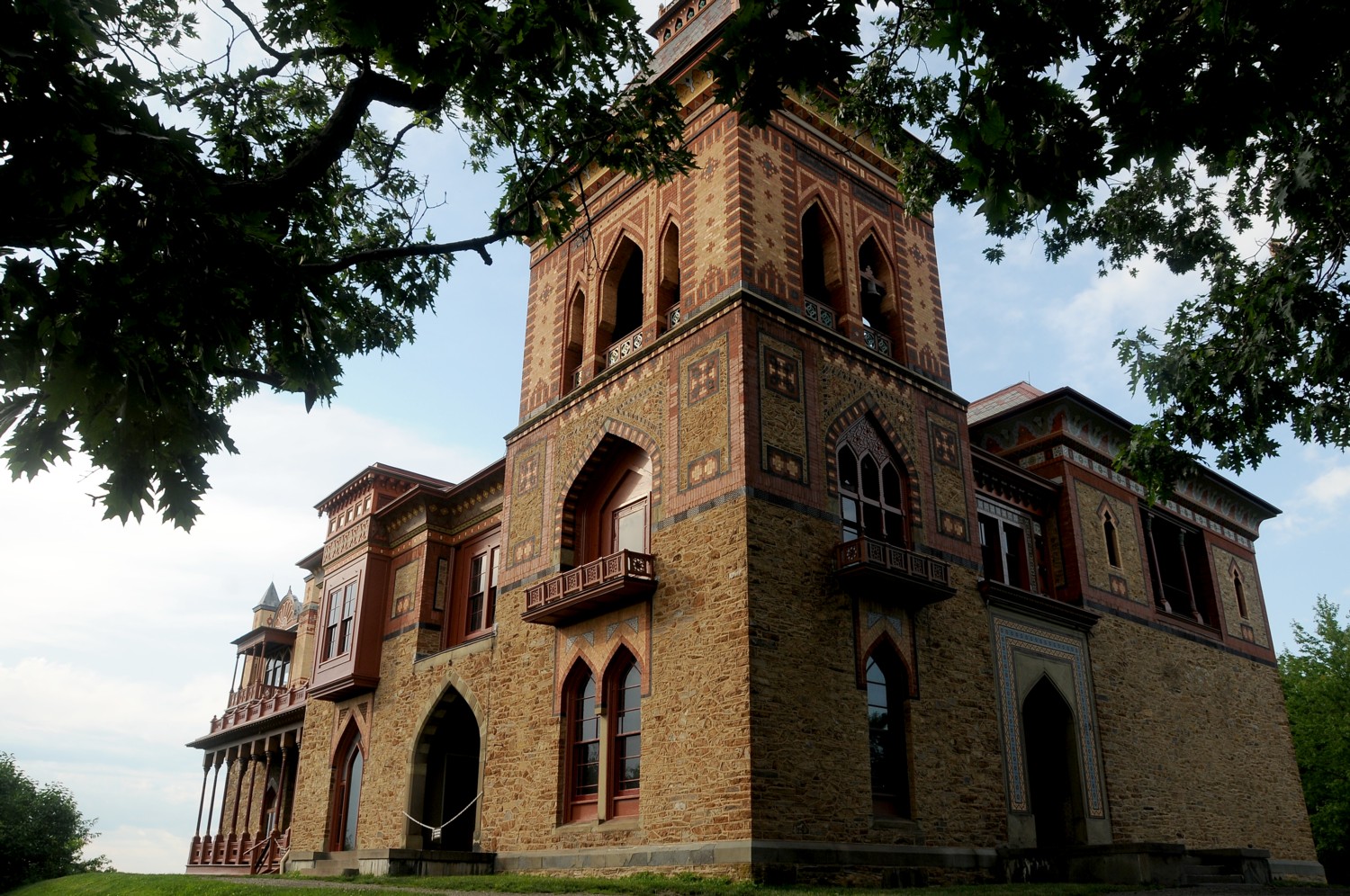
Fort Stanwix, in Rome, New York, is a revelation. Hardly anyone knows of it – it doesn’t even seem to merit a footnote in history – but it played a role in two incidents, one during French & Indian War and one during Revolutionary War, that proved pivotal for American history, like a tiny peg in the giant cogwheel of history.
A National Historic Site, Fort Stanwix also offers one of the best presentations of tribal Indians and European settlers in the colonial and Revolutionary War period. Indeed, the Erie Canal was built across what was the Oneida Carrying Place, vital to the earliest traders. This fort is where the British negotiated and signed the 1768 treaty with the Six Nations of the Iroquois Confederacy. I suspect this area is also where Melinda Gage drew upon what she learned of the Oneida Indian women to form key planks of women’s rights movement.
The presentation here (in contrast to how pitiful the Womens Rights National Site in Seneca Falls is) is fantastic, both in the exhibits and the commentary. Engaging, informative, dramatic, thoughtful. Also, the park rangers are in period dress so you really feel as if you have stepped back in history. You wind up speaking to these people as if it was 250 years ago.
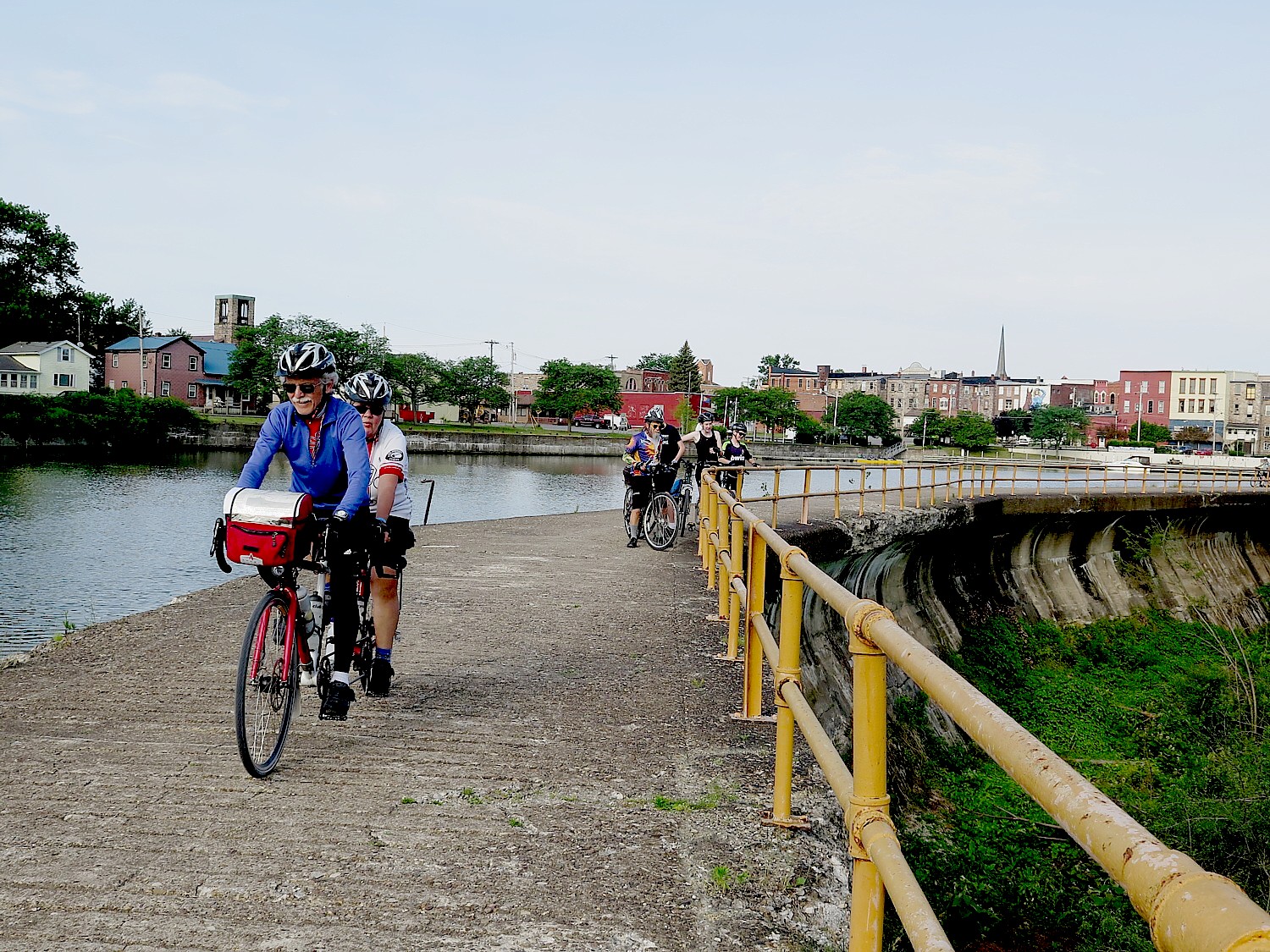
This part of the eight-day Cycle the Erie bike tour, 400 miles from Buffalo to Albany organized annually through Parks & Trails NY, takes us back to the very beginning of the United States, to its native American origins, European colonization and its emergence as an independent nation. It is 400 miles and 400 years of history.
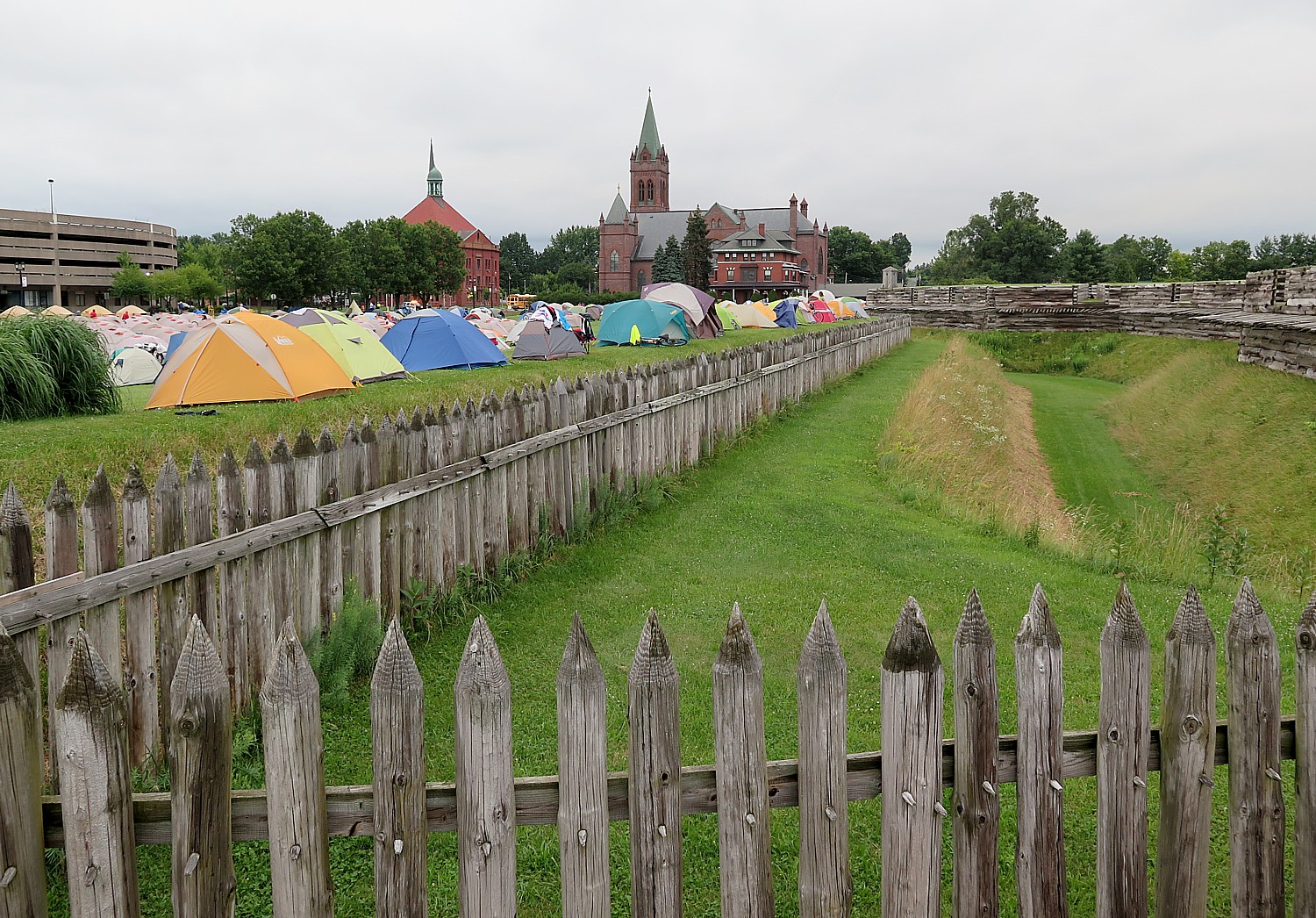

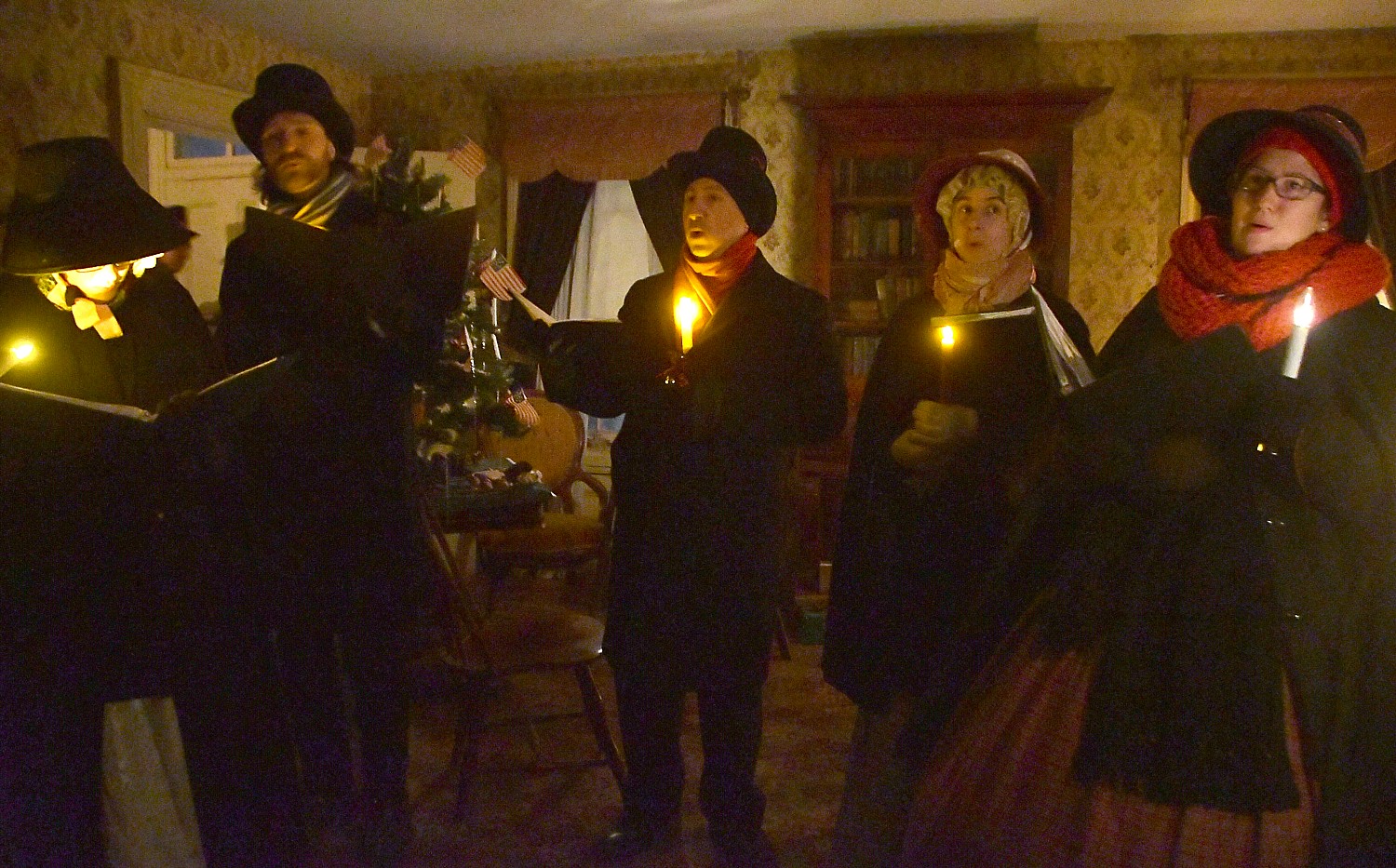
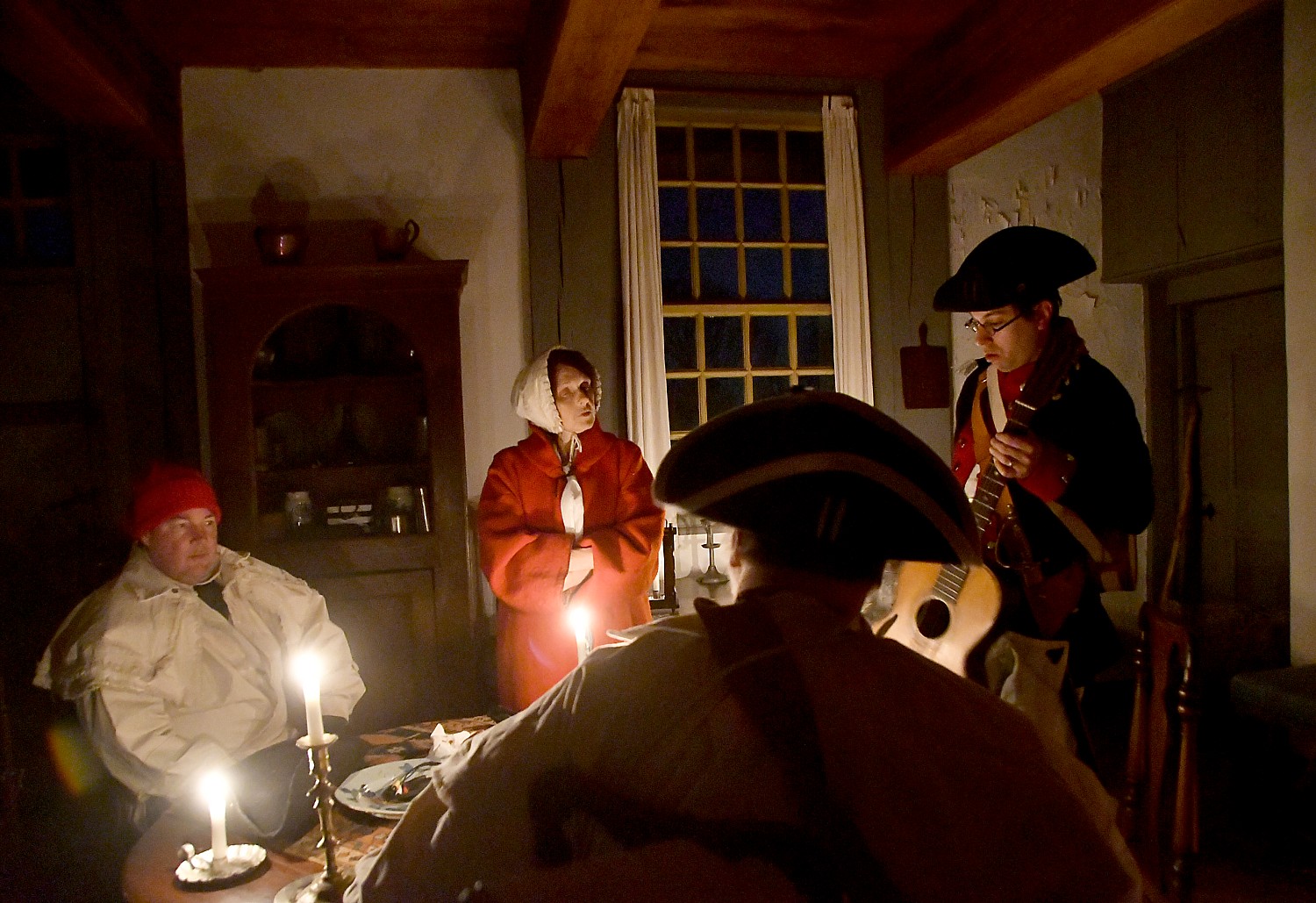
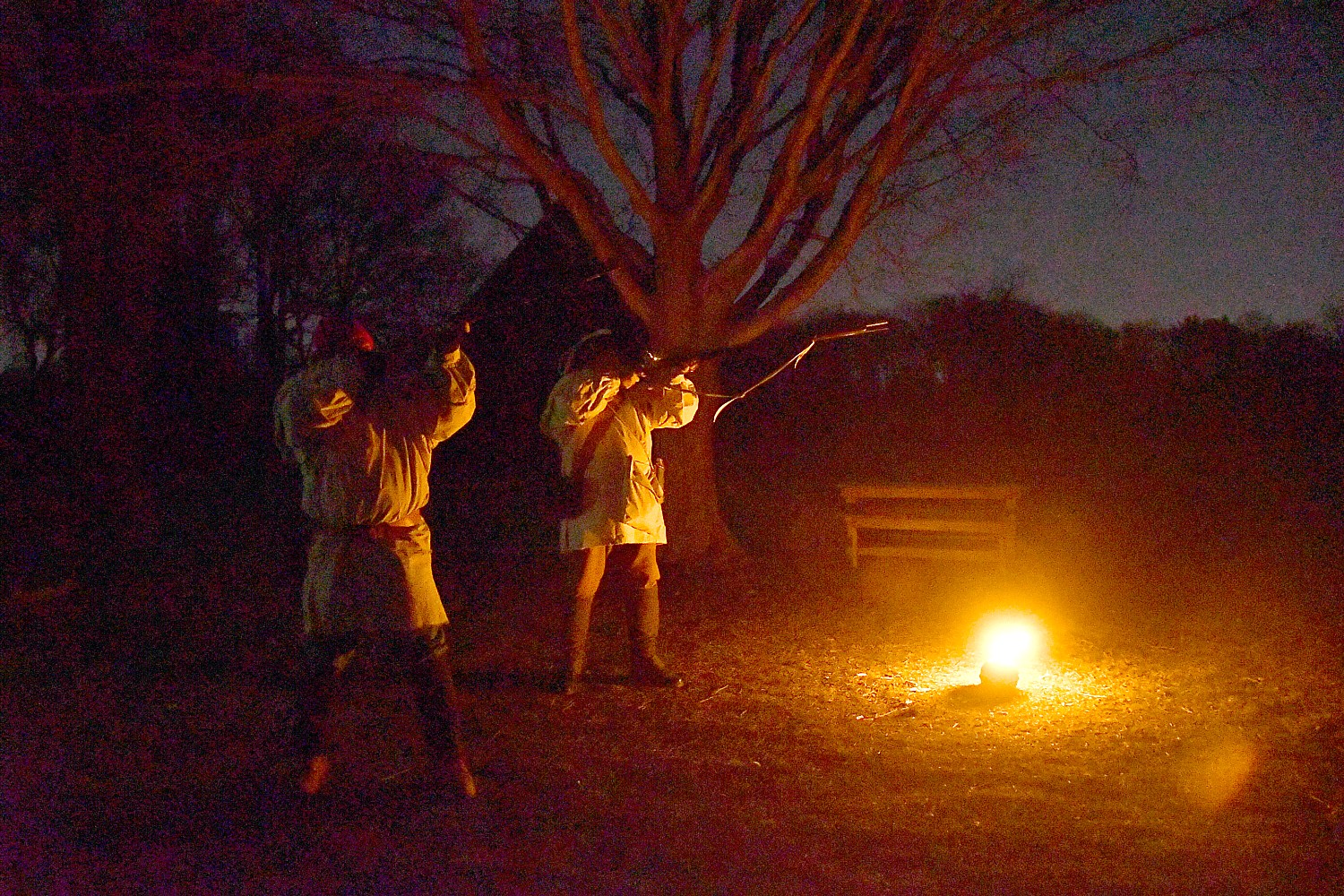
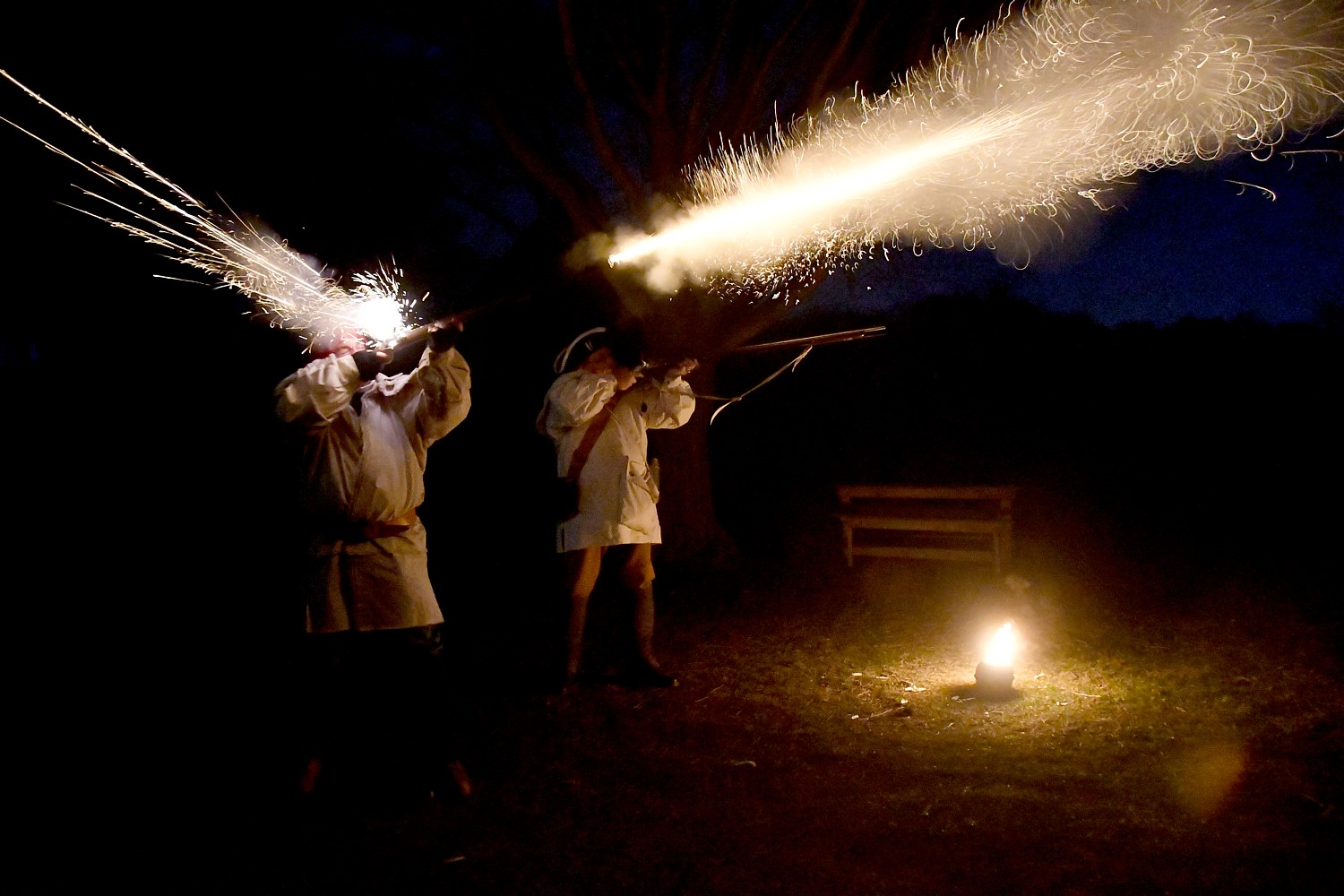
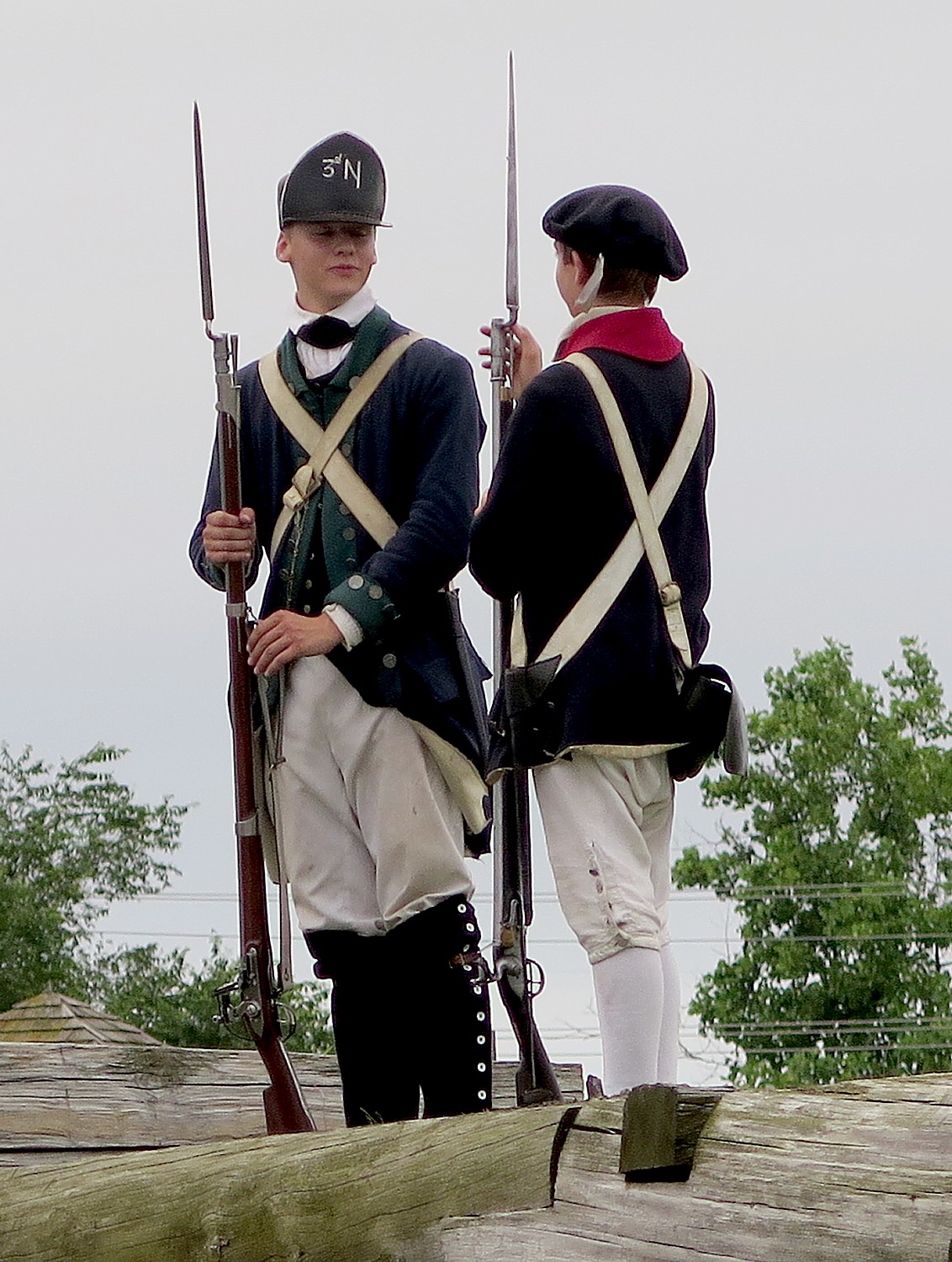
At Fort Stanwix National Monument in Rome (where the 750 of us actually camp out outside the fort, making it look like an army bivouac), we are put squarely into the drama of the American Revolution. Interpreters in period dress take on the roles of American soldiers and British prisoners in period dress – creating such realism that you appreciate so much more the context and the conditions. Most surprising, is that it also tells the story of the Native Peoples, almost entirely forgotten as having an equal stake in the Revolution. (It didn’t go well.)
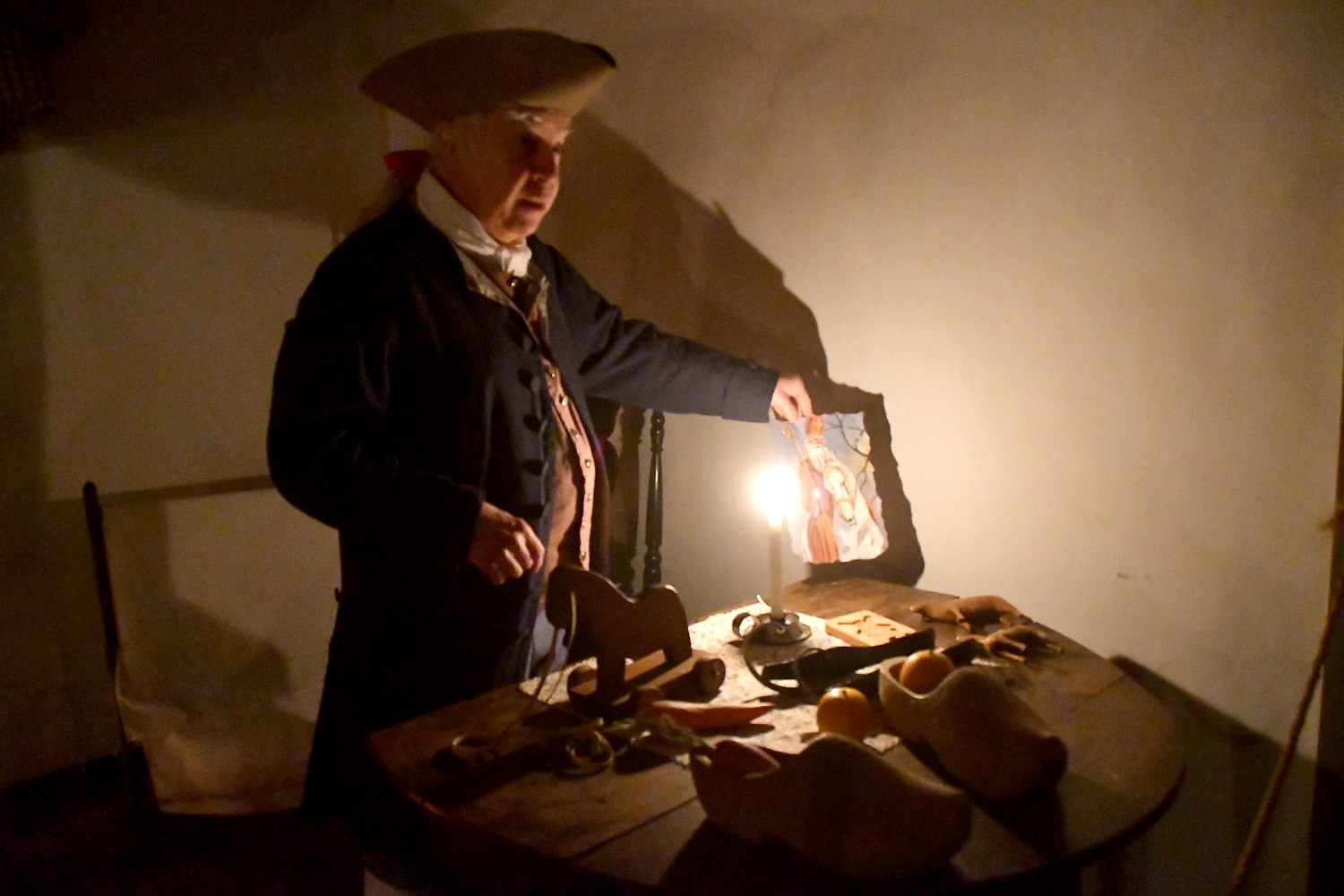
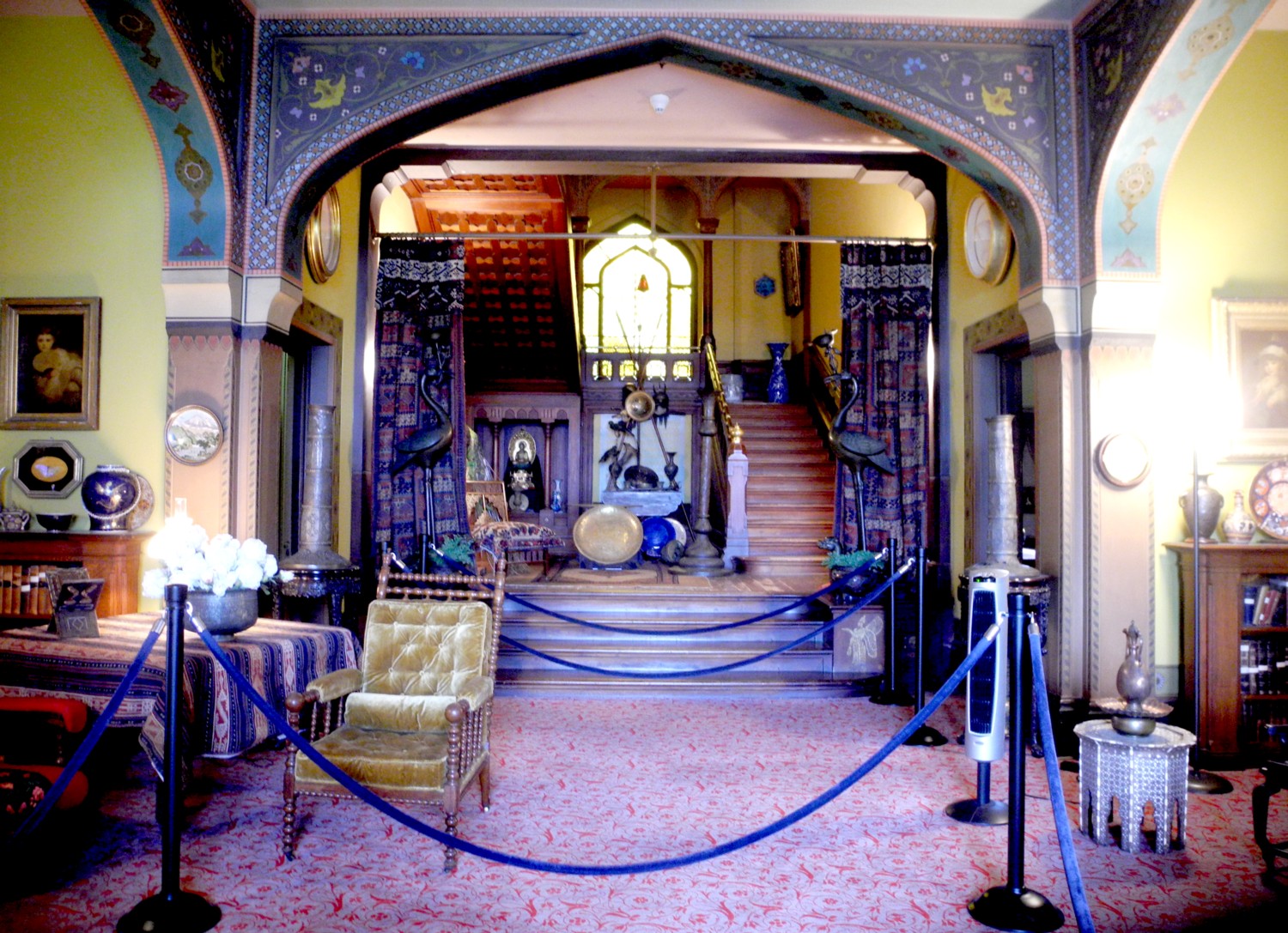
The reconstruction of Fort Stanwix comes alive through the personal stories recounted inside the fort. You get to experience the American Revolution and the Siege of Fort Stanwix through the eyes of soldiers and their families, American Indians and traders. This is accomplished through the realistic recreations (especially of the fort), the costumed interpreters, outstanding markers, artifacts, the art, portraits and graphics, and superb videos. They create characters who are composites of actual people, and you hear their voices in a context.
It’s humbling to realize how little you actually know about Colonial America and the American Revolution.
The Fort puts the competing interests of the Patriots, Loyalists and Indian peoples into balance. You have empathy for each. (Especially the Native Americans, who were dragged into the fight, upsetting a long-standing peace among the Confederacy of Iroquois nations, found their whole society upended, and were literally screwed by every European and American they dealt with. George Washington, shockingly, even betrayed the Indians who were allied with the Patriots). But you also understand better the Loyalists, whose property was being seized by the Patriots, and the Patriots, who were not necessarily British subjects, but German and Dutch colonists – whose property was being burned by the Loyalists.
The National Park Service is keeping the fort open late for us and hosting tours, and is keeping the visitors center open all night (the indoor camping location, though, is off-site at a local YMCA).
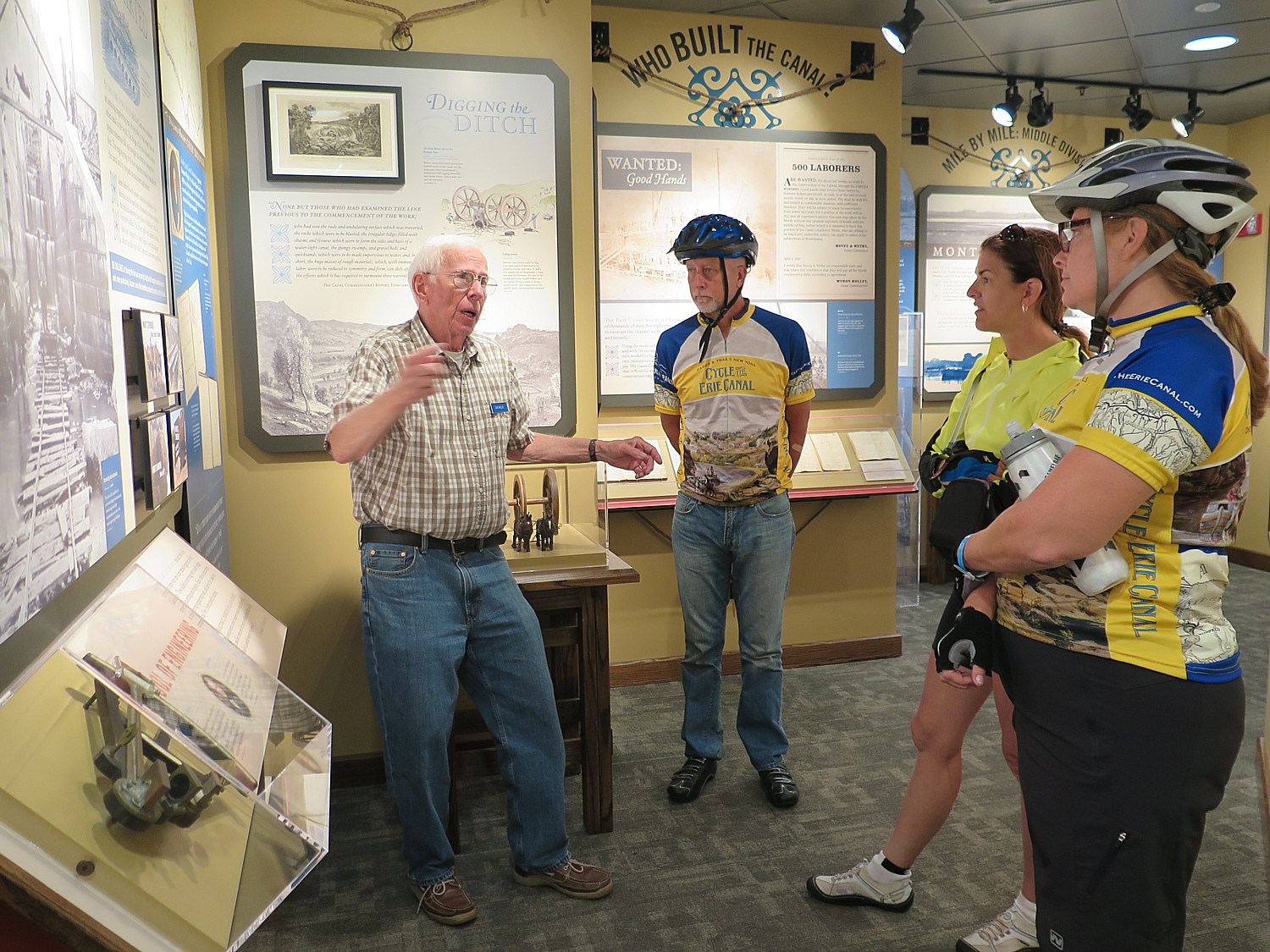
We arrive at Fort Stanwix after biking 50 miles from Syracuse, a good chunk of our Day 5 ride in drenching rain. I set up my tent (fortunately, the rain stopped just as I came into Rome), grab a shower, and race over to the visitor center to join a guided tour. I am so lucky to attach myself to the same Park Ranger as I toured with two years ago, on my first Cycle the Erie tour.
Fort Stanwix as we see it today literally rose out of ash heap of history – reclaimed from earthly grave.
At one point, the fort was the reason Rome developed at all, but ultimately Rome grew up over its ruins, from fire and neglect. Then the city Rome went through a decline. But in 1960s, as part of urban renewal, planners wanted to redevelop the dilapidated downtown. A grassroots movement grew up to excavate the fort; meticulous archaeology unearthed some 400,000 artifacts. (Visitors can actually get a back-stage view of the archaeology being done during summer tours.)
The National Park Service was faced with a quandary – its mission at the time discouraged reproduction or re-creation of a historical site. But there were strong arguments in favor of reconstructing the fort: they found the original fireplace (the only part of the fort that remains of the original, which we get to see); had the original plans (obtained from British archives); plus papers and drawings so they could reproduce it accurately; and letters of soldiers so they had a better idea of what happened here.
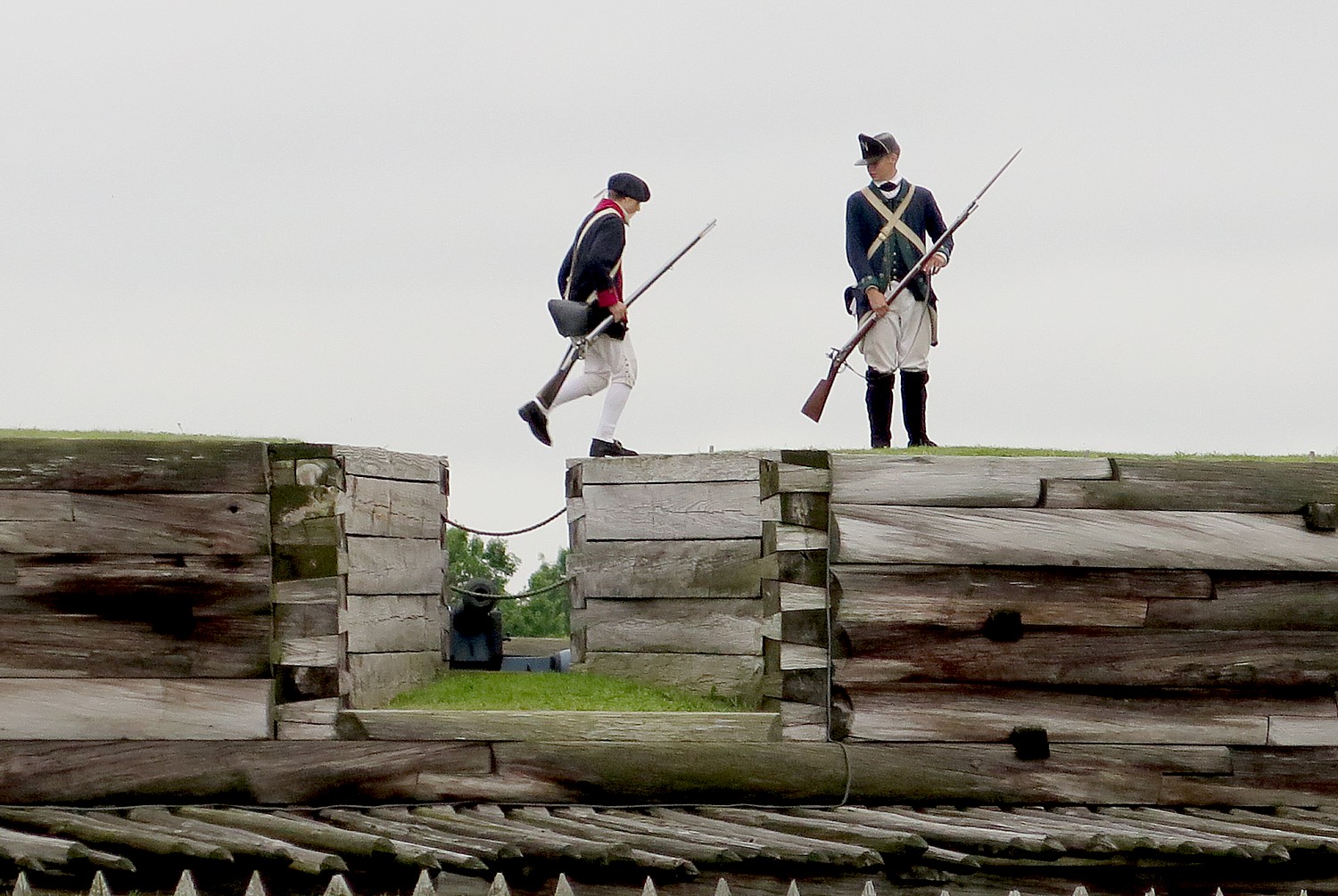

The location of this fort is significant. It sits along “Six Miles that Changed the Course of America,” reads the National Park Service brochure. “For thousands of years, the ancient trail that connects the Mohawk River and Wood Creek served as a vital link for people traveling between the Atlantic Ocean and Lake Ontario. Travelers used this well-worn route through Oneida Indian territory to carry trade goods and news, as well as diseases, to others far away. When Europeans arrived, they called this trail the Oneida Carrying Place and inaugurated a significant period in American history – a period when nations fought for control of not only the Oneida Carrying Place, but the Mohawk Valley, the homelands of the Six Nations Confederacy and the rich resources of North America as well. In this struggle Fort Stanwix would play a vital role.”
The British built the fort in 1758 with the permission of the Oneida to protect their commerce, but abandoned it to cut back on spending after the French & Indian War (taxes imposed by Britain to recoup their expenditures is what incited the American Revolution).
The fort was never put to the test, because the French were defeated elsewhere. But though Fort Stanwix fell into decay, the site was still important for trade and relations with the Six Nations.
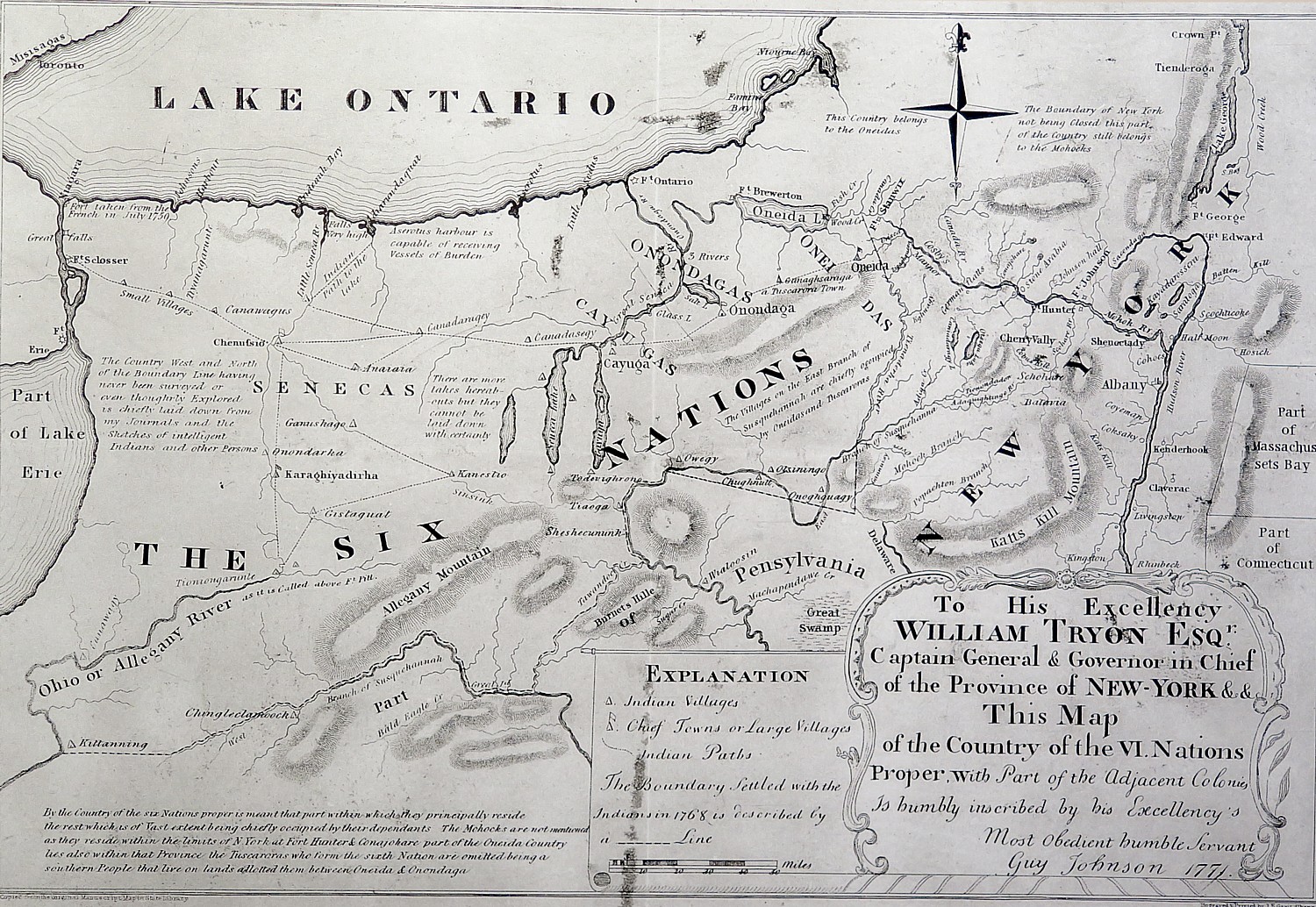
It is here at Fort Stanwix, in 1768, after the Europeans had spread into “empty” spaces and fought with the Indians, that Sir William Johnson, Indian Supervisor, negotiated a treaty with the Six Nations of the Confederacy, basically laying out the terms that everything east of the fort would be for Europeans, and everything west would be for Indians.
“Over 3,000 American Indians from the Six Nations, Shawnee, Delaware, Mingo and other dependent tribes attended the treaty negotiations,” the notes read. “Ignoring British Crown instructions, Sir William Johnson encouraged the Six Nations to draw a new boundary line favorable to their mutual interests. Rather than settling tensions, frontier strife between colonists and American Indians increased.”
“I can never look upon that (Proclamation of 1763) in any other light… than as .. temporary expedient to quiet the mind of the Indians,” land speculator George Washington wrote to surveyor William Crawford, 1767. “Any person… who neglects the opportunity of hunting out good lands…for his own, in order to keep others from settling them, will never regain it.”

Meanwhile, British attempts to govern the growing colonies from afar and the associated costs led to strained relations. Hoping to defray the cost of colonial administration, the British parliament taxed many goods arriving in North America. But growing independence and identification as Americans caused many colonists to question British rule. Tensions steadily increased until American “Patriots” declared their independence in 1776.
The exhibit gives me a new perspective: a good number of colonists were not British – they came from Germany, Holland and other places. I realize that becoming a Patriot would not have been such a hard choice as for those with British ties.
“For colonists living on the frontier, the issues included British imposed restrictions on trade, limits on settlement, and continuing violence with American Indians. As war approached, many colonists had to choose between remaining loyal to the King or joining the movement to American independence.” Each side considered themselves “patriots”. But those who stayed loyal to the Crown became known as “Loyalists,” while those who sought independence called themselves “Patriots.”
In 1775, Patriots and Loyalists began struggling for control of the New York frontier. The British invaded the Mohawk Valley in 1777. Their strategy was to capture an important east-west supply route, deprive American soldiers of food grown in the valley, and strengthen Six Nation and Loyalist Alliances, and slice the colonies.
British General John Burgoyne led an invasion of New York from the north and west. His army advanced from Montreal towards Albany. A second force commanded by General Barry St. Leger invaded the Mohawk Valley. Strategically, St. Leger aimed to control the Oneida Carrying Place, create a diversion to split Patriot forces, and reinforce Burgoyne. Politically, he wanted to rally support among American Indian allies and Loyalists.
Patriots had taken over Fort Stanwix in 1777 and renamed it for General Schuyler. The fort was under the command of Col. Peter Gansvoort when it came under siege by the British. Some 2,000 British troops set up a blockade, helped by Indians allied with the British, which went on for months.
General Nicholas Herkimer assembled an 800-man militia to come to the fort’s aid, but was betrayed (by Molly Brant, a Mohawk woman allied with the British, and the second wife of Sir William Johnson). Herkimer’s militia was ambushed along the way at Oriskany. This became one of the bloodiest battles of the Revolutionary War, in which 600 were killed in a matter of hours. General Herkimer, himself, was fatally wounded, dying 10 days later. (Later in our trip, we pass Herkimer Church where he died, and his home.)
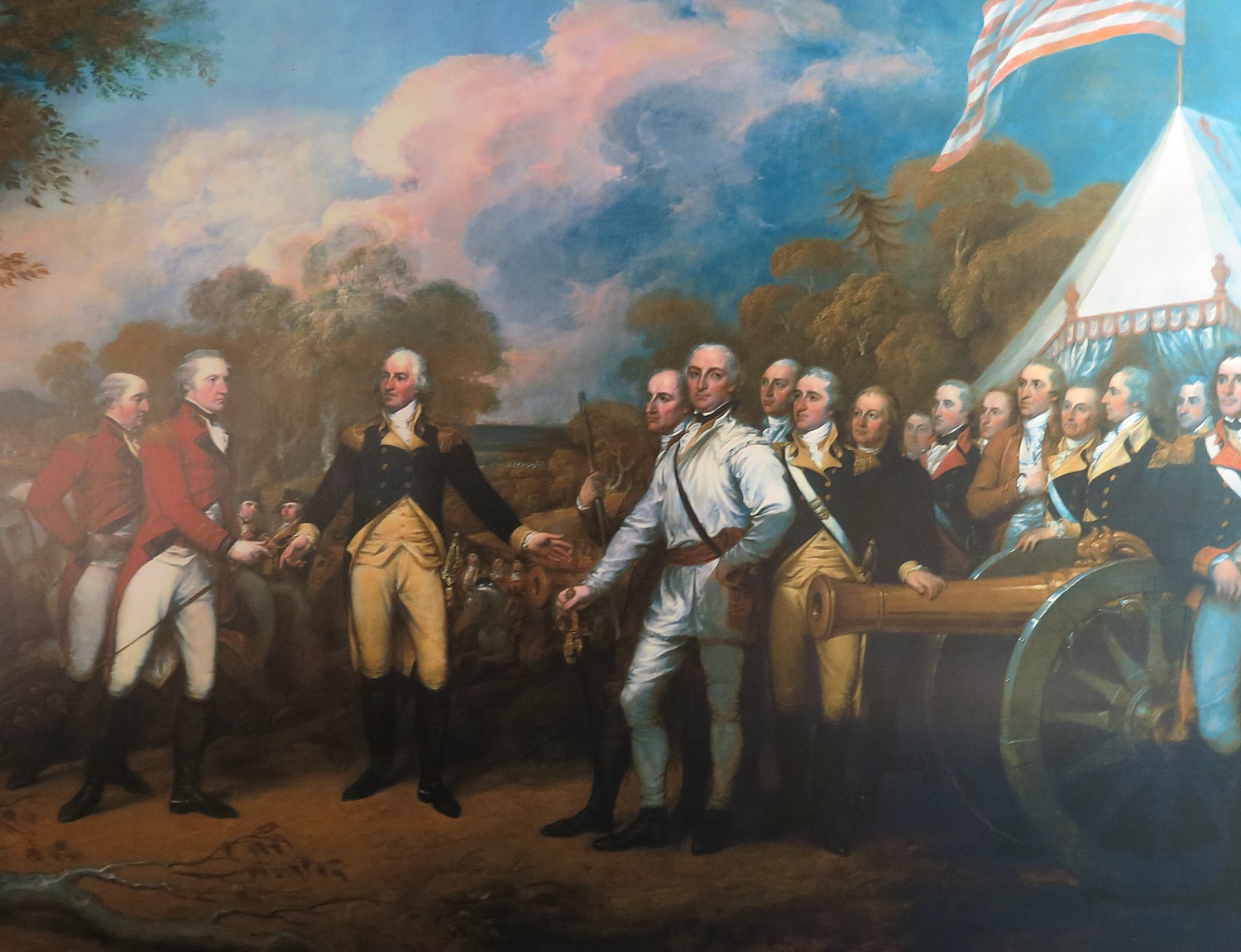

But the Indians allied with the British, hearing that the Americans had plundered their encampments, left the fort to go to their families’ aid. Fearing that more American reenforcements were on the way, the British retreated, handing the Patriots their first victory (of sorts) of the Revolutionary War. This, critically, boosted the Americans’ morale, and helped set the stage for the Patriots’ victory at Saratoga (under General Benedict Arnold).
This, then, is what changed the course of the war. Because of the victory at Saratoga, which was the unanticipated consequence of what happened at Oriskany and Fort Stanwix, Americans won the critical support of France (long time enemy of Britain), without which, the Americans could not have defeated the British and the British were forced to fight a world war.
In 1778, the British again attempted a formal invasion of New York, planning to burn the Mohawk Valley fields of grain that supplied the Continental Army.
The last battle here took place in 1780, when a work party outside the fort was ambushed by British-allied Indians and Loyalists.
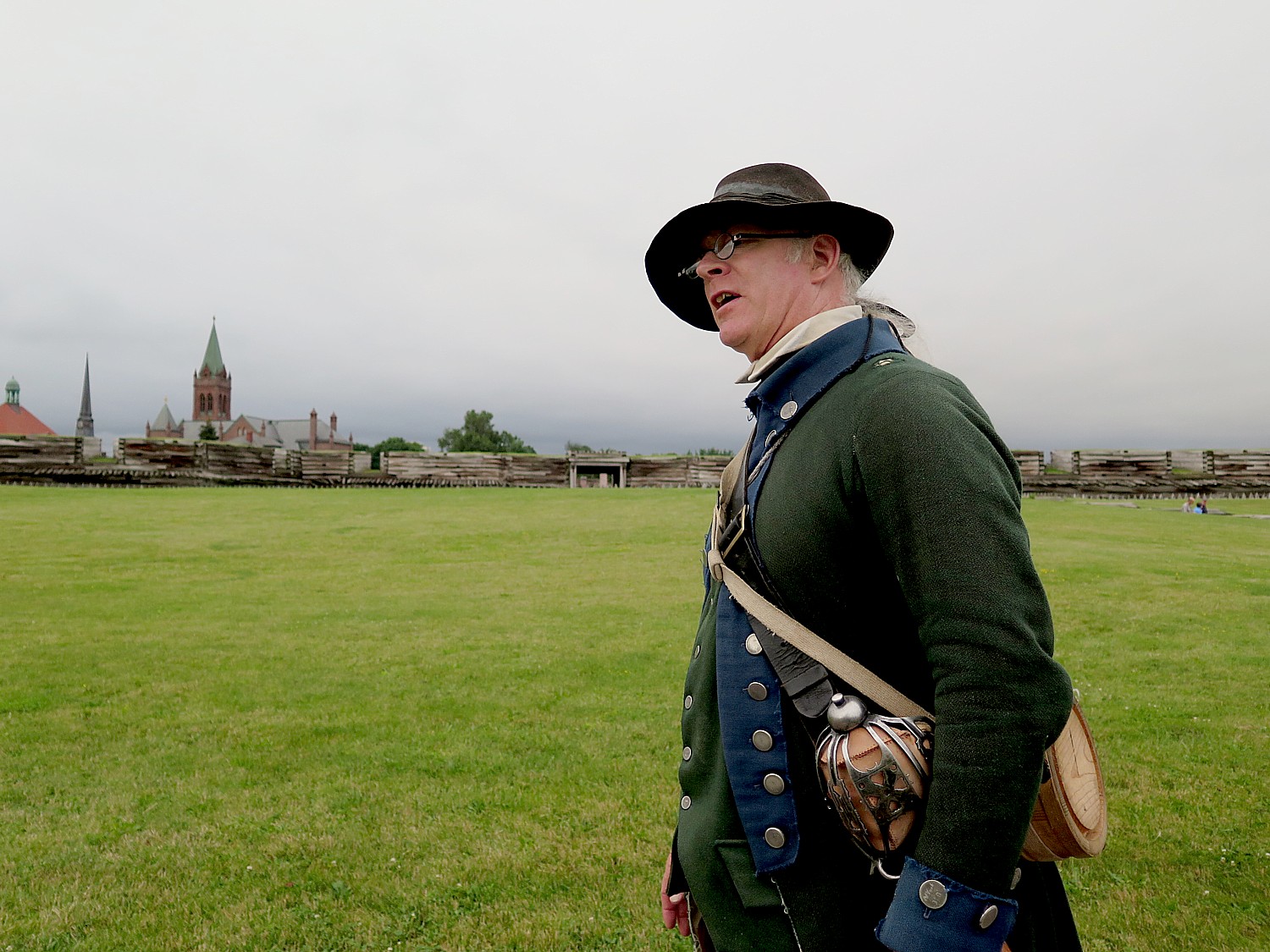

But for most of the Revolutionary War, “It is frustrating for the troops to be here, the backwater of the Revolution,” Park Ranger Bill Sawyer, who is dressed in the uniform of the 3rd New York regiment, tells us. The men were upset because they were far from the fighting. But “Washington was vindicated in his decision to keep it fortified because the British refortified Fort Ontario. Washington wanted to block the British.”
And I am certain that those disgruntled soldiers confined to Fort Stanwix never appreciated that as a result of these events at Fort Stanwix, the British grand plan to slice off New York from the rebelling colonies and cut off the Continental Army’s source of food, failed. Instead, the Americans had the critical support of France.
Fort Stanwix: Living History
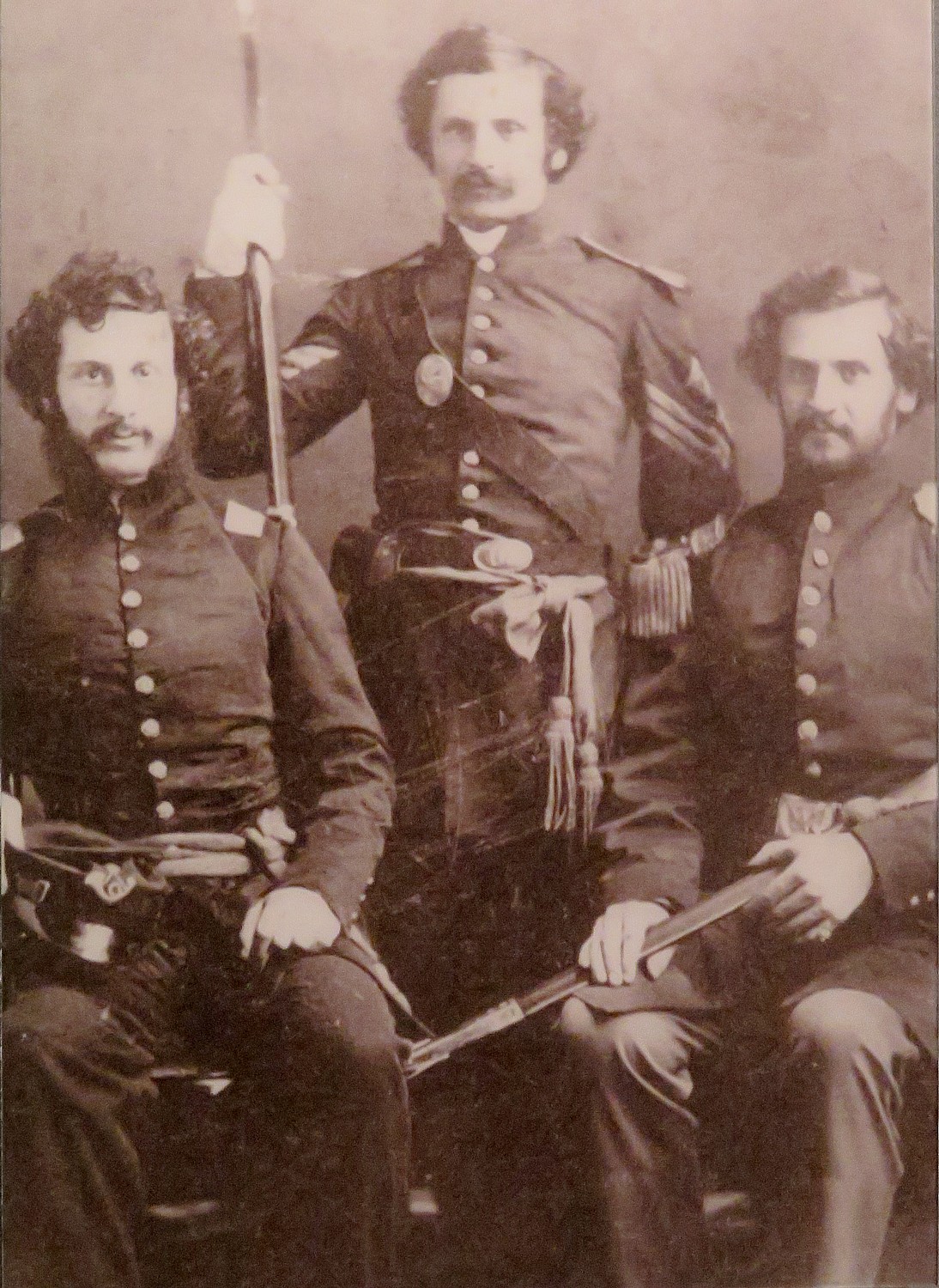
After this introduction in the Visitors Center, Park Ranger Bill Sawyer, walks us into the Fort, where we are greeted by costumed interpreters dressed as American soldiers. A couple of teenage boys (summer interns at the fort) patrol the ramparts of the fort. You are immediately transported back centuries.
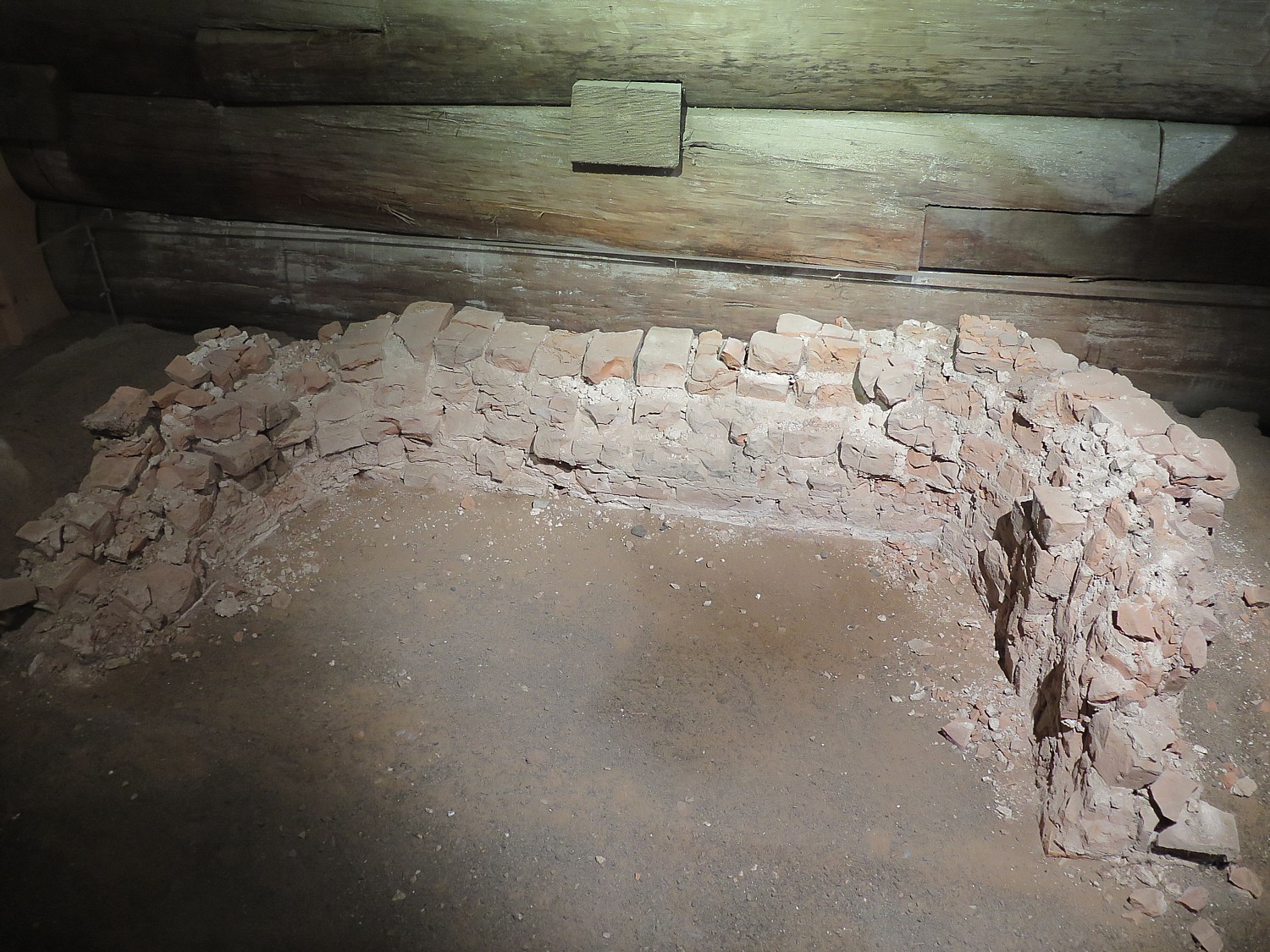

This fort is a nearly complete reconstruction on the original foundation – the only thing original is a fireplace (that can be seen in one of the rooms). Over the decades, Rome was built up on top of the fort. Archaeological excavations conducted in 1970-73 uncovered the site, but all the artifacts were removed, the site completely cleared, and the fort rebuilt with new materials.
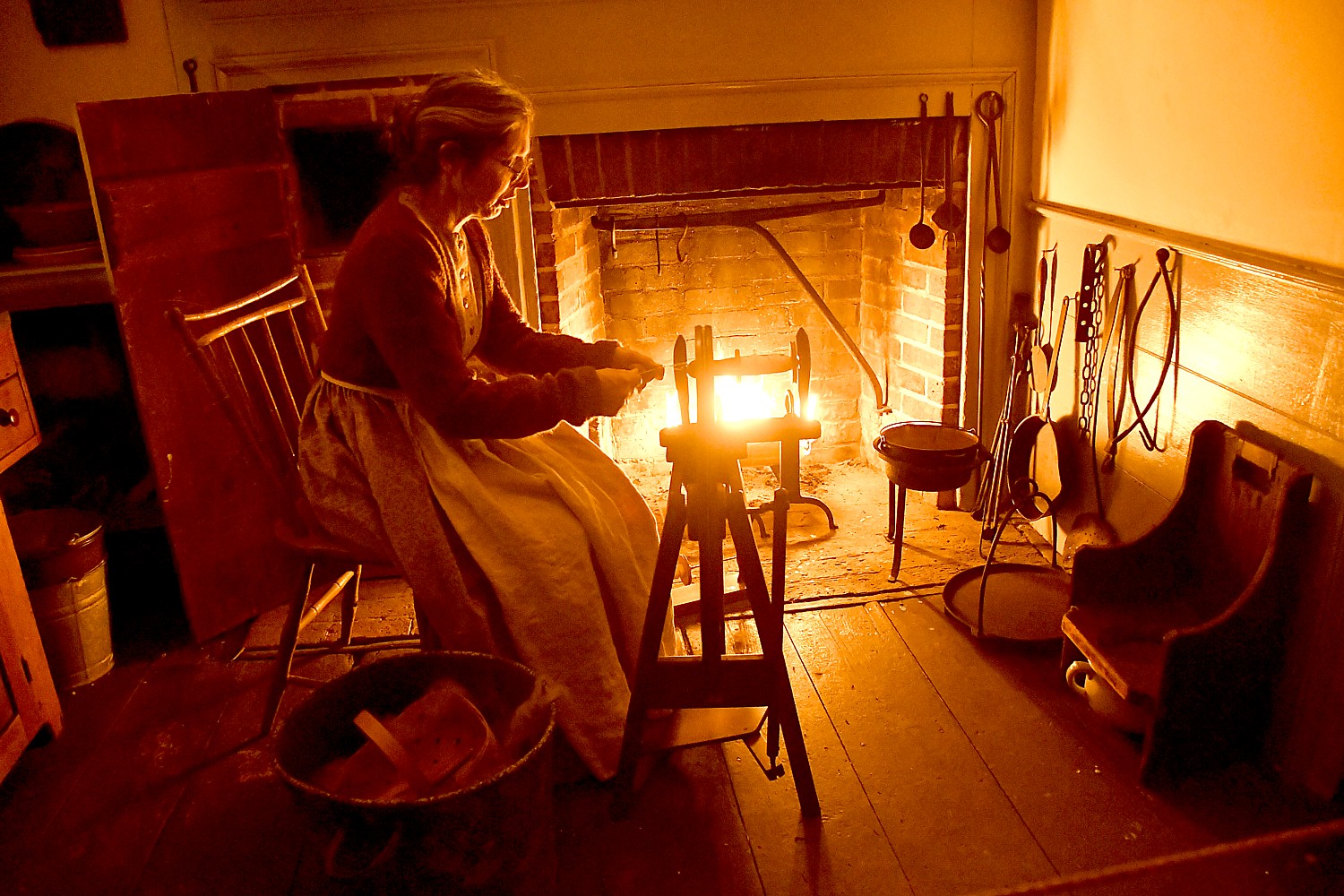
The fort held 800 soldiers (twice the number the fort was built to hold); families of soldiers (who couldn’t afford to maintain them in their homes) camped in the ditch outside the wall; women would try to get jobs within the fort. People died of disease and winter cold.
By February 1778, the soldiers’ clothing was reduced to rags, they hardly had any bedding left or blankets. They would have been stationed here for anywhere from 4 months to 2 years. Morale was terrible.
We see the harsh living conditions. Artillery men, though, had somewhat better accommodations, because they were specialists. “They had to have knowledge of math and the use of measuring tools to calculate the trajectory of cannon and mortar. They had better pay and living conditions.”
We visit the different rooms for the junior officers, a family quarters, the officers’ lodging, the orderly room, the surgeon’s day room. The Commandant’s HQ had a fine room befitting his wealth and high station and had a private assigned.

On my first visit, two years ago, I was able to see an outstanding film that depicted life in the fort and how the soldiers suffered. “The walls imprisoned them, supplies cut off. They were overcome by boredom and hunger. They wanted to go fight. Five men deserted, headed to Canada. Gansvoort sent out a band of Indians to recapture them. They were executed as an example to the rest….It was a forsaken place. Finally, they were sent to war.”
On my first visit, one of our cyclists, Peter Reeve, was British, though living in Maryland since 1981, and gave me the British perspective: “The British people didn’t care to keep America,” Reeve told me. “They didn’t want to spend the money fighting the Revolution. Most British generals were against the tax acts. General Howell supported the Americans’ grievance.”
While major battles took place in the South, minor battles and guerrilla-style warfare characterized the fighting in New York. General Washington lamented that crops that were being destroyed in these raids were needed to feed his army surrounding New York City. These raids and counter-raids were waged by Patriots, Loyalists, American Indians, British and British-allied Germans, alike, often against civilians, and were among the most brutal of the war.
The fort served as an isolated outpost for another four years after the siege. The inaction drained morale and the constant shortage of food and munitions made the soldier’s life insufferable. Regular petitions for transfer and increasing desertions reflected the wretched conditions.
By 1779, British strategy changed and they invaded the other colonies. Though Britain won most of the battles, they failed to destroy the Patriot army. Outmaneuvered, the British surrendered at Yorktown in 1781, bringing an unofficial end to the war.
Following their 1781 defeat at Yorktown, the English saw little value in continuing large scale war in America. Two years later, war ended with the signing of the Treaty of Paris by the US, France and Britain. As the British Army withdrew, Loyalists migrated to Canada and elsewhere.
American Independence Voids Treaty with Indians
The 1783 Treaty of Paris officially ended the war – at least between the British and the colonists. However, no terms of peace were negotiated for the American Indians. In later years, American Indians negotiated their own treaties with the Patriots (who tossed out the Treaty of 1768.)
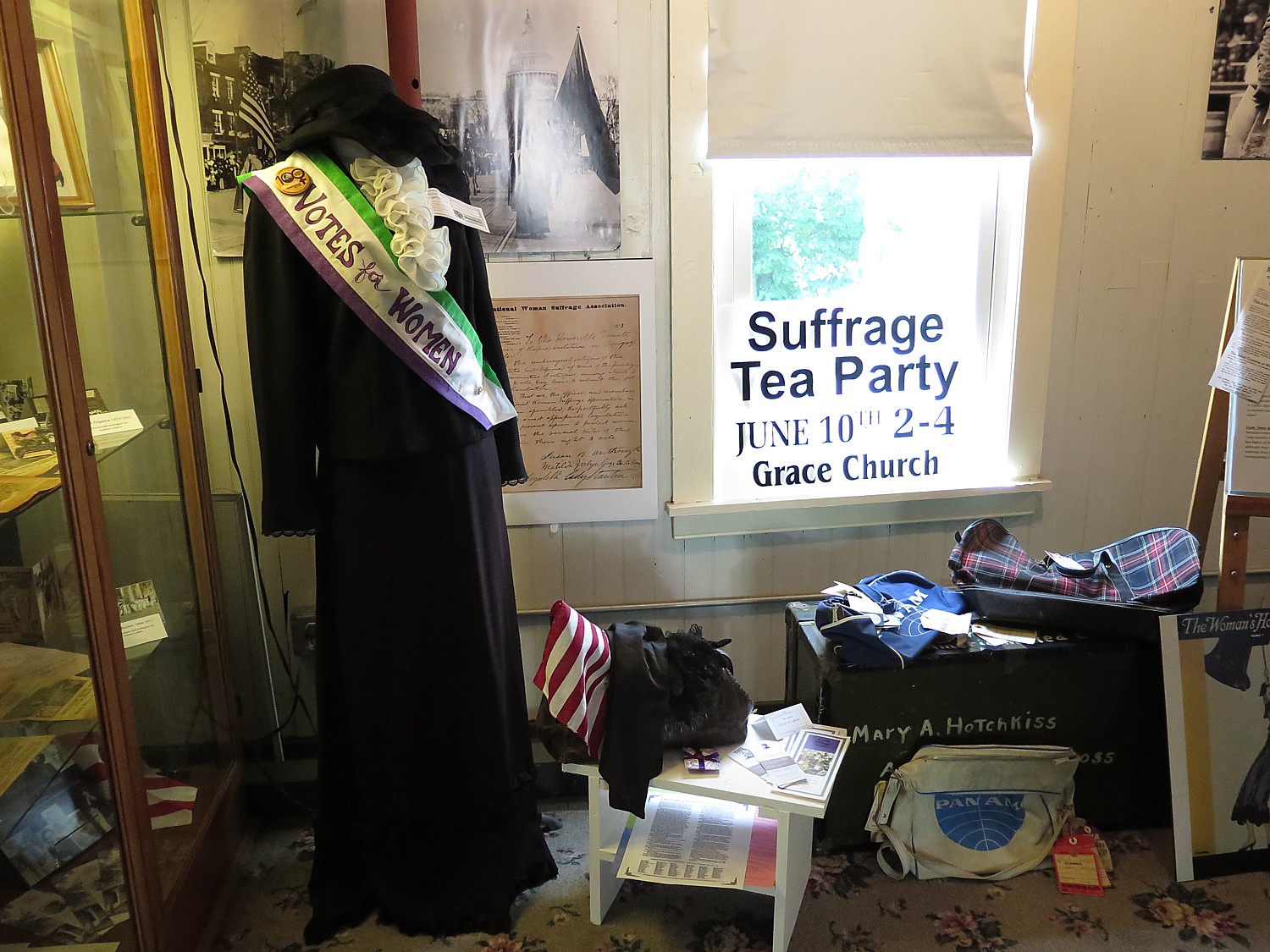
The focus at Fort Stanwix on Indian history is very clear from the first display that greets you as you enter the Visitors Center – of trappers trading with Indians.
American Indians’ history, NPS Ranger Sawyer says, “was long ignored. Now we interpret to include it.”
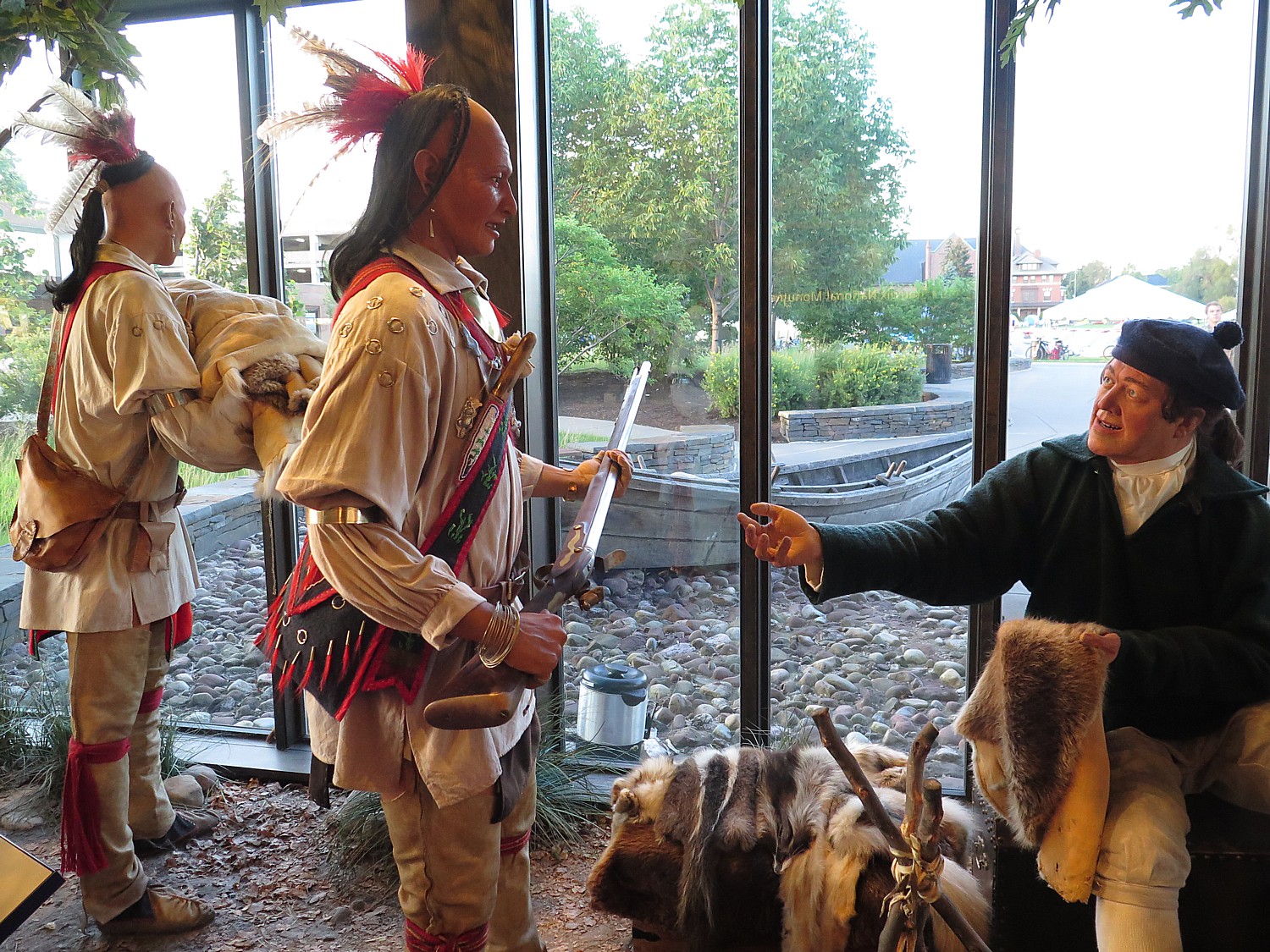

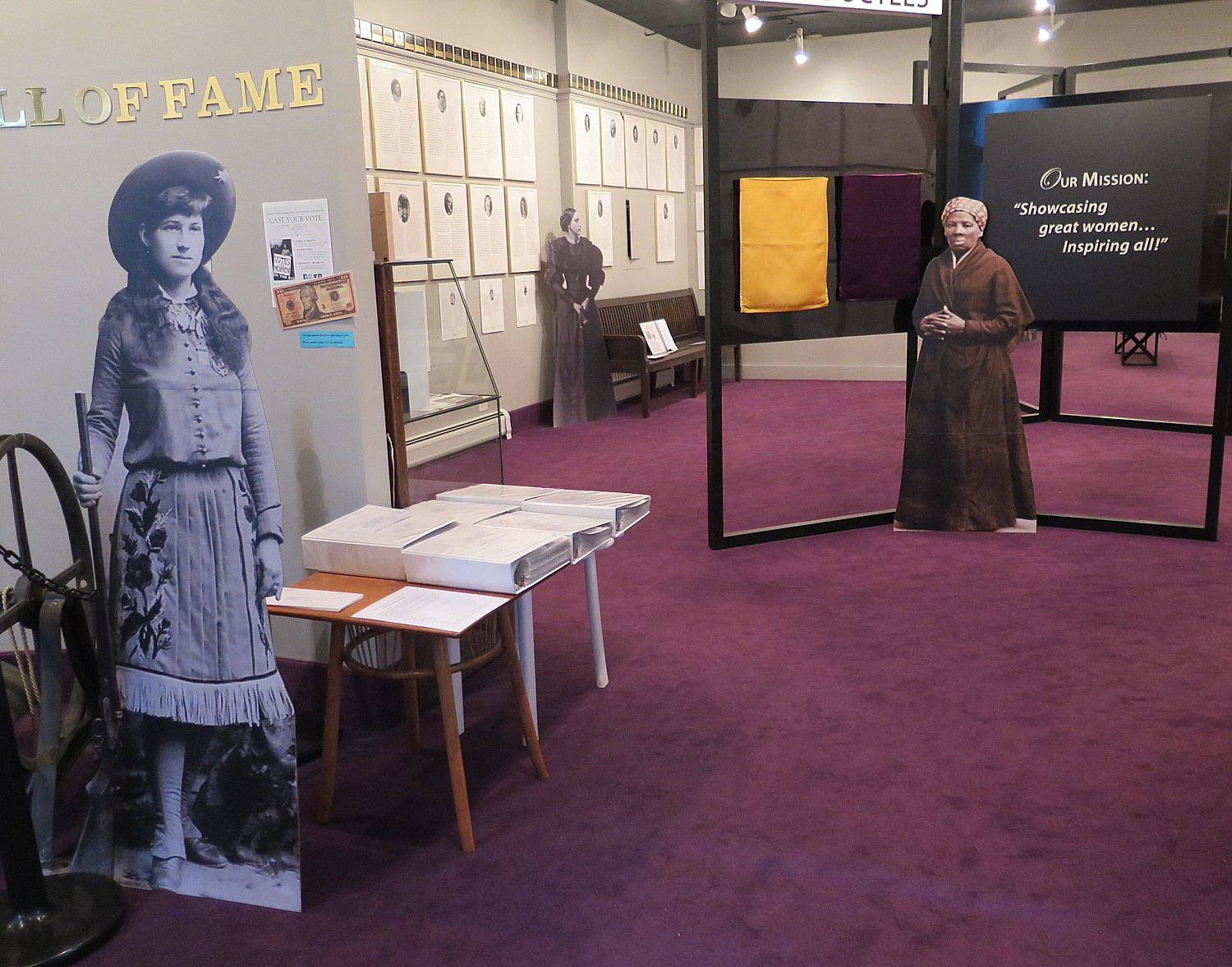
Indeed, Fort Stanwix offers one of the most interesting and informative presentations about American Indians outside of the Smithsonian’s Museum of the American Indian in Washington DC.
I am most surprised to see that the Indians lived in villages, with a grid street plan; they wore western-style shirts and many had European names. They had many of the same household goods as the colonists – an indication of how well-developed trade had become, and in fact, how dependent the Indians had become on trade.
The constant theme in the history between the Indians and European settlers, though, was how the Indians were constantly betrayed.
The Indians wanted no part of the Revolutionary War and tried to stay neutral. That changed with the Battle of Oriskany, though.
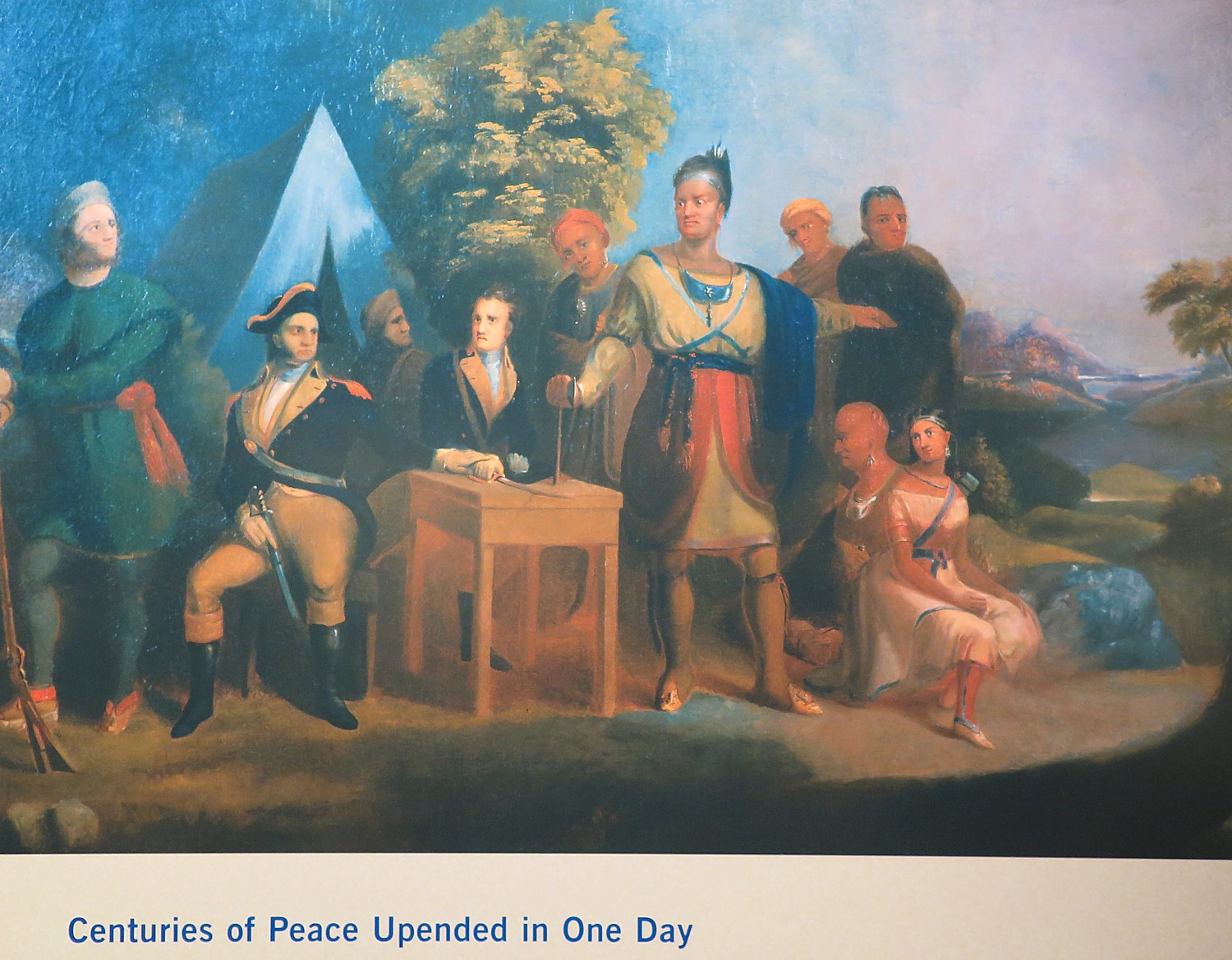

The Revolutionary War split the Iroquois Confederacy (“Iroquois” was the French name for the Haudenosaunee, “People of the Longhouse”). Mohawks led by Joseph Brant (the brother of Molly Brant who triggered the ambush of Herkimer’s militia at Oriskany) adhered to their long-standing allegiance to the British, and eventually most Cayugas, Onondagas, and Senecas joined them. But Oneidas and Tuscaroras sided with the Americans, owing in large measure to the efforts of their Presbyterian missionary Samuel Kirkland. The Revolution became a civil war for the Iroquois, as Oneidas clashed with Senecas at the Battle of Oriskany in 1777. (“Centuries of peace upended in a single day,” the notes read.) Iroquois suffering was compounded in 1779 when General John Sullivan, on orders of General Washington, led an American army through their lands, burning 40 towns and destroying crops.
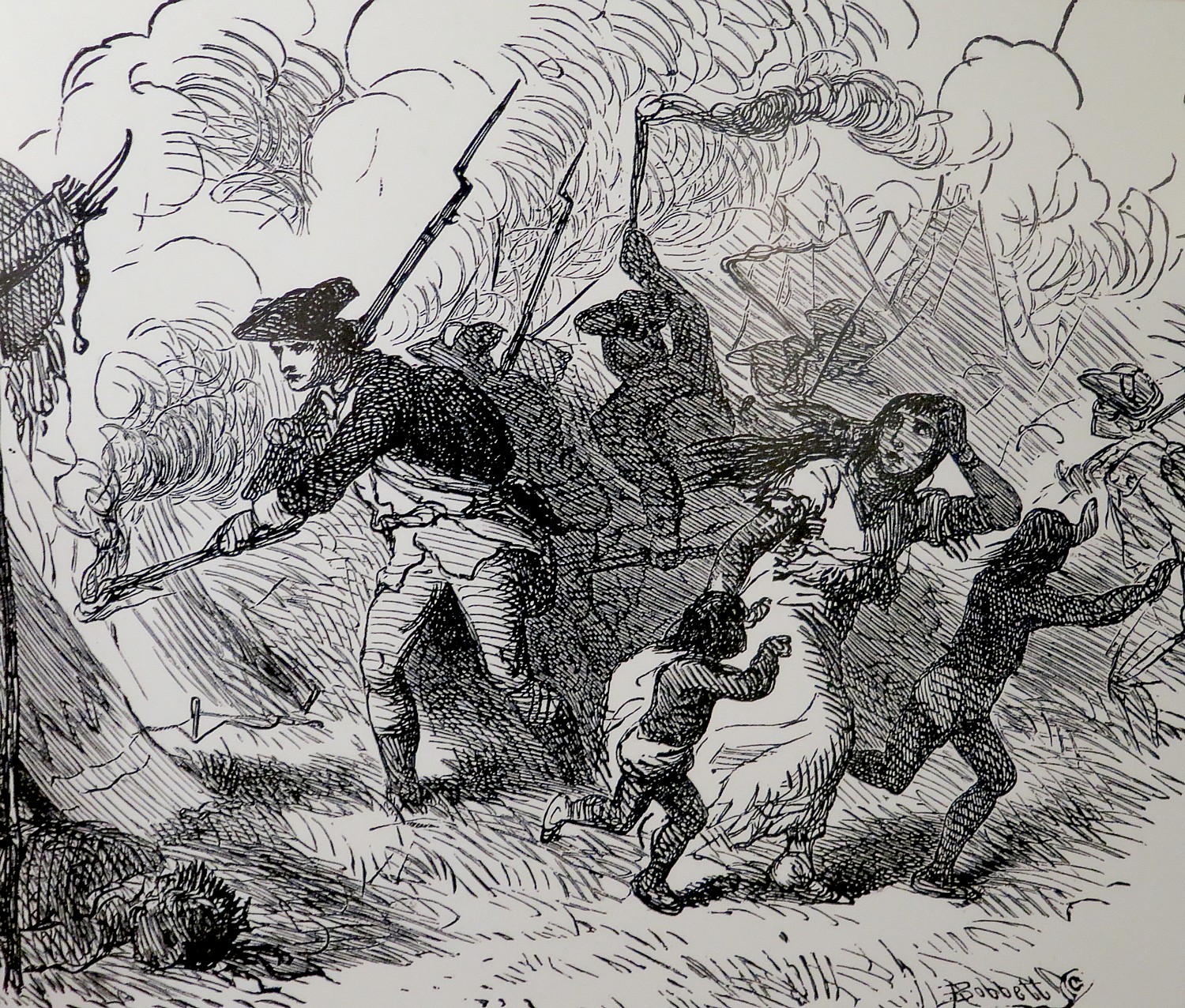

Both sides practiced a scorched earth strategy. “Raids by Loyalists and British-allied American Indians in 1778 destroyed Patriot settlements in Pennsylvania and New York. In 1779, General Washington ordered Generals Sullivan and Clinton to retaliate and destroy Six Nation towns, homes and food. Soldiers from Fort Stanwix tricked Patriot-allied Oneida warriors into raiding the British supply depot at Oswegatchie before leaving to destroy Onondaga towns. These raids and counter-raids continued until 1783.” Afterwards, General George Washington was given the name “Town Destroyer” by the Seneca people.
The Americans, who always wanted to take over Indian lands (another sore point that led to wanting independence from Britain), nullified the treaty of 1768 as soon as they won independence in 1783, claiming it was negotiated with the British and did not apply to the new nation. The Americans voided the treaty with the Cayuga, Canandagua and Mohicans claiming that these nations sided with the British, and pushed them further west.
In 1784, Governor George Clinton (uncle of Dewitt Clinton who launched the Erie Canal project), who was not a supporter of the federal Constitution, decided to make his own treaty. The new treaty, negotiated at Fort Stanwix with the Oneida who allied with the Patriots, effectively relegated three Oneida Indian nations to a measly 32 acres, in which they were surrounded on all sides by settlers. (The Oneida tribe had already split, with half moving to Wisconsin).
“Now, for first time in history, the Indian nation is relegated to a reservation, surrounded by Europeans (whites),” Sawyer tells us.
By the 1790s, houses were built by the fort; by the mid-1800s, the fort was demolished and the city of Rome built on top of the ruins. In 1935, a national monument established, though by then the site a commercial district with no trace of the fort.
By the 1960s,a grassroots urban renewal effort was underway to revitalize the downtown and restore the fort, but this required the National Park Service to go against its long-standing policy: “We protect, preserve, interpret any natural thing, but nothing was left of fort.” But political pressure mounted to create a new Revolutionary War “themed park” to open in time for the bicentennial in 1976.
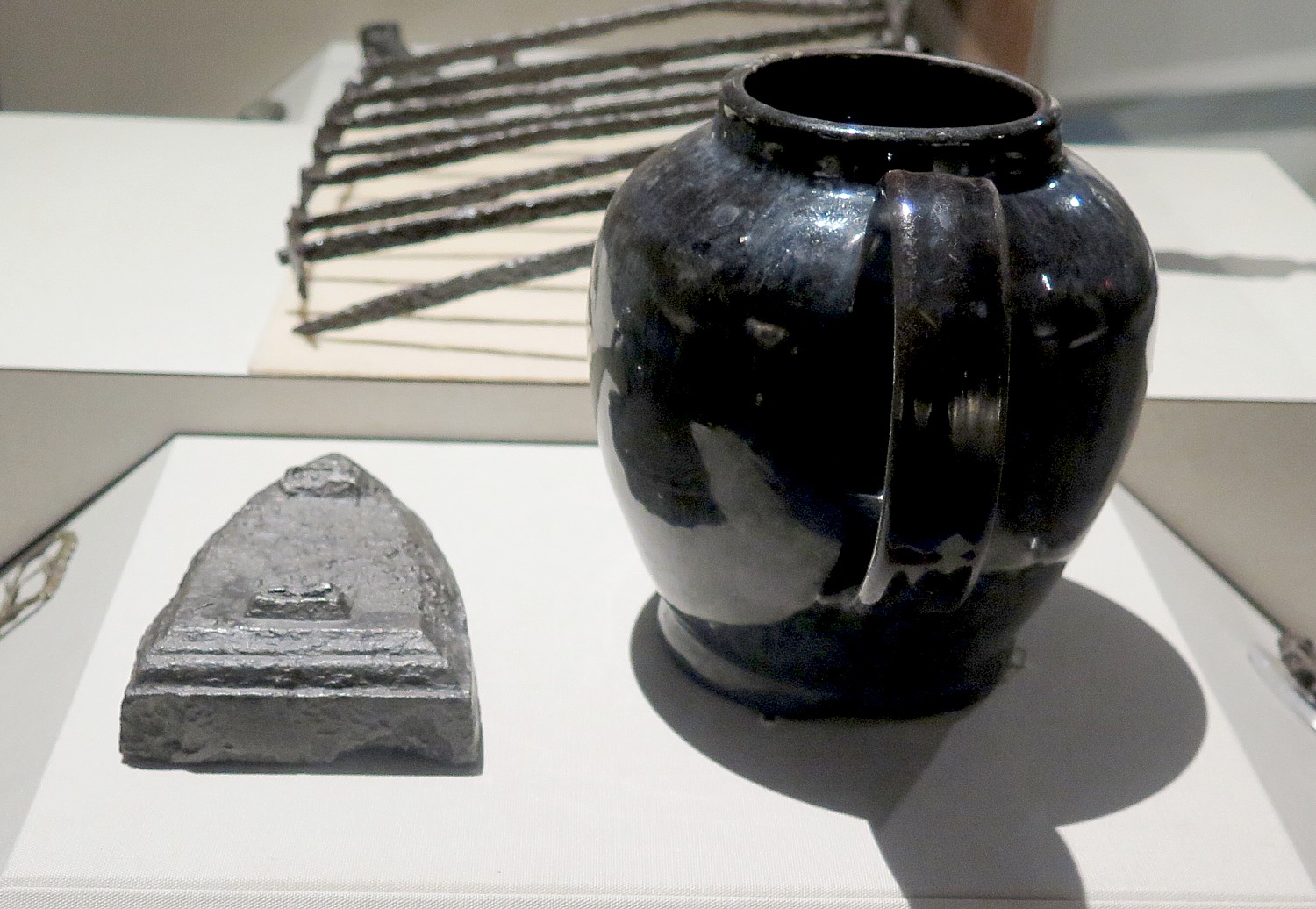

A massive excavation got underway by local volunteers and in the process, 400,000 artifacts were uncovered in three years of archaeological work.
They had a the foundation plus they had the original plans (from the British museum) and maps, clothing and receipts, enough to reconstruct the fort exactly as it would have looked.
Ranger Sawyer, who tells me his interest in becoming a park ranger was ignited during summer internship at the fort when he was a teenager and got “hooked”, says that the 400,000 artifacts are housed in a cultural conservation center in the Visitors Center.
In summer, on Wednesdays & Thursdays, at 11:15 & 1 pm, they open up back area to guided tours to see archaeologists working with the artifacts.

I am literally the last person out of the fort when they close at 9 pm, and walk a block to get some pizza for dinner (this is one of two nights when we are on our own for dinner and the city of Rome has provided a list of eateries.)
The 20th Annual Cycle the Erie Canal ride is scheduled July 8 – 15, 2018 (www.ptny.org/canaltour). In the meantime, you can cycle the trail on your own – detailed info and interactive map is at the ptny.org site (www.ptny.org/bikecanal), including suggested lodgings. For more information on Cycle the Erie Canal, contact Parks & Trails New York at 518-434-1583 or visit www.ptny.org.
The entire Erie Canal corridor has been designated the Erie Canalway National Heritage Corridor, Waterford, NY 12188, 518-237-7000, www.eriecanalway.org.
More information about traveling on the Erie Canal is available from New York State Canal Corporation, www.canals.ny.gov.
Next: Cycle the Erie, Days 6-7: Erie Canal Promotes Rise of America as Global Industrial Power
See also:
Cycle the Erie: 400 Miles & 400 Years of History Flow By on Canalway Bike Tour Across New York State
Cycle the Erie, Day 4: Seneca Falls to Syracuse, Crossing Halfway Mark of 400-Mile Biketour
_____________________________
© 2018 Travel Features Syndicate, a division of Workstyles, Inc. All rights reserved. Visit goingplacesfarandnear.com, www.huffingtonpost.com/author/karen-rubin , and travelwritersmagazine.com/TravelFeaturesSyndicate/. Blogging at goingplacesnearandfar.wordpress.com and moralcompasstravel.info. Send comments or questions to [email protected]. Tweet @TravelFeatures. ‘Like’ us at facebook.com/NewsPhotoFeatures